Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Therapeutical Medicine for Wound Healing
*Corresponding author: Muhammad Waqar Mazhar, Department of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology, Government College University, Pakistan.
Received: January 19, 2022; Published: February 25, 2022
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2022.15.002133
Abstract
Wounds are common external or internal damages to the body, usually caused by a physical, chemical, or biological agents. There exists natural repair wound healing repair in that includes immunological responses i.e., inflammation and necrosis. Naturally, body repairs wounds itself, but the period of healing is relatively slow. This healing process may further be delayed by the pathogens attack or weaker immune response. Wounds heal biochemically, but the time of the healing can be reduced by applying different herbs like the plant-based treatments. Sub-continent is rich in having an immense variety of medicinal plants as well. This literature review is about the role of different plants in wound healing, the efficacy of herbs on wound healing.
Keywords: Wound healing, biological agents, therapeutics plant, immune response
Introduction
The wound is defined as loss or disturbance of the proper anatomic functioning of the tissue. In this damage, microbes can reach the site of injury, and this could be very dangerous. Naturally, the healing of the wound is slow, and this slowness is very painful for the patient and for the soldiers i.e., solder’s wound should be healed rapidly, and the soldier must be returned to the field [1]. Sub-continent is rich in the plant-based knowledge of the treatment of cuts, wounds, and burns. In the pharmaceutical industry, there are a lot of drugs that are synthesized with modern techniques and have only antibacterial effects. Therefore, the healing of the wound is natural only. [2]. Nowadays, in medicine, the plants or plant parts are used extensively [3]. Besides, most of the compounds used in medicines are derived from plants [4]. The healing property of plants was identified by our ancestors through many trials and errors. That took time but after hundreds or thousands of years of findings, the properties are well identified. [5] Developing or poorly developed countries face the issue of delayed wound healing because of an unhygienic environment. [6] The microbial attack is very frequent as well because the wounds are cuts or openings of the tissue. Therefore, injured persons are vulnerable to many diseases. Wounds can occur because of different events; thus, the appropriate method of treatment should be used. There are different stages of wound healing viz Hemostasis Phase, Inflammatory phase, Proliferative phase, and Remodeling phase. The metabolic disturbance also affects these phases resulting in delayed healing. According to a study in Colombia, people of small villages and countries make native herbal medicines and because of this treatment, there are very few chances of infection of resistant organisms [7]. That is the reason why people (traditionally using herbs) say that herbal medicines are more beneficial than modern medicine. The purpose of treating the wound is to reduce its healing time. For this, the identification of the agent responsible for the acceleration of wound healing is required. There are different herbs and other plants used for the wound healing i.e., Aloe vera “Aloe barbadensis miller”, Neem “Azadirachta indica”, False Daisy “Eclipta protrata”, West Indian Lantana “Lanatana camara” and tridax daisy “Tridax procumbens”. [8] The purpose of this review is to investigate some herbal plants and find their role and the process of wound healing.
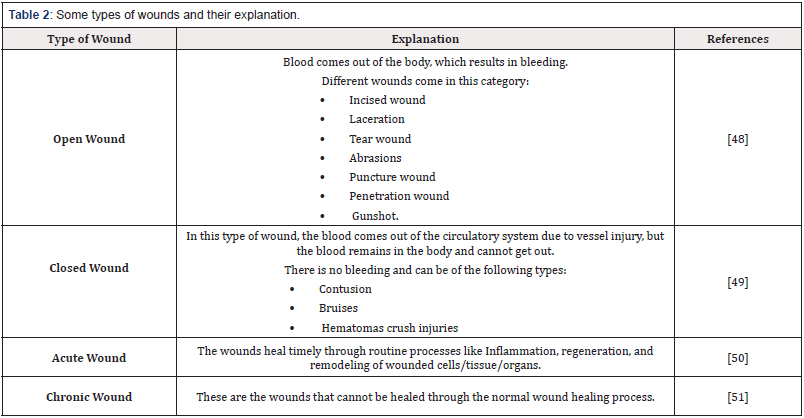
Wound
A wound is an injury to the bodyside cells/tissues/organs. It is usually resulted because of the physical, chemical, or microbial agent. It may also the result of immunologic processes such as Inflammation or necrosis. Biochemically, a wound can be the loss/ disturbance of the proper anatomic functioning of cells/tissues/ organs. During the damage, microbial pathogens can reach the site of the wound, and this could be very unsafe. Naturally, the healing of the wound is slow, and this gradualness is very painful for the patient and for the soldiers i.e., solder’s wound should be healed rapidly, and the soldier must be returned to the field [9]. There are different factors upon which the wounds are classified and different types of wounds. Some of these are mentioned and explained in (Table 2).
Wound healing
Healing of skin and soft tissue wounds involves three major steps which are inflammatory, proliferative, and remodeling stage. In the inflammatory stage, homeostasis is maintained by the platelets. [10] Platelets induce the clotting. It is the immediate response that is generated after the damage has happened. Blood vessels coagulate, thrombocytes and platelets collectively form a fibrin network. The formation of this fibrin network depends on the action of some factors [11]. This fibrin network restores the skin’s function by organizing the matrix for cellular movement at the site of the wound. The Fibrin network also protects against microorganisms [12]. This inflammatory response is generated by the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines e.g., IL-1 β (Interleukin 1 beta), TNF-α (Tumor necrosis factor), and INF-γ (Interferongamma) [13]. Then macrophages reach the site of the wound to remove the cell debris. Macrophages also attract the other inflammatory cells to the wound area by releasing the chemotactic factors e.g., cytokines, pro-angiogenic, inflammatory, and fibro genic factors [5,6]. The proliferative stage of damaged tissue starts on the 4th day of the injury and ends on the 21st day. Different cells are involved in the proliferation i.e., macrophages, lymphocytes fibrocytes, neurocytes, and amniocytes. These cells collectively re-establish the function of skin and fill the defects (closure of wound). Re-modeling of tissue is just like the interior finishing i.e., maturation. The time of re-modeling starts from the 21st day and lasts for 2 years. Fibrocytes play their role the re-modeling fibrocytes to develop tensile strength. Now the healed tissue exactly looked like the undamaged tissue. [7].
Causes of wounds
The cause of the wound must be identified before the initiation of treatment so that it can be controlled accordingly. There are different causes of the wound which are listed in (Table 1). Underlying causes of tissue damage Trauma (initial or repetitive) Scalds and burns (thermal and chemical) Animal bites or insect stings Malignancy Pressure Vascular compromise (arterial, venous, lymphatic, or mixed) Immunodeficiency Adverse effects of medications Psychosocial disorders Nutritional deficiencies Metabolic disease, including diabetes Connective tissue disorders.
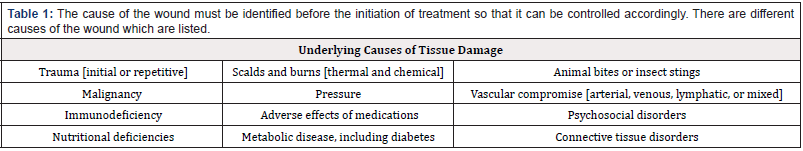
Table 1: The cause of the wound must be identified before the initiation of treatment so that it can be controlled accordingly. There are different causes of the wound which are listed.
Stages of wound healing
There are some stages of healing that are given in the (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Homeostasis is the first response generated within minutes. Platelets play their role in clotting. The period of 1-4 days of injury is Inflammation. during this period neutrophils and macrophages remove cell debris and involve in the process of phagocytosis. Proliferation is the period of the 4th-21st day of injury. Proliferation involves the re-establishment of skin function and different cells (Macrophages, Lymphocytes, Fibroblasts, Neurocytes, and Angiocytes) perform their function to re-establish the function of the skin.
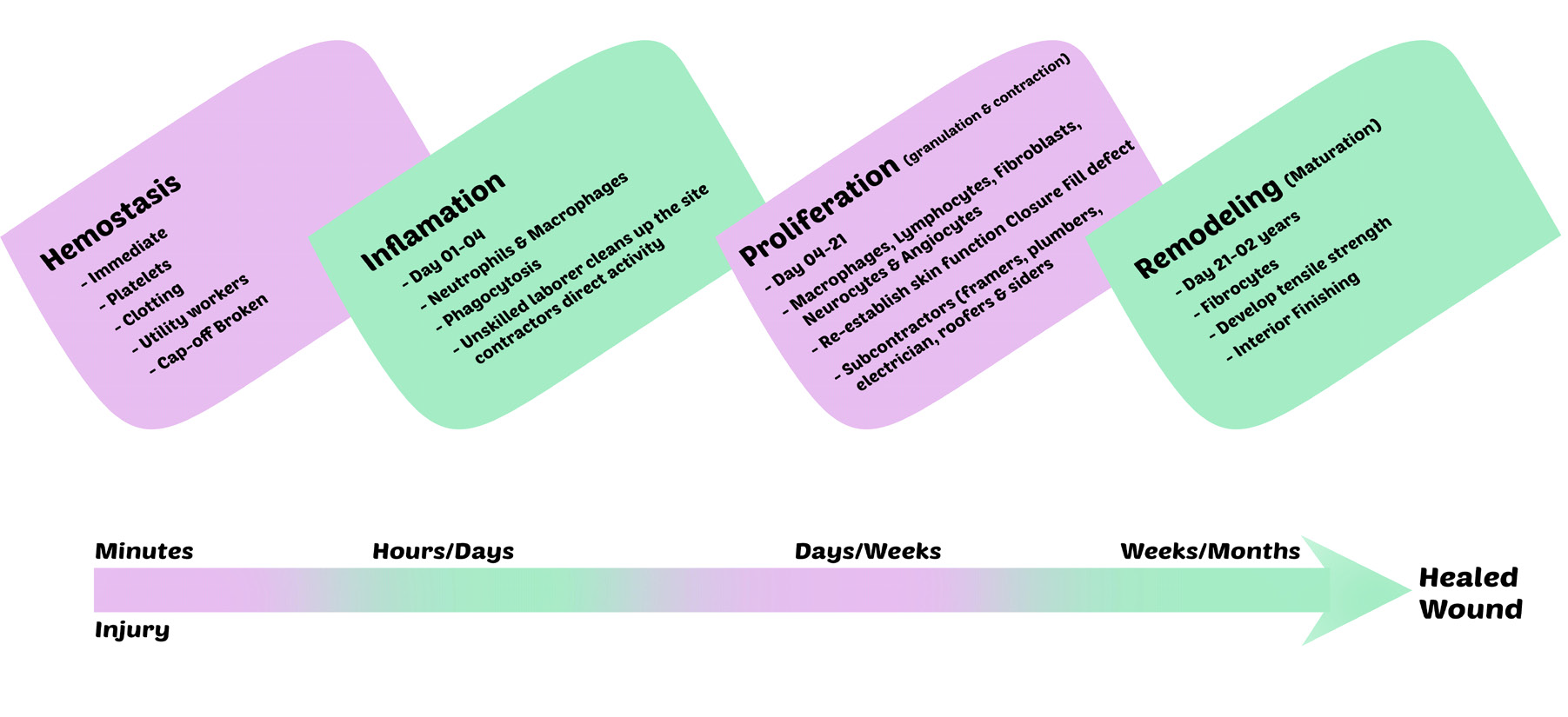
Figure 1: Homeostasis is the first response generated within minutes. Platelets play their role in clotting. The period of 1-4 days of injury is Inflammation. during this period neutrophils and macrophages remove cell debris and involve in the process of phagocytosis. Proliferation is the period of the 4th-21st day of injury. Proliferation involves the re-establishment of skin function and different cells (Macrophages, Lymphocytes, Fibroblasts, Neurocytes, and Angiocytes) perform their function to re-establish the function of the skin.
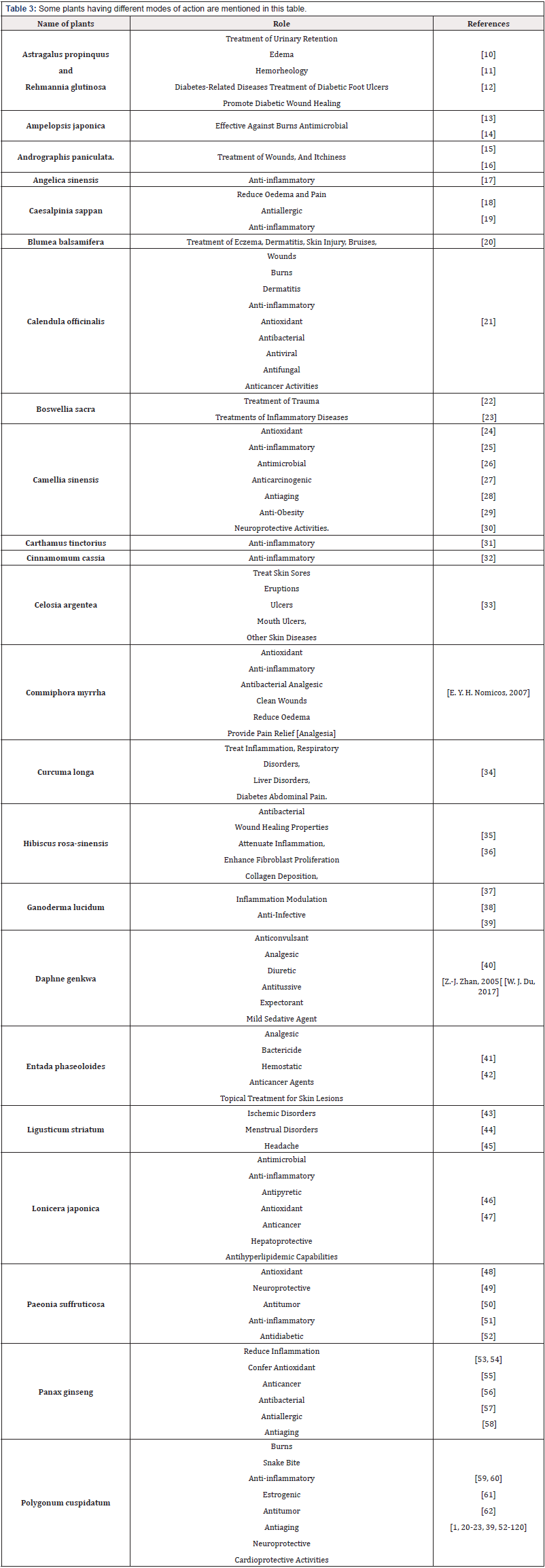
Therapeutic plants: A remedy for wounds
As mentioned earlier, different plant species can be used as a remedy for wounds. The mode of action of some plants to wound healing is mentioned in (Table 3). Some of these plant species are described below:
Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis miller)
Aloe vera is a local plant found abundantly in the sub-continent. Aloe vera is being used for the treatment of wounds for the last 5000 years in many parts of the world like Egypt, Romans and by some populations of Africa, Asia, and America. Aloe vera is the most ancient plant which is being used for the clinical purpose [14]. It has a swollen root system, small and fleshy leaves. Aloe vera is present in the forests of the sub-continent as a wild herb. This plant is commonly used for the treatment of burns, cuts, and other small wounds. It is used in the cosmetics like lotions and sun blokes as well. There are many compounds in Aloe vera which play important role in wound healing e.g., Acetone plays a role in the killing of pathogens (antimicrobial) [15]. Other compounds that have the same role are saponins, acemannan, and anthraquinone derivatives [16]. Polysaccharides present in the Aloe vera have a role in the granulation [17]. According to the past study of this plant, it was applied after every 3 days on the chemically burn wound. Then the diameter of the wound was measured after the specific period. Aloe vera showed protection of skin. when orally taken then showed effectiveness on the ulcer [18].
Tumeric (Curcuma longa)
Curcumas belong to ginger family and has curcumin in its roots [19] which is very important in medication and reservation of current food practices showed that curcumin is used to treat respiratory and liver disorder [20]. In china, curcumin use as a traditional medicine for treatment of abdominal pain. This molecular interact at transcription, translation, and post tanscriptional changesand act as a key of these cellular pathway. Cell adhesion molecules,5- LOX, aptosis, NF–κB, Cyclooxygenases-2, STAT3, prostaglandin E2, C-reactive protein, Triglycerides, apoptosis, phosphorylase kinase, creatinine, AST, ALT, transforming growth factor-β, prostate specific antigen, ET-1, heme-oxygenase-1, cell adhesion molecules, and pro-inflammatory cytokines are targated pathways. [21].in vivo studies, more than 100 studies in which curcumin as a treatment for epithelial cancer. It’s very important and benficial effects to alter extracellular and pericellular matrix. [22]. curcimum enhances granulation tissue formation, fibroblast proliferation, and collegen deposition in cutaneous wound healing. [22].
Greater burdock (Artium lappa)
It is found in some parts of America, Europe, and Asia for the treatment of skin problems like burns, acne, and rashes and some clinical uses [23,24]. Clinically Artium lappa is antidiabetic [25] antioxidants [26] anticancer [27]. But for skin problems, the qualities that make Artium lappa useful are antimicrobial [28] and antiviral [29]. It is mostly cultivated on perennial herbs [23] it is commonly known as burdock it is used for the treatment of sore in the throat and also used for skin treatment such as skin burns, rashes, and acene [30] Recent studies showed that Artium lappa is anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, antiviral [31-33], anti-cancer, antidiabetic, antioxidant [26] and hepatoprotective activities the roots extract of articium lappa for dermal ECM metabolism decrease wrinkles on the skin [34].
False Daisy (Eclipta prostrata)
This species is found in African countries and has a significant role in the wound healing. In a study, it was applied in the form of past on the wound. The diameter of the wound was measured regularly. The time of the haling was reduced to 85% than the normal conditions. (Wikipedia). Eclipta prostrata is being used locally in Pakistan but there is no pharmaceutical industry that makes medicine from this herb. An experiment was performed to check the wound healing activity of E. prostrata. Three types of extracts of E. prostrata were used i.e., aqueous, hydroethanolic extract, and vaseline. The ability of E. prostrata was observed under the microscope. E. prostrata reduced the time of all the three stages of wound healing i.e., inflammation, proliferation, and re-modeling. Different chemicals play their role in the healing process. Further work is needed to know about the chemicals that which chemicals are released, which play a role in wound healing [8,9].
Green Chiretta (Andrographis paniculata)
It is also commonly known as green chiretta; it is used for the treatment of fever, snakebite, dysentery wound infection itchiness in china, Asian countries, and India [35-37]. Its extract contains antioxidant [38] anti-inflammatory, antidiabetic, antimicrobial, and antiviral activities Recent research shows that 10 percent leaf extract of Andrographis paniculate is used to enhance the wound closure rate in Rats animals that are treated with Andrographis paniculata showed reduced rate of Inflammation, reduced rate of scarring and has more androgenesis and collagen fiber for the closure of wounds. A diterpenoid is extracted from the leaves of Andrographis paniculata which play important role in autoimmune disorders.
Pepervine (Ampelopsis japonica)
It is found all over eastern Asia and northern America. Ampelopsis japonica roots are used to treat ulcers, burns, and other indications [39]. Like this, it is also used as a neuroprotective [40] antimicrobial and also protect from cancer [41,40] Ampelopsis is also used to extract ethanol, which is used for the scold injuries in rats [42], and it is also observed that treatment with Ampelopsis japonica is more powerful than vaseline or petroleum gel; it improved reepithelialization, vascularization, and collagen formation.
Indian pennywort (Centella asiatica)
In a study, rat’s skin wounds were created with radiations. These wounds were healed earlier when applied with Centella asiatica than naturally [43] A compound derived from Centella asiatica known as Asiaticoside enhances the formation of collagen and epithelial layer in the guinea pig [44] A compound madecassoside derived from Centella asiatica when orally applied to the mouse, it was effective in collagen formation and angiogenesis [45].
Neem (Azadirachta indica)
Neem is present abundantly all over the sub-continent. Local people are very familiar with it. Neem has small leaves and a strong stem. The oil extracted from it and the leaves are used for treatment because neem has antimicrobial characteristic so kill the pathogens and protect the wound from further damage. It protects the patient from secondary diseases so promotes wound healing. [46]
Onion (Allium cepa)
Allium cepa has many uses in the medicinal field but its role in wound healing is also identified. Allium cepa reduces the time of healing and plays an important role by producing collagen concentration [47]. The method and the chemical composition are unknown.
Future perspectives
At present some herbal plants are used for wound healing and are safe compared to synthetic drugs.
Conclusion
This review discussed why different medicinal is used to treat serious infectious diseases and skin disorders. Over millennia human develop different ways to use botanical resources as medicine. Wounds heal naturally, but this review article tells that nature has provided so many plants to heal the wounds more rapidly. Some scientific industries use modern technology in making drugs for the treatment of wounds. However, traditional methods should be standardized.
References
- Lazarus GS, Cooper DM, Knighton DR, Margolis DJ, Pecoraro RE, et al., (1994) Definitions and guidelines for assessment of wounds and evaluation of healing. Arch Dermatol 130(4): 489-93.
- Rathinamoorthy R, Thilagavathi G (2014) Terminalia chebula-review on pharmacological and biochemical studies. Int J PharmTech Res 6(1): 97-116.
- Lule F (2019) Evaluation of the Opportunities of Medical Plants in the Treatment of Diseases. Evaluation 6(2).
- Principe PP (1996) Monetizing the pharmacological benefits of plants. Medicinal resources of the tropical forest: biodiversity and its importance to human health. Columbia University Press 191-219.
- Gurib Fakim A (2006) Medicinal plants: traditions of yesterday and drugs of tomorrow. Mol Aspects Med 27(1): 1-93.
- Hart RA (2013) Children's participation: The theory and practice of involving young citizens in community development and environmental care. Routledge.
- Vallejo MC, Pérez Rincón MA, Martinez Alier J (2011) Metabolic Profile of the Colombian Economy from 1970 to 2007. Journal of industrial Ecology 15(2): 245-267.
- Budovsky A, Yarmolinsky L, Ben Shabat S (2015) Effect of medicinal plants on wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 23(2): 171-183.
- Budovsky A, Yarmolinsky L, Ben Shabat S (2016) Effect of poly‐herbal preparations on wound healing. Wound Repair Regen 24(1): 196-197.
- Enoch S, Leaper DJ (2005) Basic science of wound healing. Surgery (Oxford) 23(2): 37-42.
- Heemskerk J, Mattheij N, Cosemans J (2013) Platelet‐based coagulation: different populations, different functions. J Thromb Haemost 11(1): 2-16.
- Ferguson MW, O'Kane S (2004) Scar–free healing: from embryonic mechanisms to adult therapeutic intervention. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 359(1445): 839-850.
- Cavaillon JM (2001) Pro-versus anti-inflammatory cytokines: myth or reality. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand) 47(4): 695-702.
- Garcia Orue I, Garazi Gainza, Franciso Borja Gutierrez, Jose Javier Aguirre, Carmen Evora, et al. (2017) Novel nanofibrous dressings containing rhEGF and Aloe vera for wound healing applications. Int J Pharm 523(2): 556-566.
- Lawrence R, Tripathi P, Jeyakumar E (2009) Isolation, purification, and evaluation of antibacterial agents from Aloe vera. Braz J Microbiol 40(4): 906-915.
- Martínez Romero D, Alburquerque N, Valverde JM, Guillén F, Castillo S, et al., Postharvest sweet cherry quality and safety maintenance by Aloe vera treatment: a new edible coating. Postharvest Biology and Technology 39(1): 93-100.
- Jettanacheawchankit S, Siriruk Sasithanasate, Polkit Sangvanich, Wijit Banlunara, Pasutha Thunyakitpisal, (2009) Acemannan stimulates gingival fibroblast proliferation; expressions of keratinocyte growth factor-1, vascular endothelial growth factor, and type I collagen; and wound healing. J Pharmacol Sci 109(4): p. 525-531.
- Nair GR, Giridhar Seetharam Naidu, Supreet Jain, Ravleen Nagi, Ramanpal Singh Makkad, et al. (2016) Clinical effectiveness of aloe vera in the management of oral mucosal diseases-a systematic review. J Clin Diagn Res 10(8): ZE01-7.
- Tonkal A, Morsy TA, (2008) An update review on Commiphora molmol and related species. J Egypt Soc Parasitol 38(3): 763-796.
- Fadus MC, Cecilia Lau, Jai Bikhchandani, Henry T Lynch (2016) Curcumin: An age-old anti-inflammatory and anti-neoplastic agent. J Tradit Complement Med 7(3): 339-346.
- Gupta SC, Patchva S, Aggarwal BB (2013) Therapeutic roles of curcumin: lessons learned from clinical trials. AAPS J 15(1): 195-218.
- Joe B, Vijaykumar M, Lokesh B (2004) Biological properties of curcumin-cellular and molecular mechanisms of action. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 44(2): 97-111.
- Yuk-Shing Chan, Long-Ni Cheng, Jian-Hong Wu, Enoch Chan, Yiu-Wa Kwan, et al. (2011) A review of the pharmacological effects of Arctium lappa (burdock). Inflammopharmacology 19(5): 245-254.
- Batra R, Konstantinos Charizanis, Mini Manchanda, Apoorva Mohan, Moyi Li, et al. (2014) Loss of MBNL leads to disruption of developmentally regulated alternative polyadenylation in RNA-mediated disease. Mol Cell 56(2): 311-322.
- Ahangarpour A, Hamid Heidari, Ali Akbar Oroojan, Farhang Mirzavandi, Khalil Nasr Esfehani, et al. (2017) Antidiabetic, hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective effects of Arctium lappa root’s hydro-alcoholic extract on nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced type 2 model of diabetes in male mice. Avicenna J Phytomed 7(2): 169-179.
- Fierascu I, Cristina Elena Dinu Pirvu, Radu Claudiu Fierascu, Bruno Stefan Velescu, Valentina Anuta, et al. (2018) Phytochemical profile and biological activities of Satureja hortensis L.: A review of the last decade. Molecules 23(10): 2458.
- Yanchang Wei, Cai Rong Yang, Yan Ping Wei, Zhen Ao Zhao, Yi Hou, et al. (2014) Paternally induced transgenerational inheritance of susceptibility to diabetes in mammals. Proc Natl Acad Sci 111(5): 1873-1878.
- Pereira JV, Débora Cristina Baldoqui Bergamo, José Odair Pereira, Suzelei de Castro França, Rosemeire Cristina Linhares Rodrigues Pietro, et al. (2005) Antimicrobial activity of Arctium lappa constituents against microorganisms commonly found in endodontic infections. Braz Dent J 16(3): 192-196.
- Lima MJ, Cláudia G.Silva, Adrián Silva MT, José C.B.Lopes, Madalena Dias M, et al. (2017) Homogeneous, and heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of antibiotics using an innovative static mixer photoreactor. Chemical Engineering Journal 310: 342-351.
- Gao Q, Yang M, Zuo Z (2018) Overview of the anti-inflammatory effects, pharmacokinetic properties, and clinical efficacies of arctigenin and arctiin from Arctium lappa L. Acta Pharmacol Sin 39(5): 787-801.
- Vanine Gomes Mota, Luciana Muratori Costa, Jéssica Pereira Costa, Reinaldo Nóbrega de Almeida, Rivelilson Mendes de Freitas, et al. Antinociceptive and antioxidant activities of phytol in vivo and in vitro models. Neurosci J 2013: 949452.
- Veeramani A, Dias GM, Kirkpatrick SI (2017) Carbon footprint of dietary patterns in Ontario, Canada: A case study based on actual food consumption. Journal of cleaner production 162: 1398-1406.
- Pattanayek SK, Pham T, Pereira G (2005) Morphological structures formed by grafted polymers in poor solvents. The Journal of chemical physics 122(21): 214908.
- Knott AB, Guy Perkins, Robert Schwarzenbacher, Ella Bossy-Wetzelet (2008) Mitochondrial fragmentation in neurodegeneration. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 9(7): 505-518.
- Scartezzini P, Speroniet E (2020) Indian traditional medicinal plants: A concise review. J Ethnopharmacol 5(5): 174-190.
- Shedoeva A, David Leavesley, Zee Upton, Chen Fan (2019) Wound healing and the use of medicinal plants. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2019: 2684108.
- Jannat K (2020) Some Plants Used as Phytomedicine by Tribal Healers of Chittagong Hill Tracts, Bangladesh, in Wild Plants. CRC Press 90-120.
- Adeolu Alex Adedapo, Falayi OO, Oyagbemi AA (2015) Evaluation of the analgesic, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, phytochemical, and toxicological properties of the methanolic leaf extract of commercially processed Moringa oleifera in some laboratory animals. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 26(5): 491-499.
- Lee K, Byonghee Lee, Mi Hwa Lee, Bumjung Kim, Khanita Suman Chinannai, et al. (2015) Effect of Ampelopsis Radix on wound healing in scalded rats. BMC Complement Altern Med 15(1): 1-9.
- Lee YW, Dong Hyun Kim, Su Jin Jeon, Se Jin Park, Jong Min Kim, et al. (2013) Neuroprotective effects of salvianolic acid B on an Aβ25-35 peptide-induced mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Eur J Pharmacol 704(1-3): 70-77.
- Nho KJ, Jin Mi Chun, A Young Lee, Ho Kyoung Kim (2015) Anti-metastatic effects of Rheum Palmatum L. extract in human MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 40(1): 30-38.
- Lee DH, Dong Young Kim, So Young Yoon, Hyun Sun Park, Hyun-Sun Yoon, et al. (2015) Retrospective clinical trial of fusidic acid versus petrolatum in the postprocedure care of clean dermatologic procedures. Ann Dermatol 27(1): 15-20.
- Chen YJ, YS Dai, BF Chen, A Chang, HC Chen, et al. (1999) The effect of tetrandrine and extracts of Centella asiatica on acute radiation dermatitis in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 22(7): 703-706.
- Camacho Alonso F, Torralba Ruiz MR, García Carrillo N, Lacal Luján J, Martínez Díaz F, et al. (2019) Effects of topical applications of porcine acellular urinary bladder matrix and Centella asiatica extract on oral wound healing in a rat model. Clin Oral Investig 23(5): 2083-2095.
- Liu M, Yue Dai, Ying Li, Yubin Luo, Fang Huang, et al. (2008) Madecassoside isolated from Centella asiatica herbs facilitates burn wound healing in mice. Planta Med 74(08): 809-815.
- Raina R, Shahid Prawez, Pawan Kumar Verma, Nrip Kishore Pankaj (2008) Medicinal plants and their role in wound healing. Online Veterinary J 3(1): 21.
- Ju-Ye Ro, Jin-Hyeob Ryu, Hwa-Jin Park, Hyun-Jeong Cho (2015) Onion (Allium cepa L.) peel extract has anti-platelet effects in rat platelets. Springerplus 4(1): 1-8.
- Baldwin T, Sakthianandeswaren A, Curtis JM, Kumar B, Smyth GK, et al. (2007) Wound healing response is a major contributor to the severity of cutaneous leishmaniasis in the ear model of infection. Parasite Immunol 29(10): 501-513.
- Strodtbeck F (2001) Physiology of wound healing. Newborn and infant nursing reviews 1(1): 43-52.
- Sachdeva K (2011) Pharmacological Evaluatio Of Jatropha Curcas Li (Stem Bark) For Wou D Heali G Pote Tial I Rats.
- van Koppen CJ, Hartmann RW (2015) Advances in the treatment of chronic wounds: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 25(8): 931-937.
- Adedapo AA, Bisi Olajumoke Adeoye, Margaret Oluwatoyin Sofidiya, Ademola Adetokunbo Oyagbemi (2015) Antioxidant, antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory properties of the aqueous and ethanolic leaf extracts of Andrographis paniculata in some laboratory animals. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol 26(4): 327-334.
- Akbar S (2011) Andrographis paniculata: a review of pharmacological activities and clinical effects. Altern Med Rev 16(1): 66-77.
- Ali Khanh Z, Syed Ali-Raza Naqvi, Ammara Mukhtar, Zaib Hussain, Muhammad Yar, et al. (2014) Antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Hibiscus Rosa-sinensis Linn flower extracts. Pak J Pharm Sci 27(3): 469-474.
- ASYHARI, N.P.O., PENGARUH PEMBERIAN EKSTRAK BUAH OKRA (Abelmoschus esculentus) TERHADAP PENINGKATAN EKSPRESI VASCULAR ENDHOTELIAL GROWTH FACTOR (VEGF)(Studi Eksperimental Laboratoris pada Proses Penyembuhan Luka Bekas Pencabutan Gigi Tikus Wistar dengan Diabetes melitus). 2019, Universitas Airlangga.
- Baig MN, Shahid AA, Ali M (2015) In vitro assessment of extracts of the lingzhi or reishi medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (higher basidiomycetes) against different plant pathogenic fungi. Int J Med Mushrooms 17(4): 407-411.
- Banno N, Toshihiro Akihisa, Ken Yasukawa, Harukuni Tokuda, Keiichi Tabata, et al. (2006) Anti-inflammatory activities of the triterpene acids from the resin of Boswellia carteri. J Ethnopharmacol 107(2): 249-253.
- Chandran PK, Kuttan R (2008) Effect of Calendula officinalis flower extract on acute phase proteins, antioxidant defense mechanism and granuloma formation during thermal burns. J Clin Biochem Nutr 43(2): 58-64.
- Chen BT, Wei-Xi Li, Rong-Rong He, Yi-Fang Li, Bun Tsoi, et al. (2012) Anti-inflammatory effects of a polyphenols-rich extract from tea (Camellia sinensis) flowers in acute and chronic mice models. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2012: 537923.
- Chen LX, Hao He, Hao He, Kai-Lan Zhou, Feng Qiu (2014) A new flavonoid from the aerial parts of Andrographis paniculata. Nat Prod Res 28(3): 138-143.
- Chen M, Jiang-Jiang Qin, Jian-Jun Fu, Xiao-Jia Hu, Xiao-Hua Liu, et al. (2010) Blumeaenes A-J, sesquiterpenoid esters from Blumea balsamifera with NO inhibitory activity. Planta Med 76(9): 897-902.
- Chen Z, Chen Zhang, Fei Gao, Qiang Fu, Chaomei Fu, et al. A systematic review on the rhizome of Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort. (Chuanxiong). Food Chem Toxicol 119: 309-325.
- Chiu CY, Wei-Hsiang Hsu, Hui-Kang Liu, Shing-Hwa Liu, Yun-Lian Lin (2018) Prepared Rehmanniae Radix oligosaccharide regulates postprandial and diabetic blood glucose in mice. Journal of Functional Foods 41: 210-215.
- Dias MM, Ohana Zuza, Lorena R Riani, Priscila de Faria Pinto, Pedro Luiz Silva Pinto, et al. (2017) In vitro schistosomicidal and antiviral activities of Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) against Schistosoma mansoni and Herpes simplex virus 1. Biomed Pharmacother 94: 489-498.
- Eming SA, Krieg T, Davidson JM (2007) Inflammation in wound repair: molecular and cellular mechanisms. J Invest Dermatol 127(3): 514-525.
- Sinem Er, Miriş Dikmen (2017) Camellia sinensis increased apoptosis on U2OS osteosarcoma cells and wound healing potential on NIH3T3 fibroblast cells. Cytotechnology 69(6): 901-914.
- Espinosa C, José A López Jiménez, Francisca Pérez-Llamas, Francisco A Guardiola, Maria A Esteban, et al. (2016) Long‐term intake of white tea prevents oxidative damage caused by adriamycin in kidney of rats. J Sci Food Agric 96(9): 3079-3087.
- Fierascu RC, Milen I Georgiev, Irina Fierascu, Camelia Ungureanu, Alina Ortan, et al. (2018) Mitodepressive, antioxidant, antifungal and anti-inflammatory effects of wild-growing Romanian native Arctium lappa L. (Asteraceae) and Veronica persica Poiret (Plantaginaceae). Food Chem Toxicol 111: 44-52.
- Figueroa-Espinoza MC, Andrea Zafimahova, Pedro G Maldonado Alvarado, Eric Dubreucq, Céline Poncet-Legrand, et al. (2015) Grape seed and apple tannins: Emulsifying and antioxidant properties. Food Chem 178: 38-44.
- Fukuyama N, Shibuya M, Orihara Y (2012) Antimicrobial polyacetylenes from Panax ginseng hairy root culture. Chem Pharm Bull 60(3): 377-380.
- Gu J, Juan Chen, Nan Yang, Xuefeng Hou, Jing Wang, et al. (2016) Combination of Ligusticum chuanxiong and Radix Paeoniae ameliorate focal cerebral ischemic in MCAO rats via endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent apoptotic signaling pathway. J Ethnopharmacol 187: 313-324.
- Hasani-Ranjbar S, Jouyandeh Z, Abdollahi M (2013) A systematic review of anti-obesity medicinal plants-an update. J Diabetes Metab Disord 12(1): 1-10.
- Hong H, Qin-mao Wang, Zhi-ping Zhao, Guo-qing Liu, Ye-shou Shen, et al. (2003) Studies on antidiabetic effects of cortex Moutan polysaccharide-2b in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Yao Xue Xue Bao 38(4): 255-259.
- Hwang E, Sang-Yong Park, Chang Shik Yin, Hee-Taek Kim, Yong Min Kim, et al. (2017) Antiaging effects of the mixture of Panax ginseng and Crataegus pinnatifida in human dermal fibroblasts and healthy human skin. J Ginseng Res 41(1): 69-77.
- Ibrahim A, Noman Albadani R (2014) Evaluation of the potential nephroprotective and antimicrobial effect of Camellia sinensis leaves versus Hibiscus sabdariffa (in vivo and in vitro studies). Adv Pharmacol Sci 2014: 389834.
- Jadoon S, Sabiha Karim, Arif Malik, Chunye Chen, Ghulam Murtaza, et al. (2015) Anti-aging potential of phytoextract loaded-pharmaceutical creams for human skin cell longetivity. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015: 709628.
- Jahandideh M, Homa Hajimehdipoor, Seyed Alireza Mortazavi, Ahmadreza Dehpour, Gholamreza Hassanzadeh, et al. A wound healing formulation based on Iranian traditional medicine and its HPTLC fingerprint. Iran J Pharm Res 15(Suppl): 149-157.
- Jiao L, Bo Li, Mingzhu Wang, Zhen Liu, Xiaoyu Zhang, et al. (2014) Antioxidant activities of the oligosaccharides from the roots, flowers and leaves of Panax ginseng CA Meyer. Carbohydr Polym 106: 293-298.
- Kabir MH, Nur Hasan, Md Mahfuzur Rahman, Md Ashikur Rahman, Rownak Jahan, et al. (2014) A survey of medicinal plants used by the Deb barma clan of the Tripura tribe of Moulvibazar district, Bangladesh. J Ethnobiol Ethnomed 10(1): 1-28.
- Khan G, M F Alam, Mohammad M Safhi, Tarique Answer, Mohd Neyaz Ahsan, et al. (2014) Cardioprotective effect of green tea extract on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Acta Pol Pharm 71(5): 861-868.
- Kim HG, Gunhyuk Park, Ying Piao, Min Seo Kang, Youngmi Kim Pak, et al. (2014) Effects of the root bark of Paeonia suffruticosa on mitochondria-mediated neuroprotection in an MPTP-induced model of Parkinson’s disease. Food Chem Toxicol 65: 293-300.
- KLOTOE, J., et al., JATROPHA MULTIFIDA LINN (EUPHORBIACEAE): EXPLORATION DES PROPRIETES ANTIBACTERIENNES ET DU POUVOIR CICATRISANT DE LA SEVE DE CETTE PLANTE CHEZ LE RAT ALBINOS DE SOUCHE WISTAR.
- Knott A, Urte Koop, Martina Kausch, Ludger Kolbe, Nils Peters, et al. (2008) Natural Arctium lappa fruit extract improves the clinical signs of aging skin. J Cosmet Dermatol 7(4): 281-289.
- Kumar RA, K Sridevi, N Vijaya Kumar, S Nanduri, S Rajagopal (2004) Anticancer and immunostimulatory compounds from Andrographis paniculata. J Ethnopharmacol 92(2-3): 291-295.
- Lee MH, Kao L, Lin CC (2011) Comparison of the antioxidant and transmembrane permeative activities of the different Polygonum cuspidatum extracts in phospholipid-based microemulsions. J Agric Food Chem 59(17): 9135-9141.
- Li C, Zhen-Nan Tian, Jian-Ping Cai, Ke-Xin Chen, Bao Zhang, et al. (2014) Panax ginseng polysaccharide induces apoptosis by targeting Twist/AKR1C2/NF-1 pathway in human gastric cancer. Carbohydr Polym 102: 103-109.
- Li J, Chen J, Kirsner R (2007) Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin Dermatol 25(1): 9-18.
- Li Y, Weiyan Cai, Xiaogang Weng, Qi Li, Yajie Wang, et al. (2015) Lonicerae Japonicae Flos and Lonicerae Flos: a systematic pharmacology review. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015: 905063.
- Lin SC, Chia-Hsien Lin, Chun-Ching Lin, Yun-Ho Lin, Chin-Fa Chen, et al. (2002) Hepatoprotective effects of Arctium lappa Linne on liver injuries induced by chronic ethanol consumption and potentiated by carbon tetrachloride. J Biomed Sci 9(5): 401-409.
- Martin P (1997) Wound healing aiming for perfect skin regeneration. Science 276(5309): 75-81.
- Mi J, Chunjie Wu, Chuntong Li, Fengmin Xi, Zhijun Wu, et al. (2014) Two new triterpenoids from Ampelopsis japonica (Thunb.) Makino. Nat Prod Res 28(1): 52-56.
- Miglani A, Manchanda RK (2014) Observational study of Arctium lappa in the treatment of acne vulgaris. Homeopathy 103(3): 203-207.
- Min BS (2012) Compounds from the heartwood of Caesalpinia sappan and their anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry letters 22(24): 7436-7439.
- Nho KJ, Jin Mi Chun, Dong-Seon Kim, Ho Kyoung Kim (2015) Ampelopsis japonica ethanol extract suppresses migration and invasion in human MDA‑MB‑231 breast cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 11(5): 3722-3728.
- Nomicos EY (2007) Myrrh: medical marvel or myth of the magi? Holist Nurs Pract 21(6): 308-323.
- Oluba OM, Augustine O Olusola, Bamidele S Fagbohunka, E Onyeneke (2012) Antimalarial and hepatoprotective effects of crude ethanolic extract of lingzhi or reishi medicinal mushroom, Ganoderma lucidum (W. Curt.: Fr.) P. Karst. (higher Basidiomycetes), in Plasmodium berghei-infected mice. Int J Med Mushrooms 14(5): 459-466.
- Park H, Jin Sup Shim, Hyo Geun Kim, Hyejung Lee, Myung Sook Oh (2013) Ampelopsis Radix protects dopaminergic neurons against 1-methyl-4-phenylpyridinium/1-methyl-4-phenyl-1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-induced toxicity in Parkinson’s disease models in vitro and in vivo. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2013: 346438.
- Peng W, Rongxin Qin, Xiaoli Li, Hong Zhou (2013) Botany, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and potential application of Polygonum cuspidatum Sieb. et Zucc.: a review. J Ethnopharmacol 148(3): 729-745.
- Peng Peng, L, Guo-Shun Shan, Fan Zhang, Jiang-Ning Chen, Tian-Zhu Jia (2018) Metabolomics analysis and rapid identification of changes in chemical ingredients in crude and processed Astragali Radix by UPLC-QTOF-MS combined with novel informatics UNIFI platform. Chin J Nat Med 16(9): 714-720.
- Pereira JV, Débora Cristina Baldoqui Bergamo, José Odair Pereira, Suzelei de Castro França, et al. (2005) Antimicrobial activity of Arctium lappa constituents against microorganisms commonly found in endodontic infections. Braz Dent J 16(3): 192-196.
- Priya KS, Gnanamani Arumugam, Bhuvaneswari Rathinam, Alan Wells, Mary Babu (2004) Celosia argentea Linn. leaf extract improves wound healing in a rat burn wound model. Wound Repair Regen 12(6): 618-625.
- Ran X, Li Ma, Cheng Peng, Hong Zhang, Lu-Ping Qin (2011) Ligusticum chuanxiong Hort: a review of chemistry and pharmacology. Pharm Biol 49(11): 1180-1189.
- Rao PV, Gan SH, Cinnamon: a multifaceted medicinal plant. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2014: 642942.
- Rho S, Hwan-Suck Chung, Moonkyu Kang, Euna Lee, Chongwoon Cho, et al. (2005) Inhibition of production of reactive oxygen species and gene expression profile by treatment of ethanol extract of Moutan Cortex Radicis in oxidative stressed PC12 cells. Biol Pharm Bull 28(4): 661-666.
- Shang X, Hu Pan, Maoxing Li, Xiaolou Miao, Hong Ding (2011) Lonicera japonica Thunb.: ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry and pharmacology of an important traditional Chinese medicine. J Ethnopharmacol 138(1): 1-21.
- Shaw TJ, Rognoni E (2020) Dissecting fibroblast heterogeneity in health and fibrotic disease. Curr Rheumatol Rep 22(8): 1-10.
- Shivananda Nayak B, Sivachandra Raju S, Orette FA, Chalapathi Rao AV (2007) Effects of Hibiscus rosa sinensis L (Malvaceae) on wound healing activity: a preclinical study in a Sprague Dawley rat. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 6(2): 76-81.
- Su PW, Cheng-Hong Yang, Jyh-Ferng Yang, Pei-Yu Su, Li-Yeh Chuang (2015) Antibacterial activities and antibacterial mechanism of Polygonum cuspidatum extracts against nosocomial drug-resistant pathogens. Molecules 20(6): 11119-11130.
- Sumiyoshi M, Sakanaka M, Kimura Y (2010) Effects of Red Ginseng extract on allergic reactions to food in Balb/c mice. J Ethnopharmacol 132(1): 206-212.
- Sundar RDV, Sugashini Settu, Saranya Shankar, Gayathri Segaran, et al. (2018) Potential Medicinal Plants to Treat Leprosy-A Review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology 11(2): 813-821.
- Widsten P, Cristina D Cruz, Graham C Fletcher, Marta A Pajak, Tony K McGhie (2014) Tannins and extracts of fruit byproducts: antibacterial activity against foodborne bacteria and antioxidant capacity. J Agric Food Chem 62(46): 11146-11156.
- Wong M, Leung P, Wong W (2001) Limb salvage in extensive diabetic foot ulceration-a preliminary clinical study using simple debridement and herbal drinks. Hong Kong Med J 7(4): 403-407.
- Yang D, Xu Jh, Shi Rj (2017) Root extractive from Daphne genkwa benefits in wound healing of anal fistula through up-regulation of collagen genes in human skin fibroblasts. Biosci Rep 37(2): BSR20170182.
- Yang Y, Woo Seok Yang, Tao Yu, Gi-Ho Sung, Kye Won Park, et al. (2014) ATF-2/CREB/IRF-3-targeted anti-inflammatory activity of Korean red ginseng water extract. J Ethnopharmacol 154(1): 218-228.
- Yao D, Zheng Wang, Li Miao, Linyan Wang (2016) Effects of extracts and isolated compounds from safflower on some index of promoting blood circulation and regulating menstruation. J Ethnopharmacol 191: 264-272.
- Yodsaoue O, Sarot Cheenpracha, Chatchanok Karalai, Chanita Ponglimanont, Supinya Tewtrakul (2009) Anti‐allergic activity of principles from the roots and heartwood of caesalpinia sappan on antigen‐induced β‐hexosaminidase release. Phytother Res 23(7): 1028-1031.
- Zhang W, Junyan Tao, Xiaoping Yang, Zhuliang Yang, Li Zhang, et al. (2014) Antiviral effects of two Ganoderma lucidum triterpenoids against enterovirus 71 infection. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449(3): 307-312.
- Zhang Wq, Yong-Li Hua, Man Zhang, Peng Ji, Jin-Xia Li, et al. (2015) Metabonomic analysis of the anti‐inflammatory effects of volatile oils of Angelica sinensis on rat model of acute inflammation. Biomed Chromatogr 29(6): 902-910.
- Zhengyuan W, Zhiwei Luan, Xiaohan Zhang, Kai Zou, Shiting Ma, et al. (2019) RETRACTED ARTICLE: Chondro-protective effects of polydatin in osteoarthritisthrough its effect on restoring dysregulated autophagy via modulating MAPK, and PI3K/Aktsignaling pathways. Scientific Reports 9(1).
- Zimowska M, Edyta Brzoska, Marta Swierczynska, Wladyslawa Streminska, Jerzy Moraczewski (2008) Distinct patterns of MMP-9 and MMP-2 activity in slow and fast twitch skeletal muscle regeneration in vivo. Int J Dev Biol 52(2-3): 307-314.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.