Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Application Value of Staged Continuous Health Education in Cesarean Section Nursing
*Corresponding author: Libin Sun, Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology, Beijing Di-Tan Hospital, Capital Medical University, Beijing 100015, China.
Received: March 11, 2021; Published: April 05, 2021
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2021.12.001756
Abstract
Objective: To explore the application value of staged continuous health education in cesarean section nursing. Methods: 90 cases of cesarean section in our hospital from August 2019 to July 2020 were randomly divided into two groups, 45 cases in each group. The control group was given routine nursing, while the observation group was given periodic continuous health education based on routine nursing. The breastfeeding, 24-hour anal exhaust rate, anxiety and depression after nursing were analysed and scored. Results: compared with the control group, the success rate of breastfeeding, 24-hour anal exhaust rate, comfort, and sense of security of the observation group were significantly improved (P < 0.05), and the anxiety score and depression score were significantly reduced (P < 0.05).
Conclusion: The staged continuous health education can not only improve the psychological state of the puerpera, but also improve the success rate of breast-feeding and promote the recovery of the puerpera as soon as possible.
Keywords: Staged continuous health education, Cesarean section nursing, Breastfeeding, Puerpera
Introduction
With the change of birth policy, there are more and more elderly mothers in China, and some of them suffer from serious diseases during pregnancy, such as gestational diabetes. In addition, some pregnant women worry about vaginal delivery and have a strong fear, so some pregnant women choose cesarean section for delivery, so cesarean section has also been widely used. In the nursing of cesarean section, it is very necessary to provide effective health education to help mothers develop good behaviour habits, to ensure the health of mother and baby, and to improve the breastfeeding rate [1,2]. 90 cases of cesarean section puerperae who delivered in our hospital from August 2019 to July 2020 were selected to analyze the application value of staged continuous health education in cesarean section nursing.
Materials and Methods
Patient Information
90 cases of cesarean section puerperio, due to uterine scar, abnormal fetal position and other reasons, voluntarily chose cesarean section and delivered in our hospital from August 2019 to July 2020 after getting the informed consent were selected, the random number table method was used as the grouping method and divided into a control group and a study group, with 40 cases in each group. Study group: 22-39 years old, the average age was (32.74 ± 3.91) years; the gestational age was 38-41 weeks, the average was (37.52 ±2.62) weeks. Control group:22-38 years old, the average age was (32.67± 3.78) years; the gestational age was 38-40 weeks, the average was (37.54 ± 2.65) weeks. There was no significant difference in average age and gestational weeks, between the two groups (P>0.05), the baseline material in two groups were comparable.
A. Inclusion criteria:
i. No breastfeeding contraindications, such as AIDS, active tuberculosis, etc.
ii. singleton pregnancies
iii. No psychosis, no mental retardation, can communicate normally.
iv. Informed consent has been signed, and this study meets the requirements of medical ethics.
B. Exclusion criteria:
i. Premature delivery
ii. Breast disease
iii. Patients with postpartum depression
iv. Combined with malignant tumor, liver and kidney dysfunction and other serious diseases.
v. AIDS, active tuberculosis, etc.
Method
The control group was given routine obstetric care and regular health education, health education on breastfeeding knowledge and the correct nursing posture should be given to pregnant women after delivery; a reasonable diet should be arranged for pregnant women; the abdominal incision should be kept clean to prevent infection; the requirements of maternal regular work and rest to promote its faster recovery. The study group was given phased continuous health education measures, the details are as follows:
Health education at admission stage: It is necessary to strengthen the guidance for puerpera from the woman was admitted to the hospital, the nurses detail the hospital environment, medical qualification and inspection items and other basic information for puerpera, at the same time, combined with the actual situation, health and medical needs of puerpera, to implement targeted services for patients, and to apply the continuous health education and nursing program, so as to ensure the scientific supply of maternal nutrition.
Preoperative health education: To understand the basic situation of the puerpera in detail, including the life indications, psychological state, nutritional status, nursing needs and medication history of the puerpera, and to explain the points for attention in the operation process for the puerpera, to reduce the anxiety, fear and other negative stress psychology of the puerpera, so that the puerpera can maintain a stable psychology and complete the operation smoothly.
Health education in rehabilitation stage: 6 hours after the operation, the nursing staff should give guidance for puerpera to keep proper rest position and try to choose supine position. On the 1st day after the operation, the puerpera should start exercise by walking back and forth as soon as possible to help maternal gastrointestinal function to accelerate peristalsis and to avoid the formation of lower extremity venous thrombosis, intestinal adhesion, and other postoperative complications. When the puerpera can exhaust smoothly, they then take proper nutrition to promote the healing of surgical incision and secrete milk as soon as possible.
Health education at discharge stage: When the puerpera leaves hospital, the nursing staff should explain the rehabilitation related knowledge to the puerpera. At the same time, they should return to the hospital regularly for re-examination.
Observation Indexes
The SAS anxiety score, SDS depression score were used to evaluate anxiety and depression of patients and to provide feedback on the clinical status of the patients. There were 20 items in both scales, and the scores were graded from 1 to 4, calculate the sum, round off, and multiply by 1.25 to get the final score, the final score was obtained, the higher the score, the more serious the anxiety and depression, if SAS score is more than 50 points, SDS score is more than 53 points, it can be diagnosed as anxiety disorder and depression. At the same time, through the anal exhaust rate, postoperative breastfeeding success rate, comfort, security and so on to judge the effect of patient care.
Statistical Methods
All the data were processed by SPSS 22.0 software, the percentage n (%) is expressed as count data, the chi square test was performed, and data are presented as the mean ± SD (x-±s) by t-test. Values of P< 0.05 were considered to indicate significant differences.
Results
Comparison of Anal Exhaust Rate and Breast-Feeding Success Rate
In the observation group, 37 cases had anal exhaust within 24 hours after operation, and the exhaust rate was 82.22%, 23 cases had anal exhaust in the control group, and the exhaust rate was 51.11%, there was significant difference in statistical comparison (P<0.05). In addition, the success rate of breast-feeding on the day after cesarean section in the observation group was 40 cases (88.89%), which was higher than that in the control group of 25 cases (55.56%).
Comparison of Emotional Changes, Comfort and Sense of Security
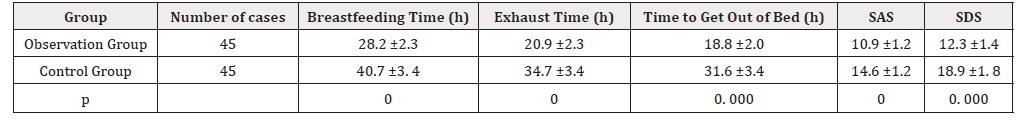
The postpartum breastfeeding time, exhaust time, ambulation time, SAS and SDS scores of the two groups were compared, the score of the observation group was significantly better than that of the control group (P < 0.05) in Table 1.
Discussion
In clinical practice, cesarean section is an effective way to solve the problem of abnormal delivery. Cesarean section can ensure the safety of mother and fetus, so it is widely used in clinical practice. At present, many parturients undergoing cesarean section are primiparas. They do not know enough about cesarean section and worry about the abnormal health of the fetus. All these factors are easy to cause anxiety, depression, and other negative emotions, which have a great impact on the smooth operation [2,3].
Phased continuous health education is to provide different nursing measures at different stages according to the specific situation of patients, to make each stage penetrate each other and ensure the integrity and continuity of synaptic therapy [4,5]. The health education of cesarean section can not only improve the awareness of cesarean section, but also improve and master the nursing knowledge of newborn [5,6]. In this study, four stages of health education were provided to puerpera, including introduction of hospitalization environment, notification of preoperative methods and preventive measures, postoperative rehabilitation guidance, discharge instructions and breast-feeding knowledge [7]. The results showed that the success rate of breastfeeding, the improvement of anxiety and depression in the observation group were better than those in the control group (P< 0.05).
To sum up, giving cesarean section maternal phased continuous health education, not only can improve the psychological situation of the maternal, but also can improve the success rate of breastfeeding, anal exhaust rate, postpartum out of bed activity time, improve comfort and maternal safety, which is worthy of promotion and application.
References
- Curtis EM, Moon RJ, Harvey NC, Cooper C (2017) The impact of fragility fracture and approaches to osteoporosis risk assessment worldwide. Bone 104: 29-38.
- Bottani M, Banfi G, Lombardi G (2019) Perspectives on mirnas as epigenetic markers in osteoporosis and bone fracture risk: A step forward in personalized diagnosis. Frontiers in genetics 10: 1044.
- Chandran S, John A (2019) Osseointegration of osteoporotic bone implants: Role of stem cells, silica and strontium - a concise review. Journal of clinical orthopaedics and trauma 10(Suppl 1): S32-s36.
- Jackson RD, Mysiw WJ (2014) Insights into the epidemiology of postmenopausal osteoporosis: The women's health initiative. Seminars in reproductive medicine 32(6): 454-462.
- Shibahara T (2019) Antiresorptive agent-related osteonecrosis of the jaw (aronj): A twist of fate in the bone. The Tohoku journal of experimental medicine 247(2): 75-86.
- Bhattacharyya S, Pal S, Chattopadhyay N (2018) Targeted inhibition of sclerostin for post-menopausal osteoporosis therapy: A critical assessment of the mechanism of action. European journal of pharmacology 826: 39-47.
- Esbrit P, Alcaraz MJ (2013) Current perspectives on parathyroid hormone (pth) and pth-related protein (pthrp) as bone anabolic therapies. Biochemical pharmacology 85(10): 1417-1423.
- Tella SH, Kommalapati A, Correa R (2017) Profile of abaloparatide and its potential in the treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. Cureus 9(5): e1300.
- Ghasroldasht MM, Irfan-Maqsood M, Matin MM, Bidkhori HR, Naderi-Meshkin H, et al. (2014) Mesenchymal stem cell based therapy for osteo-diseases. Cell biology international 38(10): 1081-1085.
- Knight MN, Hankenson KD (2013) Mesenchymal stem cells in bone regeneration. Advances in wound care 2(6): 306-316.
- Tan J, Xu X, Tong Z, Lin J, Yu Q, et al. (2015) Decreased osteogenesis of adult mesenchymal stem cells by reactive oxygen species under cyclic stretch: A possible mechanism of age-related osteoporosis. Bone research 3: 15003.
- Kiernan J, Davies JE, Stanford WL (2017) Concise review: Musculoskeletal stem cells to treat age-related osteoporosis. Stem cells translational medicine 6(10): 1930-1939.
- Dernowsek JA, Pereira MC, Fornari TA, Macedo C, Assis AF, et al. (2017) Posttranscriptional interaction between mir-450a-5p and mir-28-5p and stat1 mrna triggers osteoblastic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Journal of cellular biochemistry 118(11): 4045-4062.
- Hesse E, Taipaleenmaki H (2019) Micrornas in bone metastasis. Current osteoporosis reports 17(3): 122-128.
- Xie Y, Chen Y, Zhang L, Ge W, Tang P (2017) The roles of bone-derived exosomes and exosomal micrornas in regulating bone remodelling. Journal of cellular and molecular medicine 21(5): 1033-1041.
- Zeng Q, Wang Y, Gao J, Yan Z, Li Z, et al. (2019) Mir-29b-3p regulated osteoblast differentiation via regulating igf-1 secretion of mechanically stimulated osteocytes. Cellular & molecular biology letters 24(11).
- Lv H, Sun Y, Zhang Y (2015) Mir-133 is involved in estrogen deficiency-induced osteoporosis through modulating osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Medical science monitor: international medical journal of experimental and clinical research 21: 1527-1534.
- Frohlich LF (2019) Micrornas at the interface between osteogenesis and angiogenesis as targets for bone regeneration. Cells 8(2): 121.
- Schmitt MJ, Margue C, Behrmann I, Kreis S (2013) Mirna-29: A microrna family with tumor-suppressing and immune-modulating properties. Current molecular medicine 13(4): 572-585.
- Li Z, Hassan MQ, Jafferji M, Aqeilan RI, Garzon R, et al. (2009) Biological functions of mir-29b contribute to positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation. The Journal of biological chemistry 284(23): 15676-15684.
- Xie Y, Zhang L, Xiong Q, Gao Y, Ge W, Tang P (2019) Bench-to-bedside strategies for osteoporotic fracture: From osteoimmunology to mechanosensation. Bone research 7: 25.
- Compston J (2020) Practical guidance for the use of bisphosphonates in osteoporosis. Bone: 115330.
- Kotak DJ, Devarajan PV (2020) Bone targeted delivery of salmon calcitonin hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for sublingual osteoporosis therapy (slot). Nanomedicine: nanotechnology, biology, and medicine 24: 102153.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.