Short Communication 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Success of Endoscopy with Narrow Band Imaging in Diagnosis of Cervical Metaplasia
*Corresponding author: Salwa samir Anter, MD obstetrics gynecology, Cairo University, Egypt
Received: December 18, 2018; Published: December 28, 2018
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2018.01.000501
Abstract
Background: Flexible magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging [ME-NBI] has outstanding diagnostic correctness for gastrointestinal metaplasia and is hope for to be highly useful for diagnosis cervical metaplasia in this study aiming to detect the feature findings and access the diagnostic power of ME-NBI for diagnosis of cervical metaplasia.
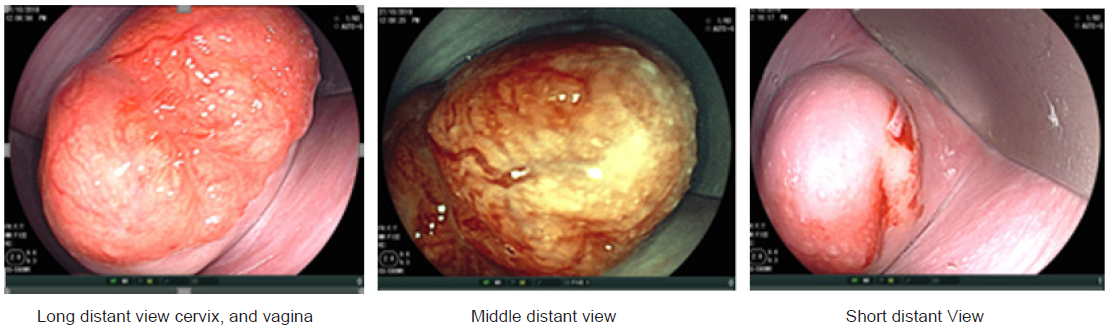
Method: 20 women were undergoing vaginal smear and at the same time Flexible NBI-ME was performed. After that Written consent was obtained from all patient’s vaginal examination were done. Cusco speculum is used to examine a cervix by endoscopy using white light imaging, and. Narrow band image at long, middle, and short distances. Images and video of ME-NBI were taken to investigate the cervical lesions. The images were analysis built on cytology result.
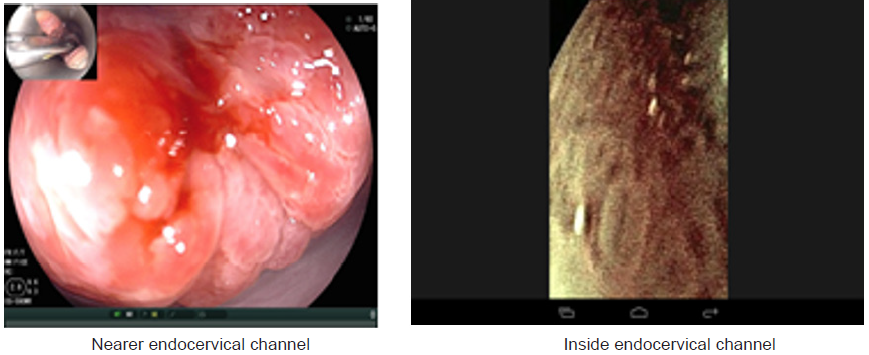
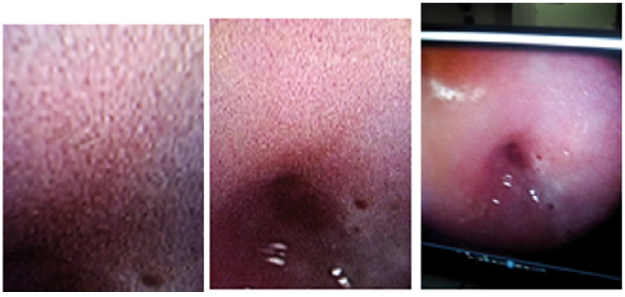
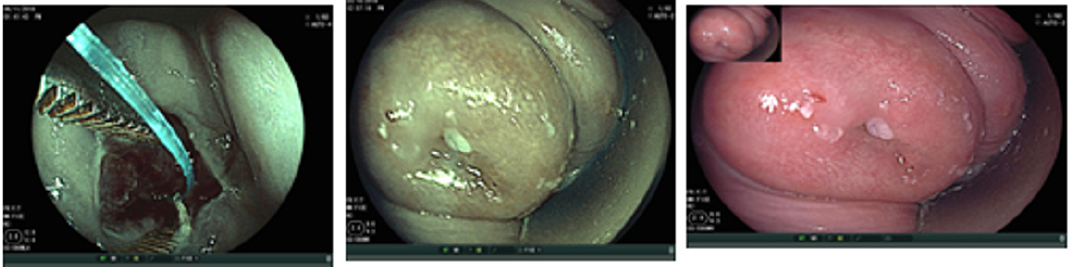
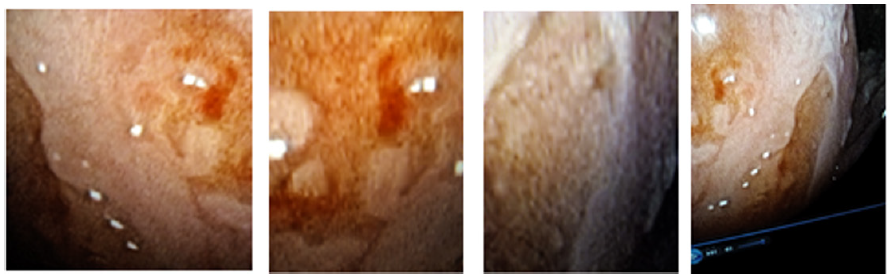
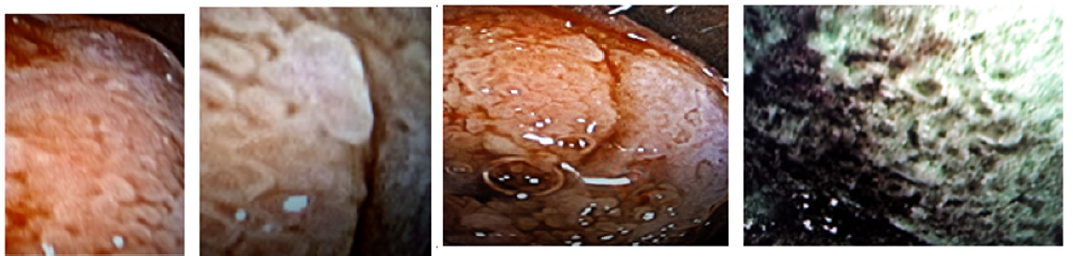
Results: The NBI-ME images revealed the following abnormal findings Tongue-like projections of the epithelium, nabothian follicles, gland ostium, met aplastic cells with special features. Transformation zone both type, normal vascularity. Of cervix and change shape of all types of epithelial cells, cell nuclear density &thickness of epithelium. If you know how to diagnose squamous metaplasia 50 percent of correct diagnosis of cervical lesion. Will be able to be diagnosed.
Conclusion: This study indicates that ME-NBI may have novel value for metaplasia diagnosis without use of acetoacetic acid or Lugol’s iodine
Keywords: Cervical metaplasia Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging
Introduction
Cervical metaplasia
Metaplasia defined as a transformation from one mature cell type to a second mature. Cervical metaplasia has always generated major interest because of its neoplastic potential [1]. Metaplasia begins the movement of the original squamocolumnar junction onto the portion, usually as a result of estrogen production or interval vaginal deliveries. The exposure of the delicate columnar cells to an acidic bacteria _laden vaginal environment initiates the process of inflammation and replacement with stratified squamous cell [1,2].
At birth there is an abrupt junction between the squamous epithelium of the ectocervix [the original squamous epithelium] and the columnar epithelium of the endocervix. Through exposure to estrogen [at birth, during puberty, and throughout reproductive life], the glycogen in the exfoliated cells of the vagina is converted into lactic acid, accounting for the acidity of the vaginal secretions [pH<4.5]. This acidity, along with other factors, stimulates the replacement of the columnar epithelium with squamous epithelium. This process is known as metaplasia [3]. Metaplasia results in the formation of a new SCJ. The area between the original SCJ and the new SCJ is known as the transformation zone. Metaplastic changes usually start from the periphery of the ectropion and spread towards the external os. Changes can also occur in discrete patches on the columnar epithelium. The new squamous cells originate from the totipotent “reserve” cells that remain dormant beneath the columnar cells.squmous metaplasia can divided into three stages [4].
The common procedure has been traditional for uterine cervical cancer is the Pap smear followed by colposcopy [5]. Flexible magnifying endoscopy is at present time used for the gastrointestinal tract and is tolerable for the diagnosis of GI neoplasms. Magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging can be used to clearly imagine the microstructures of the mucosal surface and interstitial capillaries [6,7].
As regard of used of flexible endoscopy in examination cervix lesion. The first was studied by Nishiyama et al was reported the used of endoscopy for diagnosing cervical neoplasms revealed micro-vascular pattern differences at different stages [9]. The second study of K Uchita et al study feature findings of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or more on magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging. So, it is anticipated to be useful for diagnosing metaplsia. This study aimed to identify characteristic findings of metaplsia visualized using flexible endoscopy and confirmed by the cytology result.
Methods
20 women were undergoing vaginal smear and at the same time Flexible endoscopy was performed. After written consent was obtained from all patient’s vaginal examination were done follow by using a Cusco speculum to examine the cervix by endoscopy using white light imaging and narrow band image at long, middle, and short distances. Video and picture taken and reviewed based on the known characterized finding of metaplasia and confirmed by cytology examination.
Results and Discussion
Cervical metaplasia is natural process but as transformation zone is liable to human papilloma
Virus infection and dysplsia can occur and may proceed to caner for that point it take important of early diagnosis of metaplasia for not to be mistaken from dysplsia and also we try to find an accurate method of diagnosis of metaplsia two study were done on flexible endoscopy with narrow band image for study of evaluation of cervical cancer.
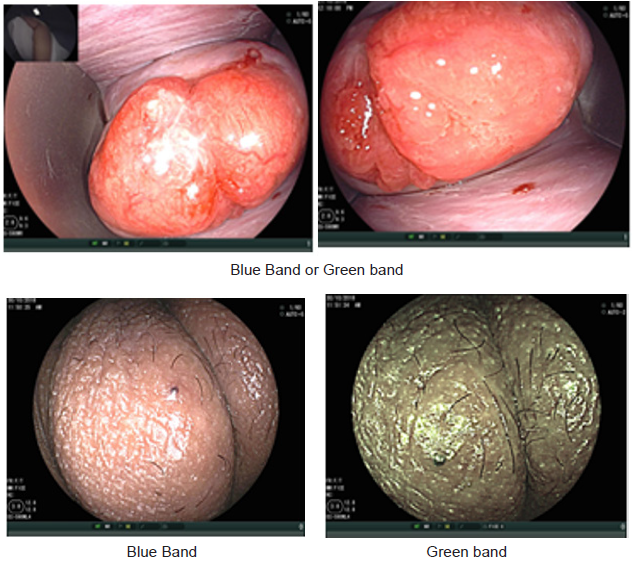
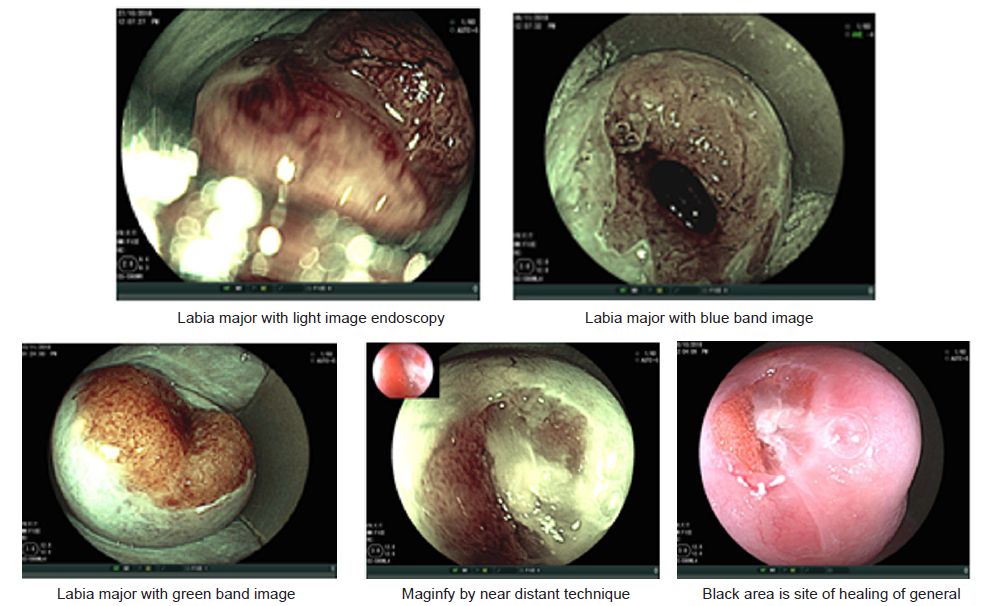
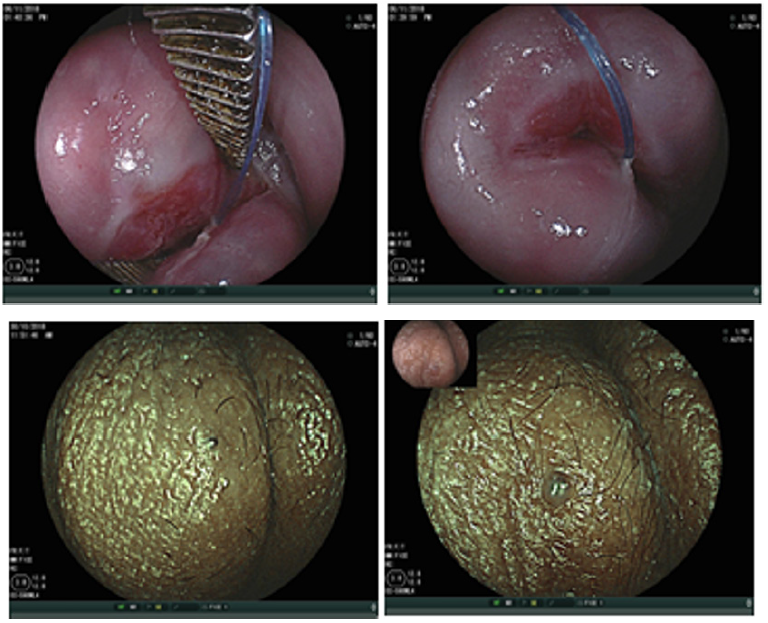
Advantages of flexible endoscopy are high magnification ability and increase the degree of image clarity succeed to obtain clear images of any location of cervix by manual movement of endoscopy and facilitate vision of both surface and vascular structures without use of acetic acetic or lugo’s iodin. the first study of flexible endoscopy was done by Nishiyama et al. for diagnosis of cervical neoplasms show micro-vascular pattern distinguished at different stages [10].other study by K Uchita who was focused not only on vascular pattern but also on epithelium thickness in our study focused on vascularity and thickness of epithelium and change in shape of cells and nuclear density in addition to that known pictures of diagnostics futures of metaplasia that found in all cases.
In summary, endoscopy demonstrated characters of the metaplsia clearer and the magnification. Power adds to that access to all around the cervix and endocervical channel and assement of blood vessels by narrow band by blue band and green band as we met of cells shape nuclear density Thickness of epithelium.
References
- Slack JM, Tosh D (2018) Trans differentiation and metaplasia—switching cell types. Curr Opin Genet Dev 23(4): 707–714.
- Uchita K, Kanenishi K, Hirano K, Kobara H, Nishiyama N et al. (2018) Feature findings of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia or more on magnifying endoscopy with narrow band imaging. 1: 11:58.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.