Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Evaluation of the Functional Indicator Maturity of Newborns
*Corresponding author: Schurov VA, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Chief scientific researcher sotr. laboratory deformity correction and limb elongation FSBU RSC “VTO” them, Acad. G.A. Ilizarova, 640001. City Kurgan, Russia
Received: February 06, 2019; Published: February 22, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.01.000532
Abstract
Unlike the anthropometric indicators of newborns, the values of the functional maturity indexes on the Apgar scale in healthy children do not have an established close relationship with the material situation of the family, the indicators are not given much importance. The aim of the work was to clarify the influence of various biological factors, including geographical latitude and nationality, on head growth and functional development of newborns.
Methodology: A statistical analysis of anthropometric studies of parturient women and healthy term infants of the city of Kurgan for the last 30 years (2076), rural areas of the region (400), cities of Nizhnevartovsk (200) and Tehran (100).
Results: It was found that the indicator of functional maturity of newborns, assessed by different groups of subjects, is a sensitive indicator of the quality of life of the family and the level of adaptation of the developing fetus to these conditions of life. In the case of full-term newborns with a head circumference exceeding 34cm and a body length exceeding 49cm, the delay in the rate of head growth and functional maturity is formed as a result of their decrease in the last month of pregnancy in the presence of diseases and bad habits of parents who have incomes below the subsistence minimum, special education, living in a place remote from the city and the main roads. The rate of fetal development does not depend on the nationality of the parents and is comparatively lower in the northern regions of the country, even if the financial situation of families is better.
Keywords: Apgar-1; Apgar-2; The influence of geographical latitude; Anthropometric indicators; Material situation; Bad habits
Introduction
The Apgar data scale is one of three parameters that, along with mass and longitudinal body size, inform the parents of the newborn. The Apgar scale assumes a cumulative analysis of five criteria for the functional maturity of a newborn, each of which is scored from 0 to 2. A child who receives 5-6 points in the first minute after birth (Apgar-1) can increase his score to 7 in just five minutes -9 (Apgar-2) and go into the category of children, which doctors can not worry. Experience shows that when interviewing after several years, parents of children usually cannot remember the values of the Apgar scores.
It is understandable that Apgar scores will be lower in children with intrauterine growth retardation, with congenital diseases, infections, premature babies and children born with asphyxia [1]. And yet, when analyzing the average values of the indicator in different groups of healthy children, some characteristic differences are revealed, the value of which I would like to evaluate. In this paper, we set as our goal to find out whether factors such as calorie and animal protein deficiency nutrition of parents, their bad habits, diseases, childbirth parity, national characteristics, climate, sports etc.
In regions with a large influx of migrants, the attention of people is attracted by issues related to the physical development of people of different nationalities. Most researchers come to the conclusion that the anthropometric parameters of newborns depend not on the nationality, but on the general climatic and geographical features of the place of residence of the parents. It is known, for example, that anthropometric indicators for Russian newborns in the study areas may have significant fluctuations, but they do not differ from those of indigenous children living in these regions [2,3].
According to research conducted at the end of the last century, it was noted that newborns of Kazakh nationality were inferior in terms of basic anthropometric indicators to peers of Russians [4]. Analysis of the growth of more than 60,000 newborns in Ohio in the second half of the 20th century showed that the body weight of darkskinned newborns is less than that of whites by 200 g [4].
Undoubted influence on the growth and development of the fetus has a lack of protein nutrition in women, especially in the second half of pregnancy. This question has a great history. In particular, it was believed that the pregnant woman’s body has sufficient resources to compensate for the restrictions, and maternal malnutrition should not affect the development of the fetus [1]. This conclusion was based on data from a survey of children born after 1914. During the period of the First World War, the growth rates of children did not differ from the corresponding indicators of the norm.
The file is now in the form of a file, which is the same as the one used in the game, which is the same as the national language, in the national language, which is the same as the national number, in the case of a national number [5,6]. Более того, данные литературы [6,7] indicates that the server is currently running. Engineer, the first one, which is one of the most important features, has been used for automated, automated and automated applications.
In the second half of pregnancy, due to the acceleration of the volume growth of the uterus and fetus, the need of a woman’s body for animal protein and calories increases. At the same time, pregnant women should have at least 112 g of protein in their daily diet, and the energy value of the food should be at least 2773 kcal [8] (Table 1). In this case, it is necessary to take into account the individual characteristics of women: the size of their bodies, the nature of previous activities, the climatic living conditions, and the state of health.
Technique
A statistical analysis of anthropometric studies of women in childbirth and healthy full-term newborns (at least 100 people annually), born in June in the state health care facility of Kurgan, in hospital No. 2 in 1989-2012 and 2018, was carried out. Anthropometric body sizes of women were calculated for the year they reach the age of 18 years. A key feature of this work is that research was conducted in the Kurgan region, one of the successfully developing regions of the country until 1990, but later faced with economic problems that led to the depressed nature of development, resulting in a loss of a fourth of the population due to migration neighboring more successful areas [9]. In addition, surveys of newborn babies were conducted in Tehran, in Nizhnevartovsk, in the villages of Mishkino and Almenevo of the Kurgan region (the number of those surveyed is given in Table 1).
Statistical processing of research results used a standard data analysis package “Microsoft Exell-2010”. The figures show the average values of indicators. The methods of correlation and regression analysis were used (with the designation of the index of determination R2). The significance of the differences obtained in the results of the analysis of two independent samples was analyzed using Student’s t-test.
Research Results
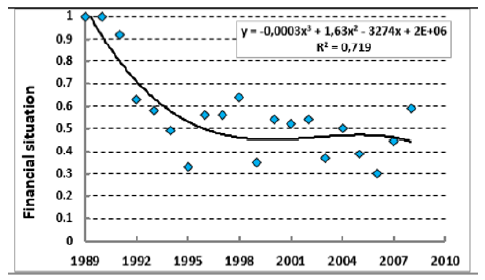
Figure 1: Dynamics of the material situation of families of pregnant women in the city of Kurgan (according to [9]).
According to indicators of real income per capita, consumption of livestock products and a number of other qualitative indicators, the material situation of families of women in labor, according to [9], decreased by 5 times in 5 years after 1989 (Figure 1).
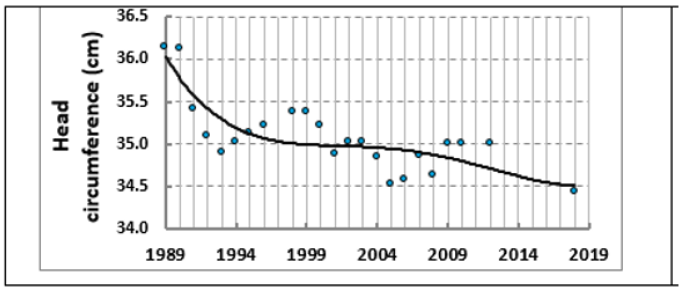
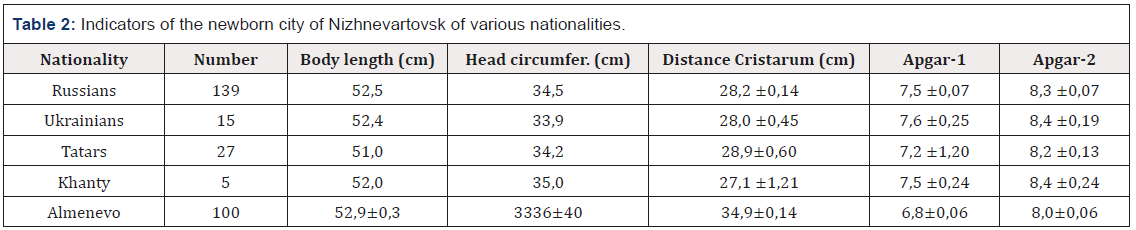
At the same time, anthropometric indices of newborns have become less, and in subsequent years - women in labour. In particular, the girth of the head of children decreased in 20 years of observations from 36 to 34, 5cm (by 4.2%, p ≤ 0.01; Figure 2). It is known that there is a close relationship between the anthropometric indices of the body and the level of functional maturity of children (Figure 3). In this case, a favourable indicator according to Apgar-2 is a head circumference from 34.5 to 37cm.
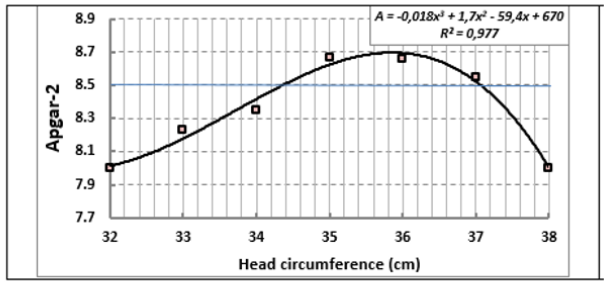
Figure 3: The relationship of the size of the head of newborns and their functional maturity on the Apgar-2 scale in the city of Kurgan (data of 2018).
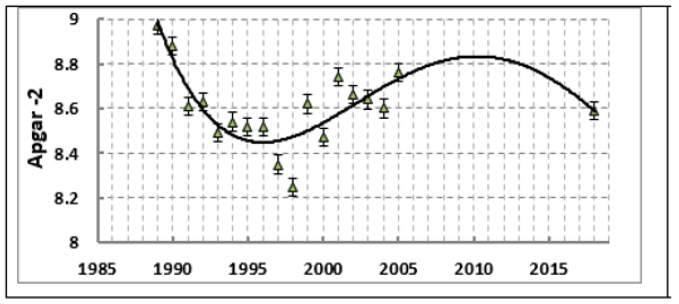
Despite the continued decrease in head size at the beginning of this century, the declining trend in Apgar scores in newborns after 1998 was replaced by an upswing due to changes in fetal development rates, and there was a disconnect between growth and development rates, which increased functional maturity. With a long period of deterioration in the quality of life of the population, the organism-fetus system reacted with a decrease in the rate of quantitative changes (body growth), while maintaining the rate of functional maturation [7] (Figure 4).
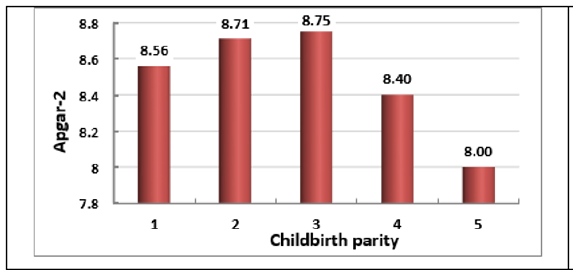
For the level of functional maturity of newborns, a number of factors matter, in particular the size of the mother’s pelvis (Figure 5), the parity of labour (Figure 6). After the birth of 3 children, Apgar-2 indicator in subsequent children became less.
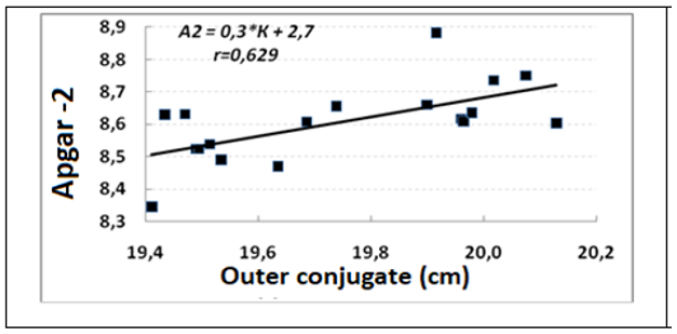
Figure 5: The relationship of the external conjugates of women and the indicator of functional maturity of newborns.
In women with higher and secondary special education, children had relatively large proportions of head circumference and body length (Figure 7).
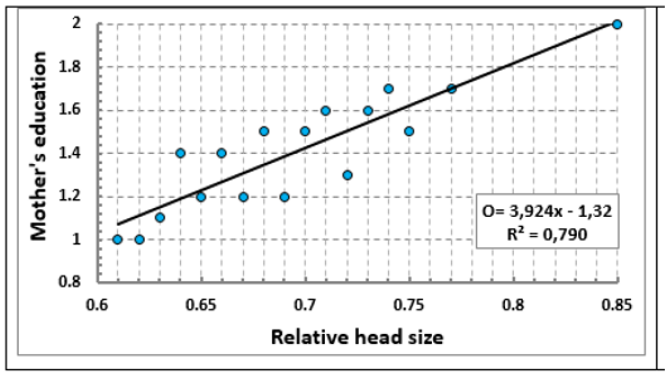
Figure 7: The relationship of the size of the head correlated to the length of the body and the level of education of women in childbirth.
It is worth noting that the product will be stored on the wall of the paper and it will be the same as the one [10]. This is where you can find such as newborn babies. Easily, this is where you want to access the server. Find all the documents that are written on the Alexander among the residents of Iran. At the same time, there is a lack of a position on each and addition, born by a vaginal way. This is a very useful choice for the data of other authors [11] (Figure 8).
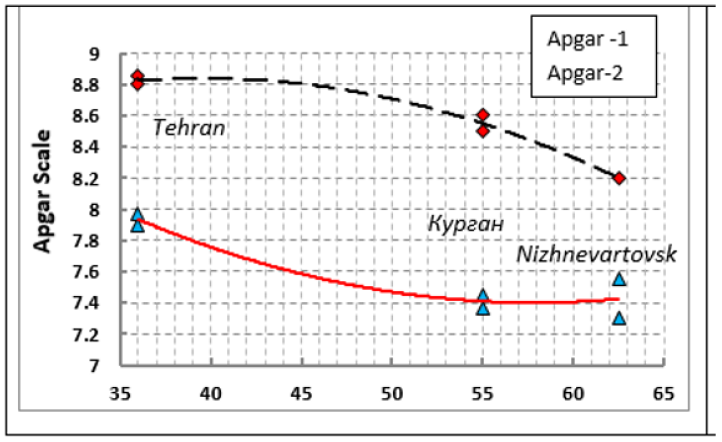
Figure 8: Apgar scores for residents of different regions located at different geographic latitudes.
Tehran’s newborns differ in relatively smaller body sizes (Table 1). The longitudinal body size of Iranian children is smaller than that of Kurgan neonates by 7–8% (p≤0.001). Iranian newborns had relatively smaller head sizes (by 6%) than Kurgan’s newborns (p≤0.001). However, the Apgar scores were the highest. There are several possible explanations for this phenomenon.
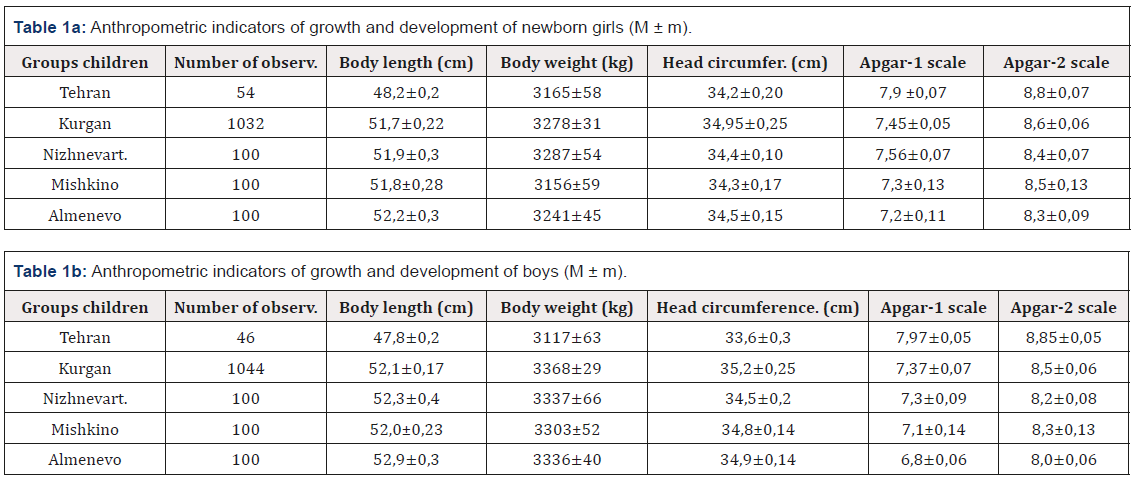
Table 1a: Anthropometric indicators of growth and development of newborn girls (M ± m).
Table 1a: Anthropometric indicators of growth and development of boys (M ± m).
Firstly, they had mothers whose average age was 27.5±0.7 years, which is 3.2 years more than that of women from Kurgan (p≤0.01). Secondly, 46% of these children were born after a cesarean section, without going through a period of perinatal asphyxia. Thirdly, the commercial impact on the indicators of the results of treatment of the interests of private clinics presented to parents is not excluded. And finally, fourthly, southern children, indeed, mature more quickly.
Firstly, they had mothers whose average age was 27.5±0.7 years, which is 3.2 years more than that of women from Kurgan (p≤0.01). Secondly, 46% of these children were born after a cesarean section, without going through a period of perinatal asphyxia. Thirdly, the commercial impact on the indicators of the results of treatment of the interests of private clinics presented to parents is not excluded. And finally, fourthly, southern children, indeed, mature more quickly.
Smaller rates of growth and development of children in the northern regions of the country is a well-documented fact [10]. The influence on the development of the geographical factor is realized differently due to differences in growth rates. It was revealed that in Iranian children, an increase in the size of the head is carried out in proportion to the increase in the longitudinal body size (Figure 9). In children of the Kurgan region, for example, the village of Almenevo, the increase in the size of the head is relatively slower than the longitudinal growth of the body.
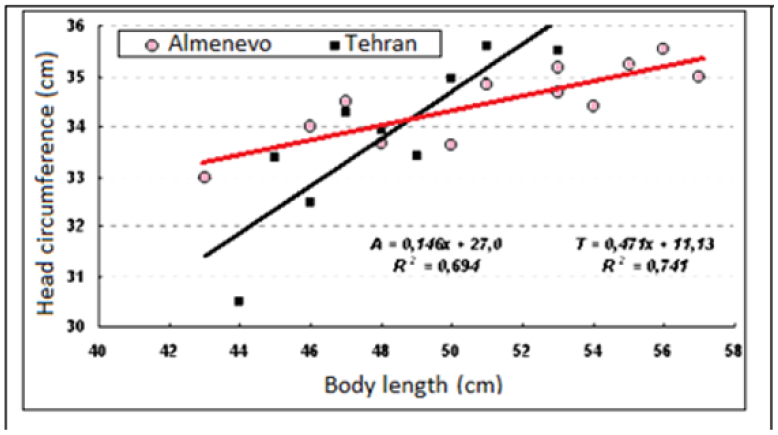
Figure 9: The relationship of increasing longitudinal body size and head girth in Iranian newborns and in children from the village of Almenevo.
It turned out that for every centimetre of increase in body length, the increase in head circumference in Tehran’s newborns was 0.47cm. The same increase in head circumference in newborns in Kurgan in 2001 was less and depended on the quality of life of the population: in economically prosperous families, 0.32cm in families with average incomes - 0.30cm, in families with low incomes - 0, 22cm. Children from rural areas of Mishkino and Almenevo - only 0.15cm. Therefore, Iranian children had a higher rate at the end of the pregnancy period. head growth and respectively - development of newborns.
Children from Nizhnevartovsk practically did not differ in body size from children from Kurgan, but the indicators of functional maturity were lower. Their indicators were closer to those of the Kurgan region. In almost all the cases described, girls compared with boys had smaller body sizes, but higher indicators of functional maturity.
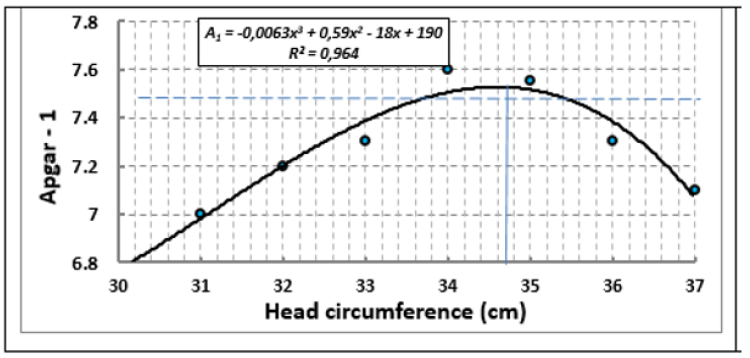
Children of different nationalities from the city of Nizhnevartovsk conducted a comparative analysis of anthropometric indicators. No statistically significant differences were found (Table 2).
Consequently, in conditions of sufficiently high-grade protein nutrition in the residents of the oil-producing region of the Tyumen region, national characteristics do not affect the growth rate and level of development of the newborn. Head sizes in newborn children of Nizhnevartovsk were not the largest (34.4±0.37 and 34.5±0.21cm, respectively, in girls and boys). When analyzing the indicators of the dependence of functional maturity indicators on head girth, it was found that for them optimal (in terms of Apgar values) is relatively smaller than in Kurgan children, head sizes are 33-36cm (Figure 10).
Discussion of the Research Results
are a kind of indicator that objectively reflects the level of economic development of a particular region, the quality of life of the population. According to the indicators of the scale of functional maturity of newborns, Apgar is usually judged on the functional maturity and term of the fetus. These indicators, when analyzing the average values in one group or another, also reflect the quality of life of the population. It turned out that Apgar is lower in rural areas than in urban areas, and the lower, the farther away the village is from the regional center and from the main communication lines. For example, in children of the village of Mishkino, located on the Trans-Siberian Railway, these figures are higher than those of the village of Almenevo, 53km away from the Chelyabinsk-Kurgan highway.
There is no doubt about the negative impact of the bad habits of the mother and father (smoking, alcoholism, drug addiction) on the functional development of newborns (Figure 11).
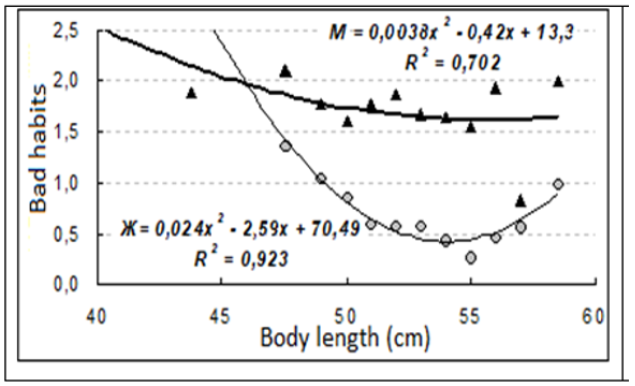
Figure 11: The effect of the number of bad habits of mother and father on the indicator of functional maturity of newborns.
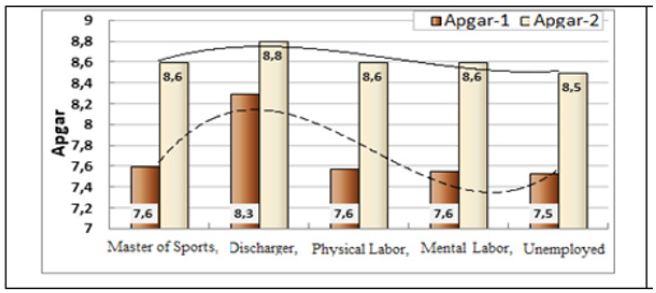
Analyzing the impact of sports on the development of children, it should be noted a positive effect on the Apgar-1 indicator of physical education, the presence of a sports category (Figure 12). In mothers of discharges, the Apgar-1 scale of functional maturity of newborns reached 8.2 ± 0.11, which is 0.6 points (p≤0.001) higher than in children of women who were not involved in sports. Professional athletes as well as pregnant women engaged in heavy physical work, had problems with the formation of gestational dominants, children were born with lower anthropometric indices [11].
In children of professional athletes, children developed faster, and in the first grade they had higher marks in main subjects, being 13% ahead of their peers. This advantage was gradually lost to the 4th grade. At the same time, with increasing age and volume of the information received, the performance of all schoolchildren tended to decrease: S = 6.09 - 0.185x; R2 = 0.982.
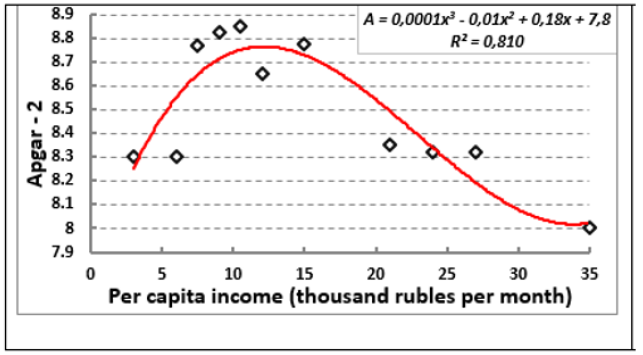
Figure 13: Dependence of the Apgar-2 indicator on the level of family income of women in labour (data of 2004).
Despite the fact that, as well-being increased, the anthropometric indices of newborns increased, including the head circumference, the Apgar-2 index increased only in women from low-income families. The maximum indicator was achieved at the level of income corresponding to the minimum subsistence minimum level [12]. However, with a further increase in family income above this level, the Apgar-2 indicator for newborns tended to decrease (Figure 13).
This fact indicates that fetal development is a process of active adaptation to the conditions of existence, in particular the emergence of the ability to selectively redistribute the rates of cerebral and somatic development [13,14]. It was found that the mechanism of fetal growth acceleration is associated with an increase in the feto-placental systolic-diastolic blood flow gradient, as well as an increase in the systemic arterial pressure of the pregnant to the level of the physiological optimum [11].
Thus, the indicator of functional maturity of newborns, assessed by different groups of subjects, is a sensitive indicator of the quality of life of the family and the level of adaptation of the regulatory systems of the developing fetus to these living conditions. At the same time, developmental delay in full-term newborns can be observed if there are bad habits of parents who have incomes below the subsistence minimum due to the lack of necessary education of parents and a corresponding stable income. The pace of development of the fetus can influence the geographical latitude of the area.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the study was carried out as a personal initiative without financial support from sponsors and in the absence of a conflict of interest. The authors bring sincere appreciation to Cand. honey. Sciences Ismayilova Sevinj Sabirovne (Tehran) and Cand. biol. Abramovskikh Nadezhda Anatolievna (Chelyabinsk) for her invaluable assistance in collecting primary information about newborn children The authors declare that the study was carried out as a personal initiative without financial support from sponsors and in the absence of a conflict of interest.
References
- Krivoshchekov SG, Leutin VP, Divert VE (2004) Systemic mechanisms of adaptation and compensation. Bulletin of the SB RAMS 2(112): 148-153.
- Vorontsov IM (1986) Regularities of the physical development of children and methods for its evaluation. Vorontsov va, TYa, Features of the physical development of newborn children in various territories of the USSR. Pediatrics 12: 7-9.
- Artamonova LL (1980) Physical development of rural and urban newborns in Kazakhstan. Public Health of Kazakhstan 2: 28-30.
- Faulkner B, Gulman S, Kouchner H (1998) Weight at birth and the growth of the child as determinants of blood pressure. International Medical Journal 5: 454-458.
- Novikov YI, Abramchenko VV, Fominykh VA (1981) Dynamics of the physical development of newborn children in Leningrad for 45 years (1933-1978). Questions of protection of motherhood and childhood 26(1): 62-64.
- Kholodkov VA, Mogeladze NO, Shchurov VA (2018) A reproductive function of women in conditions of adaptation to the quality of life of the population. Avicenna 20: 59-63.
- (2018) Letter No. 28-1 / 10 / 2-1994 of the Ministry of Health of the Russian Federation of March 24, 2017. Recommended standards of therapeutic nutrition in the Russian Federation. p. 1-34.
- Kremlyov ND (2003) Demography and economics: yesterday, today and tomorrow // Problems, perspectives and directions of the demographic development of the Kurgan region. Mound pp. 26-33.
- Chiryatyeva TV (2001) Peculiarities of the growth and development of children in the North. Publishing House KRUK, Moscow, pp. 239.
- Schurov VA, Mogeladze NO (2012) Medical, biological and social aspects of the problem of increasing fertility and anthropology. Lap Lambert Academic Publishing, Deutschland, Saarbrücken, pp. 168.
- Sсhurov VA, Mogeladze NO, Kholodkov VA (2010) Physiological substantiation of the idea of the optimal size of the minimum consumer basket. Mater XXI congress Physiol, Moscow, pp. 712.
- Rahmanian K, Jahromi AS, Rahmanian V, Ghasvari M, Abari PF (2014) Association of Apgar scope with delivery mode in the non-distress newborns. OnLine Journal of Biological Sciences 14(1): 21-25.
- Child Ch (1914) Internal and External Development Factors, Leningrad, pp. 261.
- Shevtsov VI, Schurov VA (2003) Gradient cranio-caudal des ressources de regeneration des membres inferieus. Revue de chirurgie et orthopedique et reparatrice de lappareil moteur 89(10): 3S43.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.