Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Breastfeeding Assessment; Preliminary Report on a New Scoring System as an Assessment Tool: The Eregie Breast Score (EBS)
*Corresponding author: Charles Osayande Eregie, Professor of Child Health and Neonatology, Institute of Child Health, University of Benin City, Nigeria and Consultant Pediatrician and Neonatologist, University of Benin Teaching Hospital, Benin City, Nigeria.
Received: July 10, 2024; Published: July 24, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.23.003069
Abstract
Breastfeeding is a Child Survival Intervention (CSI). Several factors affecting breastfeeding guarantee the benefits of this feeding intervention to the mother-Baby Dyad. One such factor is the Skill and Technique of Breastfeeding. Breastfeeding Assessment Tools assure improvements in Breastfeeding Practices by focusing attention on deficient Breastfeeding Assessment Domains. Several Breastfeeding Assessment Tools are briefly distilled. The LATCH Score is highlighted for its objective Scoring System, but it is deficient in its Breastfeeding Assessment Domains Coverage. The WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form is reportedly the Tool with the strongest evidence but lacks an objective Scoring System. Using the ‘B-R-E-A-S-T’ of the WHO/ UNICEF Form as a Template and Precursor, and with the developed ‘Defined and Scored Alternatives’, a New Scoring System is presented as a Breastfeeding Assessment Tool: The Eregie BREAST Score (EBS).
Keywords: Breastfeeding, Breastfeeding Assessment, Breastfeeding Assessment Domains, Breastfeeding Assessment Tool, Child Survival Intervention, Eregie BREAST Score, LATCH Score
Abbreviations: BAS: Breastfeeding Assessment Score; BEET: Breastfeeding Evaluation and Education Tool; BFHI: Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative; CSI: Child Survival Interventions; EBF: Exclusive Breastfeeding; EBS: Eregie BREAST Score; IBFAT: Infant Breastfeeding Assessment Tool; NOMAS: Neonatal Oral-Motor Assessment Scale; OIYCF: Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding; SIAB: Systematic Assessment of the Infant at Breast
Introduction
Breastfeeding, particularly Exclusive Breastfeeding (EBF), is a low-cost high-impact Child Survival Intervention (CSI) and has also been described as the ‘Mother of all Child Survival Interventions’ [1-3]. It is an integral component of Reproductive Work [4-6]. Breastfeeding is also an integral component of the Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding (OIYCF) recommended by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the United Nations Children’s Fund (UNICEF) [7,8]. The benefits and advantages of breastfeeding as they relate to the mother and the child are influenced by the plethora of factors affecting this feeding intervention. The Skill and Technique of breastfeeding are particularly important in assuring the benefits accrue to the mother-Baby Dyad. In a ‘Triple-A Process’ [9], Assessment is the first step followed by Analysis and Action in that order. Thus, Breastfeeding Assessment is a necessary first step in assuring the benefits of Breastfeeding is guaranteed to the ‘Mother-Baby Dyad’. There are several Breastfeeding Assessment Tools which have been developed to assist mothers to improve their Breastfeeding Practices guided by the outcomes of their Breastfeeding Assessments. This Communication highlights some issues related to the extant Breastfeeding Assessment Tools and disposes the Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) as a New Scoring System for improved Breastfeeding Assessment.
Breastfeeding Assessment Domains and Breastfeeding Assesment Tools
It is expected that appropriate and useful Breastfeeding Assessment Tools should cover the relevant determinant ‘Breastfeeding Assessment Domains’ [10] which reportedly include Baby’s behavior, Mother’s behavior, Position, Latching, Effective feeding, Breast health, Baby’s health, Mother’s view of feed, Number, timing and length of feeds. Other ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ have been added and include among others: Mother’s comfort level, Previous breastfeeding experience, other foods being offered to the child, Loss of more than 10% of birth weight, Delivery type etc [11-13]. The Breastfeeding Assessment Tools differ in their Form and Structure being Checklists, Questionnaires, Algorithms, Indices, History-taking Forms, listing specific aspects of breastfeeding to be assessed etc10. Some Breastfeeding Assessment Tools include among several others: Breastfeeding Assessment Score (BAS) [14], Breastfeeding Evaluation and Education Tool (BEET) [15], Infant Breastfeeding Assessment Tool (IBFAT) [16], LATCH Score [17], Neonatal Oral-Motor Assessment Scale (NOMAS)[18], Systematic Assessment of the Infant at Breast (SAIB) [19], WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form [20], WHO/UNICEF BFHI Forms [21,22], CARE Training Packages [23] etc. Some Tools have National Applicability while others have Worldwide Applicability. Also, some Tools are applicable to Hospital Settings while others are useful in the Community. Yet again, some Tools have relevance in High-income Economies while others are useful in low-and Medium-income Economies. Some Tools uniquely have applicability re: Hospital and Community, High-and Low-and Medium-income Countries and National and Worldwide [10]. Concerning ‘Breastfeeding Domains Coverage’, the most comprehensive Breastfeeding Assessment Tool is Breastfeeding Evaluation and Education Tool (BEET) [10,15]. The WHO/ UNICEF Baby-Friendly Hospital Initiative Tools and the CARE Training Packages also have reasonable coverage [10,21-23]. Several Tools do not report predicted ‘Breastfeeding Outcomes’: Breastfeeding Status, Child Growth, Maternal and Child Health, Tool Performance etc [10]. The BEET has reportedly not been part of independently documented Validation Studies [10]. The LATCH Score [17] is attractive as it objectivizes the Breastfeeding Assessment by disposing ‘Defined and Scored Alternatives’ and hence can identify specific areas and ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ requiring attention and further interventions. The LATCH Score, however, lacks coverage of certain Breastfeeding Domains [10]. The Breastfeeding Assessment Tool reportedly with the strongest evidence is the WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form [10,20], and it is applicable worldwide, in the hospital and community as well as in both High-and Low-income Countries [10]. It, however, lacks coverage of Baby’s health and Mother’s view of the feed in the ‘Breastfeeding Assessment Domains’. Additionally, it lacks the ‘Defined and Scored Alternatives’ of a ‘Scoring System’ to objectivize Breastfeeding Assessment using the WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form as with the LATCH Score. This is the relevance of the current Communication conveying the Preliminary Report on a New Scoring System for Breastfeeding Assessment: The Eregie BREAST Score (EBS).
A New Breastfeeding Assessment Scoring System: The Eregie Breast Score (EBS)
Latching on the unique advantage of the LATCH Score as an ‘Objectivizing Scoring System’ for Breastfeeding Assessment, the WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form [20] was transformed and developed to create a Quantitative Scoring System from the original Qualitative Format. With the Eregie BREAST Score (EBS), and the developed ‘Defined and Scored Alternatives’, Breastfeeding Assessment is now objectivized using the Breastfeeding Assessment Tool with the strongest evidence as the Template and Precursor with more objective and better identification of specific ‘Breastfeeding Domains’ that require attention and further intervention to improve a mother’s breastfeeding practice towards optimizing the harvest of the benefits and advantages of the Child Survival Interventions: Breastfeeding, Exclusive Breastfeeding and Optimal Infant and Young Child Feeding.
The details of the Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) are listed in Tables 1 and 2. Table 1 disposes the ‘B-R-E-A-S-T’ with defined alternatives for concluding that ‘Breastfeeding is going on well’ and ‘Good’ or ‘Breastfeeding difficulty is encountered’ and ‘Poor’. Using the conclusions of ‘Good’ and ‘Poor’ as applicable to the mother and her baby and guided by the ‘Defined and Scored Alternatives’ disposed in Table 2, ‘Scores’ are assigned to each component of the ‘B-R-E-A-S-T’ to get a ‘Cumulative Score’ which is the ‘Eregie BREAST Score (EBS)’ for objectivizing Breastfeeding Assessment. The LATCH Score virtually follows the format and structure of the APGAR Scoring System [24] and the Eregie BREAST Score similarly aligns with the APGAR and LATCH Scores Models. The Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) has all the advantages of the WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form (Worldwide Applicability, Hospital and Community Usefulness and relevant in High-and LOW-and Medium-income Countries) in addition to being an objective ‘Scoring System’ and quite ‘User-Friendly’.
Conclusion
Breastfeeding Practices are some of the factors assuring Breastfeeding Benefits to mothers and their children. Appropriate Breastfeeding Assessments facilitate better Breastfeeding Practices by attending to identified deficient ‘Breastfeeding Assessment Domains’. This Communication briefly distils and appraises Breastfeeding Assessment Tools as Interventions to assuring better Breastfeeding Practices. The WHO/ UNICEF B-R-E-A-S-T-Feed Observation Form is reportedly the Tool with the strongest evidence but lacks an ‘Objective Scoring System’. The Eregie BREAST Score (EBS), using the WHO/ UNICEF Tool as a Template and Precursor, is presented as a New Scoring System for Breastfeeding Assessment in [his Preliminary Report.

Table 1: Breastfeeding Assessment Tool (Eregie Breast Score (EBS)): Definitions of Good or Poor For B-R-E-A-S-T Components.
Note*: LEGEND/ KEY For Body Position, Responses and Emotional Bonding (Mother and Baby): Mother: Good if 50% or more of signs that breastfeeding is going on well are present; Poor if more than 50% of signs of possible difficulty are present Baby: Good if 50% or more of signs that breastfeeding is going on well are present; Poor if more than 50% of signs of possible difficulty are present For Anatomy (Mother only) and Suckling (Baby only): Good if more than 50% signs that breastfeeding is going on well are present; Poor if more than 50% signs of possible difficulty are present For Time Spent Suckling: As indicated in the Chart Adapted from Breastfeeding Counselling, A Training Course: Participants’ Manual (Part One: Sessions 1-9). WHO/ UNICEF. WHO/ CDR/ 93.5 UNICEF/NUT/93.3; 1993 and Ref 20.
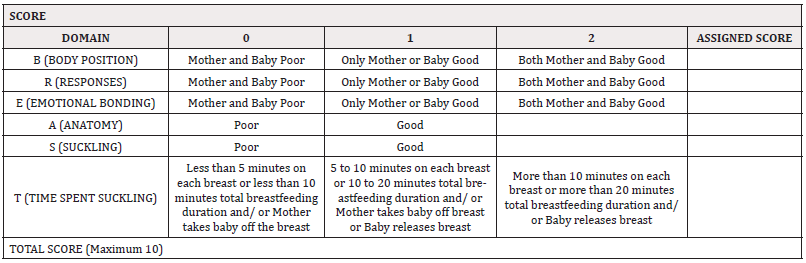
Table 2: New Breastfeeding Assessment Tool: Eregie Breast Score (EBS).
Note*: LEGEND/ KEY TOTAL Eregie BREAST Score (EBS) : 0 - 3 is Poor; Much Intervention and Help needed 4 - 6 is Fair; Moderate Intervention and Help needed ≥ 7 is Good; Little or no Intervention or Help needed Adapted from Breastfeeding Counselling, A Training Course: Participants’ Manual (Part One: Sessions 1-9). WHO/ UNICEF. WHO/ CDR/ 93.5 UNICEF/NUT/93.3; 1993 and Ref 20.
References
- (2007) Systematic reviews and meta-analyses. WHO: Evidence on the long-term effects of breastfeeding. World Health Organization.
- (2009) A survival and development priority. UNICEF: Tracking Progress on Child and Maternal Nutrition. Nations Children’s Fund.
- Eregie CO (2009) Programming the END from before the BEGINNING-: Juxtaposing TECHNOLOGY with the TEA Triad.
- (2024) Reproductive Work. European Institute for Gender Equality.
- (2024) What is Reproductive Labour. InfoScipedia.
- Eregie CO (2023) Enabling the ‘Breastfeeding-Work Dyad’ and Understanding the Contextual Pentad of Productive Work, Reproductive Work, Reproductive Health, Reproductive Rights and Reproductive Politics: The Tantalizing Microcosmic Perspectives Encapsulated with Some Imaginatively Innovative Interventions. Gynecol Reprod Health 7(5): 1-16.
- (2021) Infant and young child feeding. World Health Organization. Geneva.
- (2021) Infant and young child feeding. UNICEF. New York.
- Jonnson U (2024) Ethics and child nutrition.
- Brugaletta C, Le Roch K, Saxton J, Bizoueme C, McGrath M, et al., (2021) Breastfeeding assessment tools for at-risk and malnourished infants aged under 6 months old: a systematic review.
- Milligan RA, Flenniken PM, Pugh LC (1996) Positioning intervention to minimize fatigue in breastfeeding women. Appl Nurs Res 9(2): 67-70.
- Darmstadt GL, Baqui AH, Choi Y, (2009) Validation of community health workers' assessment of neonatal illness in rural Bangladesh. Bull World Health Organ 87(1): 12-19.
- Dongre AR, Deshmukh PR, Rawool AP, B S Garg (2010) Where and how breastfeeding promotion initiatives should focus its attention? A study from rural wardha. Indian J Community Med 35(2): 226-229.
- Robert T Hall, Anne M Mercer, Susan L Teasley, Deanna M McPherson, Stephen D Simon, et al., (2002) A breast-feeding assessment score to evaluate the risk for cessation of breast-feeding by 7 to 10 days of age. J Pediatr 141(5): 659-664.
- Tobin DL (1996) A breastfeeding evaluation and education tool. J Hum Lact 12(1): 47-49.
- Matthews MK (1998) Breastfeeding assessment tools.J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 27(3): 236-238.
- Jensen D, Wallace S, Kelsay P (1994) LATCH: a breastfeeding charting system and documentation tool. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 23(1): 27-32.
- Palmer MM, Crawley K, Blanco IA (1993) Neonatal Oral-Motor Assessment scale: a reliability study. J Perinatol 13(1): 28-35.
- Shrago L, Bocar D (1990) The infant's contribution to breastfeeding. J Obstet Gynecol Neonatal Nurs 19(3): 209-215.
- (1994) WHO/UNICEF: Breastfeeding counselling: a training course. World Health Organization and United Nations International Children’s Education Fund.
- (2009) WHO/UNICEF: Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative: Revised Updated and Expanded for Integrated Care-Section 3: Breastfeeding promotion and support in a baby-friendly hospital. Library Cataloguing-in-Publication.
- (2010) UNICEF: Baby Friendly Hospital Initiative: Breastfeeding Assessment Form.
- (2004) CARE: Preparation of a Trainer's Course: Mother to Mother Support Group Methodology and Breastfeeding and Complementary Feeding Basics. United States Agency for International Development (USAID) / The Infant & Young Child Nutriiton (IYCN) Project.
- Apgar V (1953) A proposal for a new method of evaluation of the newborn infant. Curr Res Anesth Analg 32: 260-267.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.