Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Study of Achievement Minimum Services Standard for Hypertension Health Services Patient in Makassar City
*Corresponding author:Siti Nurul Fajriah, School of Physiotherapy, Makassar Health Polytechnic, Makassar City, South Sulawesi Province, Indonesia and Agussalim, Parepare School of Nursing, Makassar Health Polytechnic, Parepare City, South Sulawesi Province, Indonesia.
Received: February 22, 2024; Published: February 27, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.21.002873
Abstract
The national SPM target for hypertension health services is 100%. In 2023, hypertension SPM achievement in Makassar city was 71.01%. The distribution in 47 health centers in Makassar city is uneven, which provides clues for improving health efforts through analyzing factors that influence the implementation process of SPM policies for health services for people with hypertension. This research is a qualitative study with an analytic descriptive approach in the form of in-depth interviews and direct observation in the field. The results showed that there were obstacles in achieving SPM targets, namely in terms of joint commitment that SPM for hypertension health services has not been made a priority target, the element of health worker education has not been involved in overcoming limited human resources, limited SPM achievement data entry facilities, network connections of health service facilities in the hypertension management flow have not been integrated and cross-sectoral attention in efforts to prevent hypertension risk factors early on has not been supported by policy.
Keywords: Hypertension, Target outcomes, SPM health services
Introduction
Hypertension is one of the factors of NCDs that can have a negative impact on the social, economic and psychological aspects of individuals. Globally, countries with a high prevalence of hypertension have shifted from countries with upper middle income to countries with lower middle income [1]. Hypertension generally occurs in old age, but along with the development of science and technology and changes in lifestyle that tend to be sedentary, through a phased surveillance approach WHO 2021 shows an increase in hypertension among the age group 18-69 years, this certainly requires special attention for the need for serious interventions in handling it [2]. The government has established policies in the provision of health services through Regulation of the Minister of Health of the Republic of Indonesia No. 4 of 2019 concerning Technical Standards for Fulfillment of Basic Service Quality at Minimum Service Standards (SPM) in the Health Sector. This SPM is a provision regarding the Type and Quality of Basic Services which are Mandatory Government Affairs that every Citizen is entitled to obtain at a minimum.
In Makassar City, the SPM policy is contained in the 2021-2026 Regional Medium-Term Development Plan with a target of 100% health services for people with hypertension [3]. In 2023, the percentage of SPM performance achievement for health services for people with hypertension was 71.01%, but it was not evenly distributed across 47 health centers in Makassar city, which became a clue for improving health service efforts. Therefore, the purpose of this study is to examine the achievement of SPM for health services for people with hypertension through analyzing the factors that influence the policy implementation process in aspects of the hypertension situation, hypertension prevention policies, hypertension control challenges and SPM achievements for hypertension services.
Method
The research method used is qualitative research with an analytical descriptive approach through in-depth interviews and direct observation which aims to analyze the implementation of SPM for Hypertension Health Services in Makassar City. The study was conducted at the Makassar City Health Office and Puskesmas. Researchers analyzed the achievement of SPM for health services for people with hypertension in Makassar City based on the situation of hypertension, hypertension prevention and management policies, challenges in preventing and controlling hypertension and SPM achievements for health services for people with hypertension. The research subjects were selected through purposive sampling techniques used as informants at the Makassar City Health Office, Puskesmas and program managers in the field.
Result and Discussion
An overview of the observations of the SPM study of hypertension patient services in Makassar city is as follows:
Hypertension Situation
Hypertension is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and the second leading cause of death and disability in the world [4]. It is predicted that by 2025, 29% of adults worldwide will suffer from hypertension [5]. The prevalence of hypertension in Indonesia in the population aged ≥ 18 years increased from 25.8% to 34.1% (Riskesdas, et al., 2018), this condition will certainly increase the burden on society and government, because handling it requires large costs. For this reason, a joint commitment is needed to reduce mobility, mortality and disability through intensification of prevention and control of hypertension towards a healthy Indonesia. South Sulawesi province is one of the provinces with high risk factors for hypertension as a disease burden that causes premature death with disability.
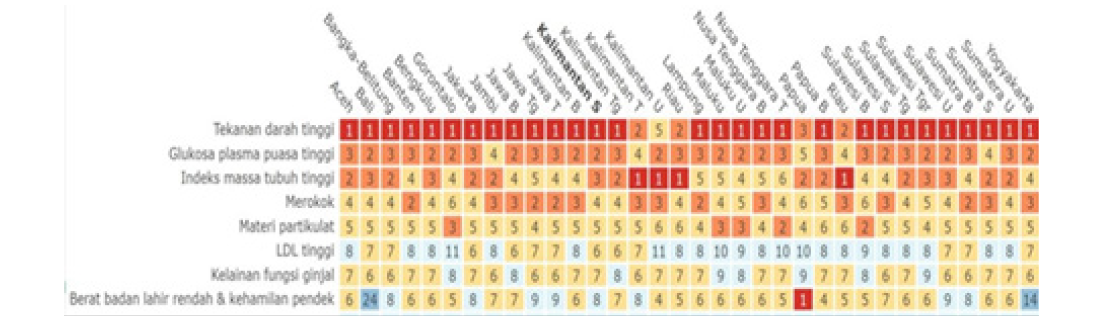
Hypertension is often called the "silent killer" because it is the deadliest disease but is often found without symptoms so it is neglected. The mortality rate is high and affects a person's quality of life and productivity [6]. There are 1 in 3 Indonesians with hypertension, even that number continues to increase every year, because people with hypertension have no complaints so early detection is very important to prevent various risks of diseases due to hypertension such as heart disease, stroke, kidney failure and other diseases that cause death and huge health costs (Menkes, 2023). Riskesdas, et al., data in 2018 showed that 8.8% of people with hypertension were diagnosed and only 50% took medication regularly (Figure 1).
Hypertension Prevention and Control Policy and Hypertension Management
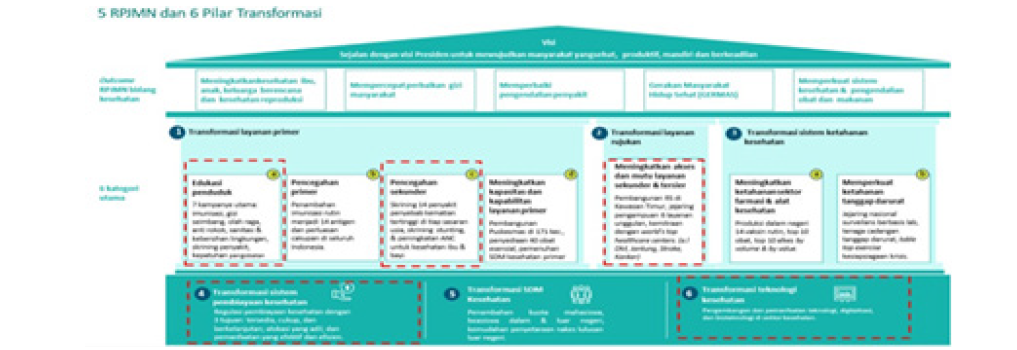
Hypertension prevention and control policies are regulated in Minister of Health Regulation No. 4/2019 on Technical Standards for Fulfillment of Basic Service Quality in Minimum Service Standards for the Health Sector. The regulation serves as a guideline for local governments in establishing policies related to the implementation of MSS in the Health Sector. This policy is strengthened by Government Regulation Number 18 of 2020 concerning the National Medium-Term Development Plan for 2020- 2024. Furthermore, the Governor of South Sulawesi Province issued South Sulawesi Governor Regulation No. 39 of 2021 concerning the Implementation of Minimum Service Standards. Through the 2021-2026 Regional Medium-Term Development Plan, Makassar City has set a target of 100% health services for hypertension patients starting in 2022-2026 [7] (Figure 2).
Along with health transformation, hypertension disease management is controlled through health system transformation by strengthening 6 (six) pillars in an integrated manner, especially on the pillars of primary service transformation (population education and secondary prevention), referral service transformation (improving access and quality of secondary and tertiary services), financing system transformation and health technology transformation. However, in terms of hypertension services according to standards and treatment compliance, the achievements are not optimal. This happens because of the multifactors that need to be addressed together in controlling hypertension in an integrated manner [8-10] (Figure 3).
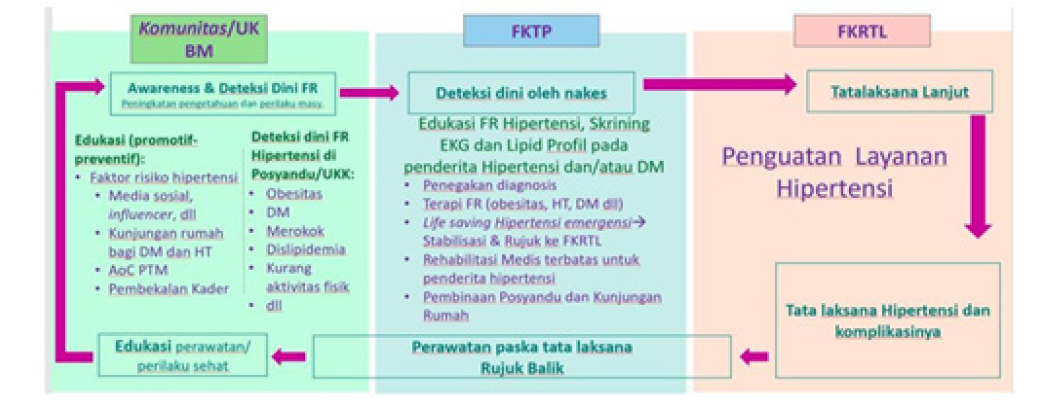
In terms of hypertension management flow, the process starts from the community with educational activities (promotive-preventive) of hypertension risk factors and conducting home visits along with forming Agents of Change.... Another program is early detection in the form of measuring blood pressure in individuals at risk of hypertension at Posyandu. The constraints of activities in the community include; limited number of human resources for health workers, the number of health programs that must be implemented and the condition of urban communities who tend to be busy working in urban areas and difficult to meet. Furthermore, early detection activities in First Level Health Facilities (FKTP) experience obstacles in terms of monitoring and evaluation given the number of FKTPs that are scattered and there is no feedback on the implementation of their activities. In services at Advanced Referral Health Facilities (FKRTL) in the form of strengthening hypertension services and their complications certainly require care in post-referral management supported by FKTP and care education supported by healthy behavior in the community. Overall, all hypertension service management flows support each other. However, with limited human resources, many priority programs and no policies strengthen efforts to optimize hypertension control efforts in an integrated manner [11-15].
Achievement of SPM for Health Services for People with Hypertension
The target percentage of performance achievement of SPM for health services for people with hypertension nationally is 100% (one percent) (Figure 4).
In 2023, the achievement is 71.01%, but it is not evenly distributed across 47 Puskesmas in Makassar City so that it becomes a guide for improving health service efforts through analyzing the factors that influence the process of implementing SPM policies for hypertension patient services in Makassar City, among others:

Figure 4: Achievement Table of Hypertension Health Services in Makassar City in 2023.
Note*: Source: Makassar City Health Office.
a. Hypertension risk factors have not been prioritized for hypertension control even though the burden of these risk factors is quite large.
b. Prevention and control of risk factors for hypertension as a major risk factor for heart and vascular disease is not optimal.
c. Early detection of hypertension at the community and primary care level is not optimal given the large number of targets, lack of human resources and limited time.
d. The division of tasks and authority for implementing SPM for health services for people with hypertension is carried out directly by the Head of the Puskesmas, so that the limited number of human resources causes duplicate positions, and the number of additional tasks causes the workload of officers to increase which affects performance, which has an impact on service quality.
e. Limited facilities for data entry also affect SPM achievements for hypertension patients, including the absence of a health facility network connection between the Community, First Level Health Facilities (FKTP), Advanced Referral Health Facilities (FKRTL) so that monitoring of SPM achievements for health services for hypertension patients has not been carried out optimally.
f. Policies to prevent hypertension risk factors from an early age have not been integrated across sectors, even though behaviors are formed early.
g. Cross-sectoral attention in controlling hypertension risk factors is still not optimal, especially in the implementation of healthy living behaviors (GERMAS) in communities and institutions. Hypertension is not only a health problem but a behavioral and environmental problem. This is evident in the lack of GERMAS implementation activities outside the health sector.
h. There is still a lack of involvement of health worker education institutions in the process of implementing SPM policies for hypertension patient services that can be integrated in the Tri Dharma of Education.
i. Low awareness, misperceptions, and ignorance due to lack of correct information, as well as obstacles in changing people's habits related to hypertension, influence the achievement of SPM for hypertension services.
Summary
The results of the study on the achievement of SPM for Health Services for Patients with Hypertension based on the situation of hypertension, hypertension prevention and management policies, and challenges in preventing and controlling hypertension show that there are obstacles to the implementation of SPM policies in terms of
a. There is a shared commitment that the hypertension SPM has not been prioritized for intensification of prevention and control of major risk factors for cardiovascular disease as a major cause of mobility, mortality and disability.
b. The education element of health workers has not been involved in the implementation of early detection and building community understanding of the importance of hypertension prevention and control to overcome the problem of limited human resources.
c. Facilities (laptop and internet network connection) for data entry of SPM achievements for hypertension patients need to be budgeted.
d. A network of healthcare facility connections in the hypertension management pathway needs to be designed to monitor the achievement of SPM for hypertension by the Ministry of Health.
e. Cross-sectoral attention must be built in an effort to prevent hypertension risk factors early on in an integrated cross-sectoral manner.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Julianty Pradono (2020) Hypertension: The Hidden Killer in Indonesia, Health Research and Development Agency of the Indonesian Ministry of Health. Publishing House of the Health Research and Development Agency (LPB), Jakarta.
- (2023) Journalism Training on Noncommunicable Diseases (NCD2) in Athens, Greece October 16-18, 2023. Word Health Organization.
- (2021) Regional Medium-Term Development Plan 2021-2026 Makassar City. Makassar City Government.
- Silva H (2009) Hypertension in seven Latin American cities: the cardiovascular risk factor multiple evaluation in Latin America (CARMELA) study. 1-11.
- (2018) Word Health Organization, 2018. World Health Statistic. Geneva.
- Nildawati Muh, ajar Pahrir, Nur Rahma N (2020) Factors Associated with the Incidence of Hypertension in the Bara-Barayya Health Center Working Area, Makassar City. Bina Gener J Kesehat 12(1): 36-41.
- (2019) Directorate General of Disease Prevention and Control. Non-communicable disease management guidebook, Jakarta.
- (2022) heart disease is the Leading Cause of Death, Ministry of Health Strengthens Primary Care.
- (2023) Minister of Health asks people to be aware of hypertension. Jakarta.
- https://infopublik.id/kategori/nasional-sosial-budaya/747850/menkes-minta-masyarakat-waspada- hipertensi.
- Nafsiah Mboi (2022) The state of health in Indonesia's provinces, 1990-2019: A systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. The Lancet Global Health 10(11): e1632-e1645.
- (2019) Minister of Health Regulation No. 4 of 2019 concerning Technical Standards for Fulfillment of Basic Service Quality at Minimum Service Standards in the Health Sector.
- (2022) Profile of the Health Office of South Sulawesi Province in 2022
- https://www.who.int/news-room/feature-stories/detail/journalism-training-on-noncommunicable-diseases-(ncds)-in-athens--greece--16 18-october-2023.
- (2023) Donors Making a Difference for Universal Health Coverage. Word Health Organization.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.