Review Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Harnessing Artificial Intelligence for Advancements in Biomedical Research
*Corresponding author: Bahman Zohuri, Adjunct Professor of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning, Golden Gate University, Ageno School of Business, San Francisco, California 94105, USA.
Received: August 06, 2024; Published: August 09, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.23.003103
Abstract
This article overviews how Artificial Intelligence (AI) shapes biomedical research, focusing on its applications, benefits, challenges, and prospects. By delving into the transformative capabilities of AI in areas such as disease diagnosis, drug discovery, personalized medicine, and biomarker identification, it underscores the significant advancements AI brings to healthcare and biological sciences. The discussion also highlights the critical challenges, including ethical considerations and data privacy issues, accompanying AI integration in biomedical research. Looking ahead, the article explores the promising future directions and collaborative efforts necessary to harness AI’s potential fully, ultimately aiming to revolutionize medical research and patient care.
Keywords: Artificial intelligence, Biomedical research, Disease diagnosis, Drug discovery, Personalized medicine, Biomarker discovery, Machine learning, Clinical laboratory, Data analysis, Translational science
Introduction
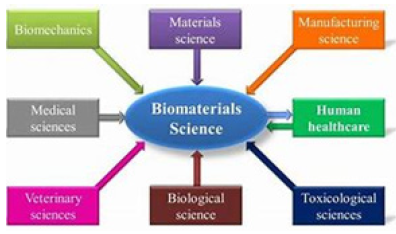
Biomedical science is an interdisciplinary field that merges principles from biology and medicine to understand, diagnose, and treat diseases. It encompasses many scientific disciplines, including molecular biology, biochemistry, genetics, pharmacology, and physiology, each contributing to a comprehensive understanding of human health and disease, as depicted in Figure 1. Biomedical science aims to translate fundamental scientific discoveries into practical medical applications, improving patient outcomes and advancing public health.
At its core, biomedical science seeks to unravel the complex mechanisms underlying normal physiological processes and pathological conditions. Researchers in this field study cellular and molecular interactions, genetic mutations, biochemical pathways, and the effects of various substances on biological systems. Biomedical scientists generate valuable insights into the causes and progression of diseases through genetic sequencing, medical imaging, and computational modeling.
This field is critical in developing new diagnostic tools, therapeutic strategies, and preventive measures. For instance, advancements in biomedical science have led to the creation of vaccines, targeted cancer therapies, and regenerative medicine techniques. Moreover, it plays a pivotal role in personalized medicine, where treatments are tailored to the individual characteristics of each patient, maximizing efficacy, and minimizing adverse effects (Figure 2).
Note that: Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals" [1,2].
A Community Health Worker (CHW) is a community member who provides basic health and medical care within their community and can provide preventive, promotional, and rehabilitation care to that community, typically without formal education equal to that of a nurse.
Furthermore, Biomedical science is confined to research laboratories and extends to clinical settings, where its findings are applied to improve patient care. Integrating biomedical science with clinical practice ensures a continuous feedback loop where clinical observations inform research, and scientific discoveries translate into clinical innovations. This dynamic interplay propels the ongoing advancement of medical science, ultimately enhancing human health and well-being.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has emerged as a transformative force in biomedical research, revolutionizing how scientists approach complex challenges in healthcare and biology. AI, a broad field that includes technologies such as computer vision, natural language processing, and machine learning, has enormous potential for biomedical data analysis and interpretation. With the exponential growth of data from medical imaging, genomic sequencing, and electronic health records, AI is poised to spur innovation in biomedical research and extract meaningful insights.
Roles Within Biomedical Science
Biomedical science encompasses a variety of specialized roles that work together to advance our understanding of health and disease. Researchers and scientists conduct fundamental studies to uncover biological mechanisms and disease processes. Clinical laboratory scientists and technologists perform diagnostic tests on patient samples to provide critical data for medical decision-making. Bioinformaticians and computational biologists analyze large datasets to identify patterns and insights that inform both research and clinical practice. Translational scientists bridge the gap between laboratory discoveries and clinical applications, developing new treatments and therapies (Figure 3).
Additionally, regulatory affairs specialists ensure that biomedical products and practices comply with governmental standards and ethical guidelines. Together, these roles drive innovation, enhance patient care, and contribute to the continuous improvement of public health.
Furthermore, Artificial Intelligence (AI) is revolutionizing each role within biomedical science by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. For more granular information about integration of AI and Biomedical, refer to the following section below.
Integrating Artificial Intelligence into Biomedical Science
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is increasingly augmenting biomedical science by enhancing the efficiency, accuracy, and scope of research and clinical applications. AI technologies, including machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing, are transforming how biomedical data is analyzed, interpreted, and utilized. This integration is driving significant advancements across various facets of biomedical science [3].
Enhanced Data Analysis and Interpretation
Biomedical research generates vast data from genomic sequencing, medical imaging, electronic health records, and clinical trials. Traditional methods need help to keep pace with this data deluge, but AI excels in processing large datasets quickly and accurately. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and correlations within complex data that human analysts might miss. For example, AI can analyze genomic data to pinpoint genetic mutations linked to specific diseases, facilitating the development of targeted therapies [4-6].
Improved Disease Diagnosis and Prediction
AI-driven technologies are revolutionizing disease diagnosis by providing more accurate and timely assessments. Machine learning models can analyze medical images, such as X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans, to detect anomalies with a precision that rivals or surpasses human experts. AI algorithms can also predict disease risk by integrating genetic information, lifestyle factors, and environmental data, enabling earlier intervention and personalized treatment plans [7,8].
Accelerated Drug Discovery and Development
The drug discovery process is traditionally time-consuming and expensive. AI accelerates this process by predicting how different compounds will interact with biological targets, identifying potential drug candidates faster than conventional methods. AI models can simulate molecular interactions and predict the efficacy and toxicity of new drugs, reducing the need for extensive laboratory testing. This streamlining of drug discovery not only saves time and resources but also brings effective treatments to patients more rapidly [9,10].
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Optimization
AI facilitates the implementation of personalized medicine by tailoring treatments to individual patients based on their unique genetic makeup, health history, and lifestyle. Machine learning algorithms can analyze patient data to predict how individuals will respond to specific treatments, optimizing therapeutic strategies. This personalized approach improves treatment efficacy, minimizes adverse effects, and enhances overall patient care [11].
Biomarker Discovery and Understanding Disease Mechanisms
AI is instrumental in identifying biomarkers-biological indicators of disease presence, progression, or response to treatment. By analyzing complex datasets, AI can uncover novel biomarkers that provide deeper insights into disease mechanisms. This understanding aids in the development of more precise diagnostic tools and targeted therapies, advancing the field of precision medicine [4-11].
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
Despite its transformative potential, the integration of AI in biomedical science poses challenges. Ensuring data privacy, mitigating algorithmic biases, and maintaining transparency and accountability are critical to the ethical deployment of AI technologies. Regulatory frameworks must evolve to address these issues, ensuring that AI-driven innovations are both safe and effective for clinical use [12].
Future Prospects
The future of AI in biomedical science is promising, with ongoing advancements in algorithm development, data integration, and computational power. Collaborative efforts between AI experts, biomedical researchers, and healthcare professionals are essential to fully harness the potential of AI. These partnerships will drive innovation, improve patient outcomes, and transform healthcare delivery [13].
Overall, the future of AI in biomedical science is bright, with advancements in algorithms, data integration, and computational power promising to further revolutionize research and patient care. Interdisciplinary collaborations will be crucial in harnessing AI's full potential to drive innovation and improve health outcomes globally as pointed out below:
Researchers and Scientists: Researchers can process and comprehend large datasets more quickly thanks to AI-driven data analysis tools, which accelerates the speed of discovery and reveals new insights. The design of experiments and the formulation of hypotheses are guided by machine learning algorithms' ability to recognize patterns and forecast results.
Clinical Laboratory Scientists and Technologists: AI-powered diagnostic tools and automated systems improve the accuracy and speed of laboratory tests. AI algorithms can analyze medical images, blood tests, and other diagnostic data with high precision, reducing human error and facilitating early disease detection.
Bioinformaticians and Computational Biologists: AI and machine learning are essential for managing and analyzing large-scale biological data, such as genomic sequences. AI tools help bioinformaticians identify genetic variants associated with diseases, understand complex biological networks, and develop predictive models for patient outcomes.
Translational Scientists: AI assists translational scientists in bridging the gap between research and clinical practice by predicting the efficacy and safety of new therapies. AI models can simulate drug interactions and optimize clinical trial designs, speeding up the development of new treatments and reducing costs.
Regulatory Affairs Specialists: AI can streamline regulatory processes by automating data collection, analysis, and reporting. AI-driven systems ensure compliance with regulatory standards, identify potential risks, and improve the efficiency of regulatory submissions, helping to bring new biomedical products to market faster.
Overall, AI enhances the capabilities of professionals in biomedical science, enabling more precise and effective research, diagnostics, and therapeutic development, ultimately improving patient care, and advancing public health.
Consequently, AI is augmenting biomedical science by enhancing data analysis, improving disease diagnosis, accelerating drug discovery, enabling personalized medicine, and uncovering novel insights into disease mechanisms.
AI has the potential to completely change patient care and biomedical research by resolving ethical issues and promoting interdisciplinary collaboration. This will bring about a new era of precision medicine and game-changing advancements in healthcare.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is a transformative force within biomedical science, revolutionizing how researchers, clinicians, and scientists approach health and disease. By enhancing data analysis, improving diagnostic accuracy, accelerating drug discovery, enabling personalized medicine, and uncovering novel biomarkers, AI has the potential to significantly advance our understanding and treatment of various medical conditions. The integration of AI-driven technologies into biomedical science roles such as researchers, clinical laboratory scientists, bioinformaticians, translational scientists, and regulatory affairs specialists highlights the vast potential of AI to drive innovation and improve patient care. Addressing challenges like data privacy, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance is crucial for the ethical deployment of AI. As we look to the future, collaborative efforts among AI experts, biomedical researchers, and healthcare professionals will be essential in harnessing AI's full potential to revolutionize biomedical research and transform healthcare delivery.
Comprehensive Result
Enhanced Data Analysis and Interpretation
AI enables researchers to process and interpret large biomedical datasets quickly and accurately, leading to novel insights and faster scientific discoveries.
Improved Disease Diagnosis and Prediction
AI-powered diagnostic tools increase the speed and accuracy of disease identification, allowing for earlier intervention and more effective treatment plans.
Accelerated Drug Discovery and Development
AI accelerates drug discovery by predicting compound interactions, reducing the time and cost associated with traditional methods, and bringing effective treatments to patients more rapidly.
Personalized Medicine and Treatment Optimization
By customizing therapies to each patient's unique traits, maximizing therapeutic approaches, and enhancing patient outcomes, artificial intelligence (AI) enables personalized medicine.
Biomarker Discovery and Understanding Disease Mechanisms
AI aids in identifying novel biomarkers and understanding complex disease mechanisms, advancing the field of precision medicine.
AI in Biomedical Science Roles
AI enhances the roles of researchers, clinical laboratory scientists, bioinformaticians, translational scientists, and regulatory affairs specialists, driving innovation and improving efficiency across the board.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations
The integration of AI in biomedical science must address data privacy, algorithmic bias, and regulatory compliance to ensure ethical and responsible deployment.
Future Prospects
The ongoing advancements in AI algorithms, data integration, and computational power, combined with interdisciplinary collaboration, promise a bright future for AI in biomedical research and healthcare innovation.
In summary, AI is poised to revolutionize biomedical science by transforming research methodologies, diagnostic processes, therapeutic development, and personalized patient care. By overcoming challenges and fostering collaboration, AI will continue to drive significant advancements in healthcare, ultimately leading to improved health outcomes and enhanced public health.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of interest
None.
References
- Gatseva PD, Argirova M (2011) Public health: the science of promoting health. Journal of Public Health 19 (3): 205-206.
- Winslow CE (1920) The untilled fields of public health. Science 51 (1306): 23-33.
- Bahman Zohuri, Simak Zadeh (2020) Artificial Intelligence Driven by Machine Learning and Deep Learning, Nova Science Pub.
- Bahman Zohuri and Farahnaz Behgounia (2021) Artificial Intelligence and High-Performance Data-Driven Medicine. Aditum Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Research: 1-5.
- Bahman Zohuri (2024) Revolutionizing Healthcare: Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) in the Radiopharmaceutical Industry. Novel Journal of Applied Sciences Research 1(2): 1-4.
- Bahman Zohuri, Farhang Mossavar Rahmani (2023) The Symbiotic Relationship Unraveling the Interplay between Technology and Artificial Intelligence (An Intelligent Dynamic Relationship). Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 17 (2023) 63-68.
- Bahman Zohuri, Farhang Mossavar Rahmani, Farahnaz Behgounia (2022) Knowledge is Power in Four Dimensions: Models to Forecast Future Paradigm: With Artificial Intelligence Integration in Energy and Other Use Cases. Academic Press, 1st
- Bahman Zohuri, Farhang Mossavar Rahmani (2020) Artificial Intelligence Versus Human Intelligence: A New Technological Race. Acta Scientific Pharmaceutical Sciences 4 (5).
- Bahman Zohuri, Farhang Mossavar Rahmani (2024) Revolutionizing Drug Discovery How Artificial Intelligence is Transforming Healthcare. Journal of Clinical and Biomedical Advances 3(4): 1-5.
- Bahman Zohuri (2023) A Handbook of Artificial Intelligence in Drug Delivery, Edited by Anil K. Philip, Aliasgar Shahiwala, Mamoon Rashid, Md Faiyazuddin, Academic Press, 1st
- Bahman Zohuri, Farhang Mossavar Rahmani (2024) The Symbiotic Evolution: Artificial Intelligence (AI) Enhancing Human Intelligence (HI), An Innovative Technology Collaboration and Synergy. Journal of Material Sciences & Applied Engineering 3(1): 1-5.
- Bahman Zohuri, Farhang Mossavar Rahmani (2023) The Symbiotic Relationship Unraveling the Interplay between Technology and Artificial Intelligence (An Intelligent Dynamic Relationship). Journal of Energy and Power Engineering 17 (2023) 63-68.
- Bahman Zohuri (2023) The Synergy of Business Resilience Systems and Artificial Intelligence Entanglement” Current Trends in Engineering Science 3(5).





 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.