Opinion 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Post-Covid-19 Vaccination Thromboembolic Stroke
*Corresponding author: Denis Nikolov, Heart and Brain Center of Excellence University Hospital Pleven, Pierre Curie N2, Bulgaria
Received: June 17, 2021; Published: June 21, 2021
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2021.13.001859
Clinical Case
39-year old male was admitted to the neurology department of University hospital “Heart and Brain Center of Excellence” - Pleven, Bulgarian on the 1st of Mar 2021, due to dizziness, sudden loss of the ability to speak and weakness in left arm and leg. The patient had no medical history of other diseases and his only risk factor for cardiovascular disease was smoking. The only medical intervention he has had so far was vaccination against COVID-19 with AstraZeneca (Lot ABV5300) vaccine, ten days prior to the hospital admission (20th Feb 2021).
The neurological examination revealed mouth asymmetry, right sided central hemiparesis, positive (+) Babinski sign on the right leg and sensory motor aphasia. NIHSS – 15 pts., GLCS – 17 pts. There were not any significant deviations on the laboratory tests. The ECG was with sinus rhythm, heart rate 75 bpm.
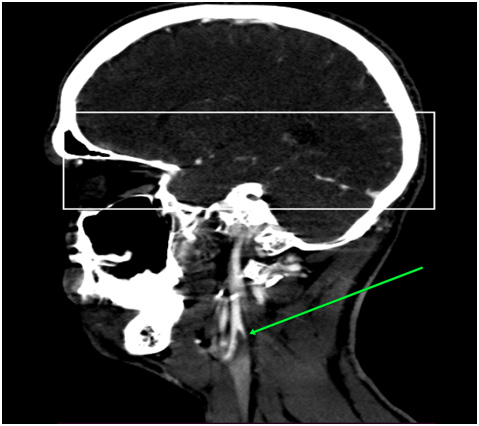
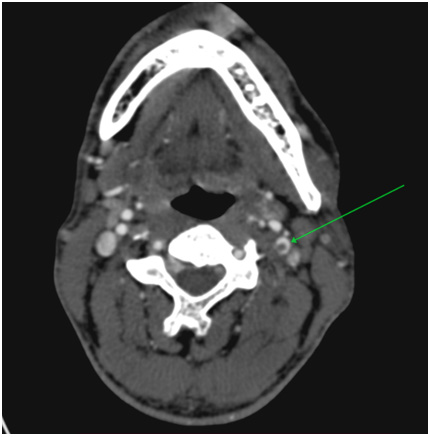
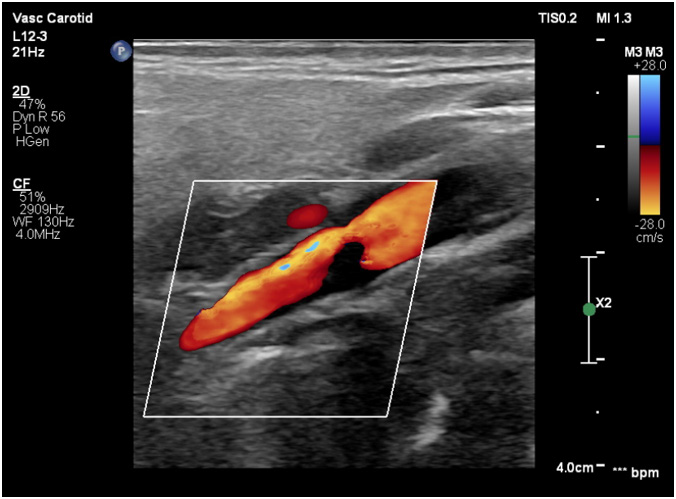
Via native and contrast CT scan intracranial hemorrhage was excluded and the contrast CT scan revealed a thrombus in the left internal carotid artery (Figure 1&2). Doppler ultrasound was also performed which showed a carotid stenosis, caused by a mural thrombus (Figure 3). Treatment with tissue plasminogen activator Actilyse was initiated. The total dose was 63 mg, 6 mg of which administered as a bolus i.v. injection and the remaining 57 mg were given as a continuous infusion for one hour. In the next 24 hours the patient received a heparin infusion, according to the aPTT values.
Control angiography and Doppler ultrasound ware performed 10 days later and full disintegration of the thrombus was observed.
After the thrombolysis there was a significant reduction in the neurological deficit with remaining sensory motor aphasia, which will be treated later on with repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS).
Discussion
Due to several cases of thromboembolic events, the Austrian National Competent authority has suspended the use of a batch of COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca (batch number ABV5300) [1], after a person was diagnosed with multiple thrombosis and died 10 days after vaccination. The ABV5300 batch consists of 1 million doses of the vaccine and was delivered to 17 EU countries (Austria, Bulgaria, Cyprus, Denmark, Estonia, France, Greece, Iceland, Ireland, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxemburg, Malta, the Netherlands, Poland, Spain, Sweden) [2]. The purpose of our clinical case is to increase awareness of a possible side effect of batch ABV5300 of the AstraZeneca vaccine. We do not claim a causal relationship between these events and the vaccination but there is a temporal coincidence of a thromboembolic event in a young person devoid of risk factors with a prior COVID-19 vaccination.
References
- COVID-19 Vaccine AstraZeneca: PRAC preliminary view suggests no specific issue with batch usedin Austria.
- Brooks M (2012) EMA Launches Review of Clot Risk with AstraZeneca COVID Vaccine.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.