Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Mitochondrial Proteins as Molecular Targets For Glutathione-Based Drugs
*Corresponding author: Igor Kvetnoy, Iva Farm LLC, Russian Federation, 190121, St. Petersburg, Pskovskaya Str. 17, Russia.
Received: February 15, 2022; Published: February 25, 2022
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2022.15.002137
Abstract
Mitochondrion is one of the most important cell organelles which provide cells with energy, participate in cell turnover and activate endogenous mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity. Research into the structural and functional organization of mitochondria is extremely important and challenging for developing target pathways of drugs for various pathologies and aging. The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of the V007 drug on the expression of mitochondrial biomarkers in myocardial and liver cells of elderly rats in vivo in order to find a possible mechanism of its target action. Molecular biological methods were used to study the expression of key mitochondrial proteins: Tom70, Tom20, VDAC, DRP1, Prohibitin, Parkin, PINK1 in myocardial and liver cells of elderly rats in the normal condition and with administration of the innovative V007 drug.
The conducted study has shown that V007 is a drug that regulates and normalizes mitochondrial functions. This study allowed to get a more detailed understanding of V007 target action at the molecular level and further verify intracellular and intertissue signal molecules that could be targets for its pharmacological action, which will enable us to extend indications and the scope of its application for prevention and treatment of socially significant diseases. The obtained results open a wide spectrum of possibilities for further investigations of V007 as a prospective drug of general regulatory and geroprotective action.
Keywords: mitochondria, mitochondrial proteins, function regulation, V007, target action
Introduction
Mitochondrion is one of the most important cell organelles which, as we understand today, in addition to their primary functionproviding cells with energy, participate in cell turnover and activate endogenous mechanisms of cell-mediated immunity. Mitochondria are active cell organelles whose structures (membranes, in particular) express a large number of signal molecules which play an important regulatory role in their active functioning [1–3].
Therefore, research into the structural and functional organization of mitochondria is extremely important and challenging for developing target pathways of drugs for various pathologies and aging. The V007 drug is pharmacologically based on oxygenated glutathione and inosine which are characterized by a wide range of metabolic transformations to various products whose signaling, and metabolic activity is required in drug treatment of disorders of stress, hypoxic, or other nature. Previous studies and analysis of V007 biological activity allow to presume that its regulatory and therapeutic action is realized through the stabilization of mitochondrial function processes, disruption of which may cause the development of a stress or pathological process of different etiology and pathogenesis.Give the above, we formed a panel of mitochondrial proteins/ biomarkers in view of their contribution to the regulation of mitochondrial activity. The panel included
Tom70
Key protein for mitochondrial function, responsible for providing the potential of the inner membrane of mitochondria [4,5].
Tom20
A Key protein for mitochondrial function, also responsible for providing the potential of the inner membrane of mitochondria [6].
VDAC
A protein providing the formation of ion channels in the external mitochondrial membrane, triggering apoptosis [7,8].
DRP1
A protein responsible for triggering mitochondrial fission, participating in the mechanisms of mitochondria-dependent apoptosis [9,10].
Prohibitin
A protein providing the regulation of mitochondrial respiratory activity, responsible for the stability of organization and copying of mitochondrial DNA, protection of cell against oxidative stress [11].
Parkin
A protein responsible for autophagy of damaged mitochondria, suppression of mitochondria-depended apoptosis [12,13].
PINK1
A protein providing protection of cells from stress-induced mitochondrial dysfunction [14,15].
The purpose of this study is to investigate the effect of the V007 drug on the expression of mitochondrial biomarkers in myocardial and liver cells in elderly rats in vivo in order to find a possible mechanism of its target action.
Materials and Methods
Characteristics of Experimental Animal Groups The study was conducted on 12 rats of Wistar line, of older age group (18 months). Two experimental groups were formed of 12 rats, 6 animals of matching ages (3 females and 3 males) in each group: group 1 (n=6) was control; group 2 (n=6) received V007. These groups are currently (given the epidemiological situation due to coronavirus pandemics) are of a special interest for investigating the effect of V007, since in elder rats inflammaging (chronic immune inflammation) processes develop, whose molecular mechanisms are in some details similar to the action of SARS-CoV.
Intramuscular administration of V007 to experimental group animals at a dose of 30mg/kg was performed daily for 7 days. Physiological saline solution (0.9% NaCl) was used as a solvent. The volume of the injected substance was 0.2ml per 250g of the animal’s weight. Intramuscular administration of physiological saline solution 0.9% NaCl) was performed to control group animals according to the same scheme as for the drug under study.
Sampling and Processing of Material
On the 8th day, the animals were withdrawn from the experiment by deep inhalation anesthesia, prosected, and fragments of their internal organs were taken out. For molecular microscopy analysis, we selected samples of the heart (myocardium, left ventricle) and liver as organs whose cells contain most of mitochondria. The tissue samples were fixed in parallel by two methods: one sample was subjected to cryopreservation in liquid nitrogen for subsequent utilization by means of immunofluorescence method and stored in 10% neutral buffered formalin (pH 7.2) then dehydrated in spirits and embedded in paraffin according to the standard histological procedure, for general morphological analysis
Histological Examination
For histological examination of myocardium and liver samples, we prepare sections (4–6 μm thick) which were stained with hematoxylin and eosin, using Weigert–Van Gieson’s method, and subjected to PAS reaction for subsequent assessment in transmittedlight microscopy. Based on the results of histological examination, to conduct an immunohistochemical study, we selected tissue samples with one-type morphological changes that characterize each group under study. Immunohistochemical Study.
The Immunohistochemical Study
The immunohistochemical study was carried out on cryostat sections using monoclonal rabbit antibodies to DRP1 (1:1000, Abcam, UK), PINK1 (1:500, Abcam, UK), Prohibitin (1:500, Abcam, UK), TOM20 (1:50, Abcam, UK), VDAC1 (1:50, Abcam, UK), monoclonal mouse antibodies to Parkin (1:500, Abcam, UK), and monoclonal rabbit antibodies to TOM70 (1:400, Invitrogen, USA).
For Fluorescent Staining, We Used the Following Secondary Antibodies
anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa Fluor 350 (Thermo Fisher, USA), anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa Fluor 405 (Abcam, UK), anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa Fluor 430 (Thermo Fisher, USA), anti-mouse conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568 (Abcam, UK), anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa Fluor 568 (Abcam, UK), anti-mouse conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594 (Abcam, UK), anti-rabbit conjugated to Alexa Fluor 594 (Abcam, UK), anti-mouse conjugated to Texas Red (Abcam, UK), anti-rabbit conjugated to TRITC (Thermo Fisher, USA). All primary antibodies were checked at standard control (positive and negative) staining to select a protocol and antibody titer.
Morphometry and Computer Analysis of Microscopy Images
To evaluate the results of immunohistochemical staining, a morphometric study was performed using the microscope image analysis system consisting of an Olympus IX73 microscope, Olympus DP80 digital camera, personal computer AMD Ryzen 3 3200G, and CellSens software. 12-bit (gray scale) images were obtained using a pseudostaining technique. In each instance, we analyzed a tissue area not less than 1mm2, with photofixation of at least five fields of view at 100x magnification. The relative area of expression of the biomarker was measured by using the immunofluorescence method against the total area of cells within the field of view. The relative expression area was expressed as a percentage.
Statistical Analysis of Results
Descriptive statistics methods included the estimation of the arithmetic mean, standard deviation from the mean, and the statistical standard error of the sample arithmetic mean. Statistical processing of the obtained results was carried out using the methods of nonparametric statistics due to the need for statistical procedures that allow processing data from small samples with variables of an unspecified type of distribution. To assess the differences between independent samples, the U-Mann-Whitney test was used, the level of statistical significance did not exceed 0,05 in all tests.
Results and Discussion
Histological examination did not reveal any differences in animals with regard to gender, yet one should account for a significant contribution of sex hormones to metabolic processes. Therefore, for the molecular marker investigation, the groups of animals were divided into two subgroups-males and females.
Examination of Cardiomyocytes in Elderly Male Rats
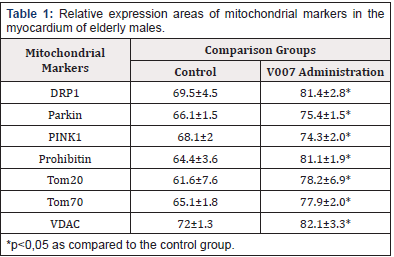
The morphological picture in the control group and V007 group was characterized by changes in the myocardium with signs of dystrophy, cardiomyocyte hypertrophy, intermuscular stromal sclerosis, vessel wall thickening. The expression of mitochondrial proteins in the control group showed relatively low values with a significant increase with administration of V007 (Table 1, Figure 1& 2 & 5).
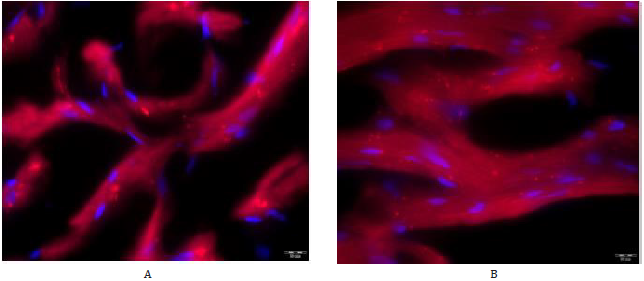
Figure 1: Immunofluorescent staining with antibodies to PINK1 of myocardial cells of elderly male rats. А – control group, ×1000; B – administration of V007, ×1000.
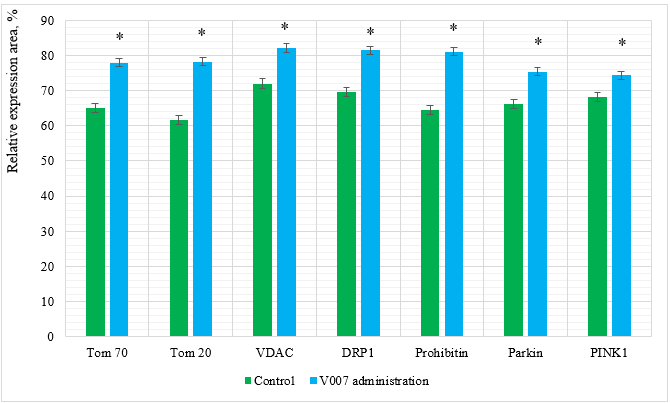
Figure 2: Relative expression area of mitochondrial proteins in myocardial cells of elderly male rats. *p<0,05 as compared to the control group.
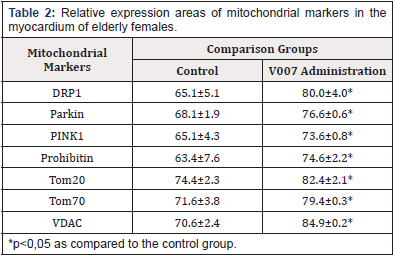
In the case of V007 administration, we observed a statistically valid increase in expression of all examined mitochondrial proteins in the myocardium of elderly male rats: Tom 70 by 1.2 times; Tom 20 by 1.3 times; VDAC by 1.1 times; DRP1 by 1.2 times; Prohibitin by 1.3 times; Parkin by 1.1 times; PINK1 by 1.1 times. Examination of Cardiomyocytes in Elderly Female Rats. The morphological picture of the myocardium was of the same type in the subgroup of elderly females, showing no differences in the signs of fibrosis, dystrophic changes, vascular bed damage, which is most probably due to a decrease in the protective effect of steroid hormones responsible for metabolic processes in the female body, especially the metabolism of fats and proteins. The expression of mitochondrial proteins in the control group showed average values which, however, were higher than in elderly males, which could also be due to the effect of steroid hormones. With administration of V007, the expression values of all mitochondrial proteins significantly increased (Table 2, Figure 3 & 4 & 5).
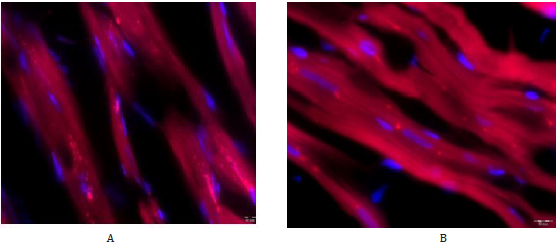
Figure 3: Immunofluorescent staining with antibodies to Tom20 of myocardial cells of elderly female rats. А – control group, ×1000; B – administration of V007, ×1000.
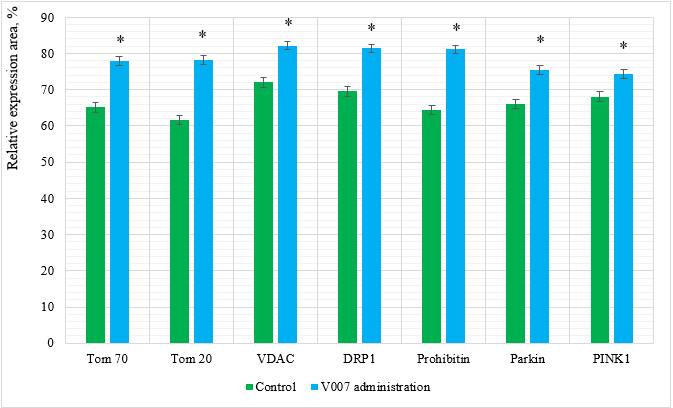
Figure 4: Relative expression area of mitochondrial proteins in myocardial cells of elderly female rats. *p<0,05 as compared to the control group.
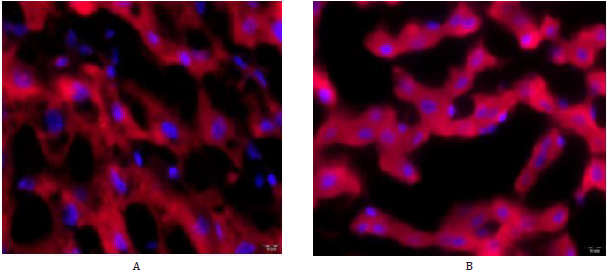
Figure 5: Immunofluorescent staining with antibodies to Prohibitin of liver cells of elderly male rats. А – control group, ×1000; B – administration of V007, ×1000.
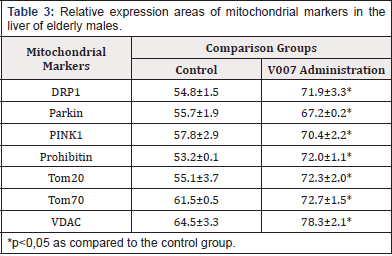
In the case of V007 administration, we observed a statistically valid increase in expression of all examined mitochondrial proteins in the myocardium of elderly female rats: Tom 70 by 1.1 times; Tom 20 by 1.1 times; VDAC by 1.2 times; DRP1 by 1.2 times; Prohibitin by 1.2 times; Parkin by 1.1 times; PINK1 by 1.1 times. Examination of Hepatocytes in Elderly Male Rats. Morphological changes in the liver tissues in the comparison groups did not differ and were presented by dystrophic and dyscirculatory changes. The expression of mitochondrial proteins in the control group showed relatively low values with a significant increase with administration of V007 (Table 3, Figure 6 & 7). In the case of V007 administration, we observed a statistically valid increase in expression of all examined mitochondrial proteins in the liver of elderly male rats: Tom 70 by 1.2 times; Tom 20 by 1.3 times; VDAC by 1.2 times; DRP1 by 1.3 times; Prohibitin by 1.4 times; Parkin by 1.2 times; PINK1 by 1.2 times.
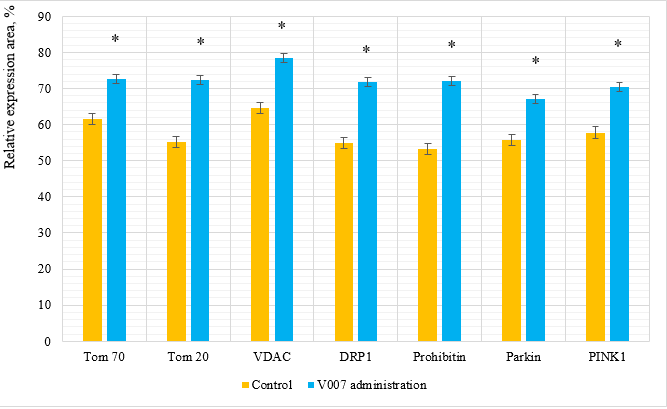
Figure 6: Relative expression area of mitochondrial proteins in liver cells of elderly male rats. *p<0,05 as compared to the control group.
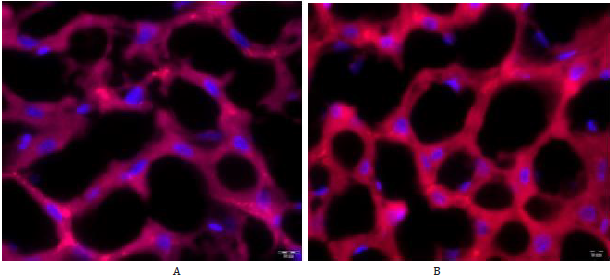
Figure 7: Immunofluorescent staining with antibodies to Parkin of liver cells of elderly female rats. А – control group, ×1000; B – administration of V007, ×1000.
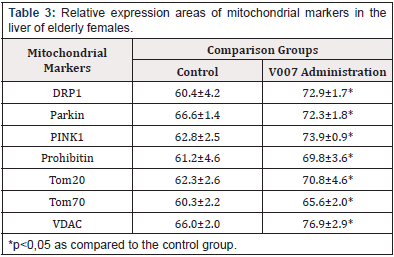
Examination of Hepatocytes in Elderly Female Rats. The liver tissues did not have morphological differences in the comparison groups. Morphological changes were presented by dystrophic and dyscirculatory changes. The expression of mitochondrial proteins in the control group showed relatively low values with a significant increase with administration of V007 (Table 4, Figure 8). In the case of V007 administration, we observed a statistically valid increase in expression of all examined mitochondrial proteins in the myocardium of elderly female rats: Tom 70 by 1.1 times; Tom 20 by 1.1 times; VDAC by 1.2 times; DRP1 by 1.2 times; Prohibitin by 1.1 times; Parkin by 1.1 times; PINK1 by 1.2 times.
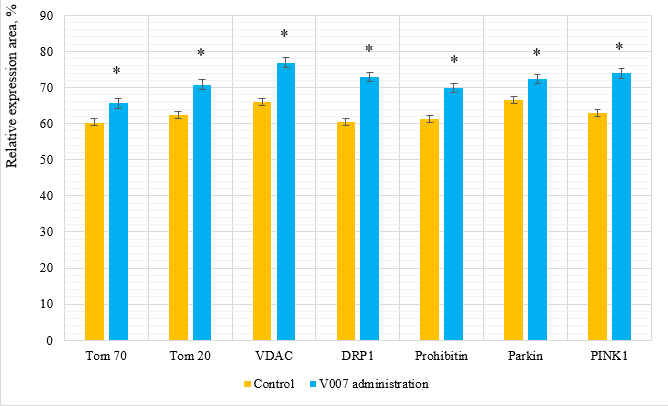
Figure 8: Relative expression area of mitochondrial proteins in liver cells of elderly female rats. *p<0,05 as compared to the control group.
It should be noted that the rates of mitochondrial protein expression in the liver are somewhat different from the rates of marker expression in the myocardium, which might be due to different intracellular regulation mechanisms. Hepatocytes possess a higher potential and alternative pathways to regulate metabolism and energy synthesis. Mitochondria demonstrate a strong tissue and particularly gender specificity as they are inherited maternally only. Sexual dimorphism of mitochondrial oxidation capacity has been described for numerous tissues, particularly in the liver. ATP stimulated respiration, protein content, and cardiolipin level in female mitochondria than in male. Cardiomyocytes of female rats have a lower content of mitochondria, but female mitochondria are more efficient and more differentiated than male mitochondria [16].
An important criterion to evaluate mitochondrial activity is the state and potential of the external mitochondrial membrane whose main proteins are Tom70 and Tom20 which participate in transport and provide the inner membrane potential for ATP production. Tom70 and Tom20 expression rates can be viewed as a baseline, which is explained by the absence of hormone fluctuations that affect general metabolic processes [17]. In the case of V007 administration, we observed a statistically valid increase in the expression rate of TOM-complex proteins, which is the highest for all groups under study and could reflect an accelerated protein import and serve as a criterion for activation of adaptive processes in the myocardium and liver, which is also confirmed by morphological changes.
Activation of mitochondria leans not only to an increase in ATP production but also to an increase in ROS produced by their own respiratory chain. Aberrant mitochondria are removed by a selective form of autophagy, termed mitophagy, which is a crucial mechanism in mitochondrial in mitochondrial quality control. Mitochondrial quality control is regulated by the PINK1/Parkin system which acts as a sensor of mitochondrial quality and is activated particularly after a change of the mitochondrial membrane potential interacting again with Tom70 [18]. VDAC1, which forms ion channels in the external mitochondrial membranes, is an extremely dynamic protein that has various conformations and isoforms. VDAC1 contributes to high membrane permeability for mitochondrial proteins with different action potential [19]. A higher expression rate of this protein was noted after V007 administration.
The function of DRP1 is to regulate the membrane conformation through oligomerization followed by a mitochondrial membrane rupture in mitophagy [20]. A significant increase in Prohibitin expression is consistent with changes in expression rate of other mitochondrial proteins, as it acts as a chaperon protein in the mitochondrial respiratory chain and structural framework [21]. Therefore, an increase in its expression can be evidence of active ATP synthesis processes.
Conclusion
Our findings provide evidence that the V007 drug has a general regulatory and geroprotective effect, being a target drug that regulates cardiomyocyte and hepatocyte functions through activating the expression of key mitochondrial proteins. Further investigation into the V007 drug will help refine our understanding of its target action at cellular level. Additionally verify intracellular and intertissue signal molecules that could be targets for its pharmacological action.
References
- Anderson AJ, Jackson TD, David A Stroud, Stojanovski D (2019) Mitochondria-hubs for regulating cellular biochemistry: emerging concepts and networks Biology, Medicine. Open Biology 9(8): 190126.
- Araiso Y, Tsutsumi A, Qiu J, Imai K, Shiota T, et al. (2019) Structure of the mitochondrial import gate reveals distinct preprotein paths. Nature 575(7782): 395-401.
- Pfanner N, Warscheid B, Wiedemann N (2019) Mitochondrial proteins: From biogenesis to functional networks. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(5): 267-284.
- Wang Pm, Wang D, Yang Y, Hou J, Wan J, et al. (2020) Tom70 protects against diabetic cardiomyopathy through its antioxidant and antiapoptotic properties. Hypertens Res 43(10): 1047-1056.
- Hira S, Packialakshmi B, Tang E, Zhou X (2020) Dexamethasone upregulates mitochondrial Tom20, Tom70, and MnSOD through SGK1 in the kidney cells. J Physiol Biochem 77(1): 1-11.
- Di Maio R, Barrett PJ, Hoffman EK, Barrett CW, Zharikov A, et al. (2016) α-Synuclein binds to TOM20 and inhibits mitochondrial protein import in Parkinson's disease. J. Sci Transl Med 8(342):342ra78.
- Fang D, Eduardo N Maldonado (2018) VDAC Regulation: A Mitochondrial Target to Stop Cell Proliferation. Adv Cancer Res 138: 41-69.
- Shoshan-Barmatz V, Shteinfer-Kuzmine A, Verma A (2020) VDAC1 at the Intersection of Cell Metabolism, Apoptosis, and Diseases. Biomolecules 10(11): 1485.
- Tian L, Neuber-Hess M, Mewburn J, Dasgupta A, Dunham-Snary K, et al. (2017) Ischemia-induced Drp1 and Fis1-mediated mitochondrial fission and right ventricular dysfunction in pulmonary hypertension. J Mol Med(berl) 95: 381-393.
- Jia-Yu Jin, Xiang-Xiang Wei, Xiu- Ling Zhi, Xin-Hong Wang, Dan Meng, et al. (2020) Drp1-dependent mitochondrial fission in cardiovascular disease. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42(5): 655-664.
- Chowdhury D, Kumar D, Sarma P, Tangutur A, Pal Bhadra M, et al. (2017) PHB in Cardiovascular and Other Diseases: Present Knowledge and Implications. Curr Drug Targets.18(16): 1836-1851.
- Da Costa CA, Duplan E, Rouland L, Checler F (2018) The transcription factor function of Parkin: breaking the dogma. Front Neurosci 12: 965.
- Gladkova C, Maslen SL, Skehel JM, Komander D (2018) Mechanism of parkin activation by PINK1. Nature 559: 410-414.
- Heo JM, Ordureau A, Paulo JA, Rinehart J, Harper JW, et al. (2015) The PINK1-PARKIN mitochondrial ubiquitylation pathway drives a program of OPTN/NDP52 recruitment and TBK1 activation to promote mitophagy. Mol Cell 60(1): 7-20.
- Sekine S, Youle RJ (2018) PINK1 import regulation; a fine system to convey mitochondrial stress to the cytosol. BMC Biol 16(1): 2.
- Ventura-Clapier R, Piquereau J, Veksler V, Garnier A (2019) Estrogens, Estrogen Receptors Effects on Cardiac and Skeletal Muscle Mitochondria. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 10: 557.
- Lazarou M, Jin SM, Kane LA, Youle RJ (2012) Role of PINK1 binding to the TOM complex and alternate intracellular membranes in recruitment and activation of the E3 ligase Parkin. Dev Cell 22(2): 320-333.
- Quinn P, Moreira P, Ambrósio, Alves C (2020) PINK1/PARKIN signalling in neurodegeneration and neuroinflammation. Acta Neuropathol Commun8(1): 189.
- Shoshan-Barmatz V, Maldonado EN, Krelin Y (2017) VDAC1 at the crossroads of cell metabolism, apoptosis and cell stress. Cell Stress 1(1): 11-36.
- Osellame LD (2016) Cooperative and independent roles of the Drp1 adaptors Mff, MiD49 and MiD51 in mitochondrial fission. J Cell Sci 129(11): 2170-2181.
- Cooper HA, Eguchi S (2018) Inhibition of mitochondrial fission as a novel therapeutic strategy to reduce mortality upon myocardial infarction. Clin Sci (Lond) 132: 2163-2167.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.