Mini Review 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Higher Incidence in Eye-Related Diseases within the German Health Insurance System
*Corresponding author:Johanna Weber, IGEL Health Solutions, Bäckerberg 9a, D-38165 Lehre, Germany.
Received: January 10, 2024; Published: March 01, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.21.002883
Abstract
In Germany, treatments due to eye-related conditions are on the rise according to health insurance providers. To get an overview on the matter, data from the central agency of health insurance in Germany (Kassenärztliche Bundesvereinigung, KBV) have been analyzed regarding the frequency of eye-related treatments between 2016 and 2022. Data hint to an increase in eye-related treatments in German health insurants. Possible reasons for the increase have to be assessed.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s Disease, Dementia, Biomarkers, Wearable devices, Diagnostics
Introduction
Currently, there is a rise in eye-related treatments in German patients, which could be related to missed check-ups due to covid-lockdowns, parallel to reports by the German health insurance provider AOK for other conditions. According to the AOK, a decrease in check-ups and cancer-surgery during the pandemic is currently causing a rise in cancer-treatments (Allgemeine Ortskrankenkasse, [1]). Reports from the UK regarding the approval of Personal Independence Payments for people who struggle with daily life (PIP, see Figure 1) show a similar trend [2]. The increase in eye-related treatments has to be researched in more detail (Figure 1).
Methods
An extensive body of data is available for all German health insurance companies, it is provided by the KBV [3]. It consists of data collected all over Germay between 2016 and 2021 and can be separated in a) insurants who had been visiting the doctor for any reason since 2016 (69 573 152 individuals) and b) insurants who had been visiting the doctor since 2016 and at the same time had visited the doctor in 2021 with a complication arising from vaccination with the novel coronavirus vaccines (2 468 531 individuals). The latter group can be characterized as the vaccinated group, whereas the first has to be considered as the group with unclear vaccination status, since in Germany it is possible for individuals to be vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 in vaccination centers without accounting by the KBV. The vaccination campaign in Germany started at the end of December 2020. Since the data arrived in the form of settlements made with the KBV per quarter, it was possible to separate the data into 25 quarters from January 2016 until March 2022, distinguishing 20 quarters before and 5 after onset of the campaign. Statistical analysis was done using Microsoft Excel 2013 and SPSS version 29. Univariate ANOVA was calculated to test for a difference in eye-related treatments before and after onset of vaccination in patients with unclear vaccination status and vaccinated patients next to Pearson’s correlation coefficient for time after onset of vaccination and number of eye-related treatments and plotting of eye-related treatments in both patient groups over time.
Results
In both groups, eye-related treatments increased significantly when comparing quarters before and after the onset of the vaccination campaign, and the increase was more pronounced in the vaccinated group (see Table 1). When comparing graphs of both groups, the increase is less pronounced in the group with unclear vaccination status (see Figure 2). When comparing correlations, the correlation between number of the quarter and number of eye-related treatments is strongest in vaccinated patients after the onset of the vaccination campaign, indicating a stronger increase over time in vaccinated patients after the onset of the vaccination campaign (Tables 1,2) (Figure 2).

Figure 1: Increase of eye-related treatments in the vaccinated group (upper plot) and in the group with unclear vaccination status (lower plot).

Table 1: Incidence of ICD-10-Codes related to eye-diseases (H-codes) in vaccinated patients and patients of unclear vaccination status during the 20 quarters before and the 5 quarters after onset of the vaccination campaign.
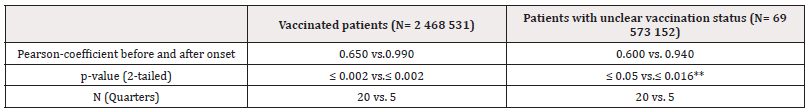
Table 2: Correlations between time after onset of vaccination campaign measured in quarters and number of eye-related treatments in vaccinated patients and patients of unclear vaccination status, correlations calculated within 20 quarters before and five after onset of vaccination.
Note*: **by trend significance.
Discussion
It is understood that due to the pandemic and lockdowns, there were fewer physician visits over time [1], which could explain the weakening of the correlation between quartile and number of eye-related treatments in patients with unclear vaccination status (see Figure 2). However, so far there is no obvious explanation for the stronger correlation between quarter after onset of the vaccination campaign and number of eye-related treatments in vaccinated patients, except for perhaps the novel coronavirus vaccines, since both patient groups were subject to lockdowns in Germany
Conclusion
There is a strong increase in eye-related treatments in Germany, especially in the vaccinated group, which can only in part be attributed to lockdowns. Further research is needed to determine whether the novel coronavirus vaccines might be a factor regarding the rise in eye diseases in Germany, or what other factors (e. g. stress due to job loss, [4]) could be involved.
Conflict of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgement
None.
References
- Rehmann C (2023) Krankenkasse warnt vor mehr Krebsfällen nach Corona [Health insurance warns of more cancer-cases after covid]. Berliner Zeitung.
- (2023) https://phinancetechnologies.com/HumanityProjects/PIP%20Analysis-Systems.htm.
- (2022) KBV Press release.
- Yanovskiy M, Socol Y (2022). Are Lockdowns Effective in Managing Pandemics? International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19(15): 9295.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.