Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Molecular Classification of Breast Cancer, it’s Correlation with Prognostic Parameters and Disease Free Survival-A 5 Year Study from the UAE
*Corresponding author: Philip H Hutchens, Independent Scientist, La Mesa, CA, USA.
Received: September 12, 2024; Published: September 17, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.24.003162
Abstract
Breast cancer became the most diagnosed cancer in the world in 2020 and is the most common cancer in the UAE. It’s a heterogeneous disease encompassing several molecular alterations as well as a diverse clinical behavior. Molecular classification of breast cancer is useful in therapeutic decision making, along with other established prognostic factors such as tumor stage, histologic grade and lymphovascular invasion. Immunohistochemical analysis of tumor based on ER, PR, her 2 and Ki67 is easier, cost effective and predicts response to hormonal therapy and Trastuzumab, which are the main modalities of adjuvant treatment. Retrospective review of 100 diagnosed cases of breast cancer for a period of 5 years from 2018 to 2023 was done. Patient demographics, prognostic parameters such as tumor size, lymph node status, histologic grade, multicentricity, proliferation index etc. were obtained. Cases were classified as Luminal A, Luminal B, Her 2 + and Triple Negative based on immunohistochemical staining and Her2 FISH testing in equivocal IHC. The various prognostic parameters were correlated with molecular classification as well as response to treatment as determined by survival rate with complete remission of cancer. Statistical analysis was done using chi square test to determine P value <0.05 considered as statistically significant correlation Luminal B was found to be the most common subtype, indicating more aggressive presentation of cancer in many women in this region. Advanced tumor stage, Lymph node positivity and higher histologic grade was more often seen in Her2 + and Triple negative cancers, in keeping with their known aggressive potential. Multicentricity was most frequently seen in Luminal A subtype, indicating that this maybe a different aspect of these type of tumors apart from their usual favorable prognosis and low stage presentation. Distant metastasis was seen more in the aggressive subtypes and absent in Luminal A type. Survival rate was highest in Luminal A and Least in Luminal B type. Even though molecular classification of breast cancer into 4 types is oversimplified in reflecting the genetic complexity of the tumor, it forms a foundation for further exploration of prognostic and predictive molecular assays facilitating better treatment outcomes.
Keywords: Breast, Cancer, Prognostic, Aggressive, Molecular classification, Outcomes
Abbreviations: None
Introduction
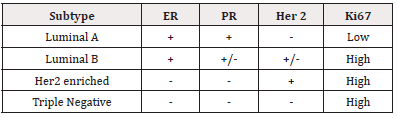
Breast Cancer is the most common cause of cancer related mortality among women and the fifth most common cause of cancer death overall [1] Molecular subtypes of breast cancer, histological grade and lymph node metastases, are strong prognostic and predictive factors. Consequently, classifying breast cancer into relevant molecular subtypes is an important aspect of therapeutic decision-making.[2] The most common and widely accepted classification of breast cancer is from an immunohistochemical perspective, based on the expression of the following hormone receptors: estrogen (ER), progesterone (PR) and human epidermal growth factor (HER2). Accordingly, the following four subtypes of breast cancer are widely recognized: luminal A, luminal B, HER2-positive, and triple-negative.[3] The characteristics of the four above subtypes are summarized as follows in Table1 [4].
Through this study, we attempted to correlate the various establishes prognostic parameters with the molecular subtypes and also with response to treatment and disease free survival.
Materials and Methods
Retrospective review of 100 diagnosed cases of breast cancer for a period of 5 years from 2018 to 2023 was done. Patient demographic data such as age and nationality was obtained. Data regarding prognostic parameters such as age, tumor size, histologic grade, multicentricity, lymph node status, ki67 proliferation index were obtained. Cases were classified as Luminal A, Luminal B, Her 2 + and Triple Negative based on immunohistochemical staining and Her2 FISH testing in equivocal IHC. The various prognostic parameters were correlated with molecular classification as well as response to treatment as determined by survival rate with complete remission of cancer, Statistical analysis was done using the chi square test.
Results
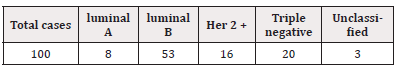
The classification of cases into the various molecular subtypes was as follows, summarized in Table2.
Patients of 15 nationalities were included in the study, confirming to the diverse population of the UAE.
The distribution of the most frequent nationalities included in the study in correlation with molecular subtypes was as follows, depicted in Figure1.
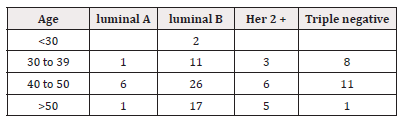
The correlation of various molecular subtypes as per the age of patients was as mentioned in Table 3.
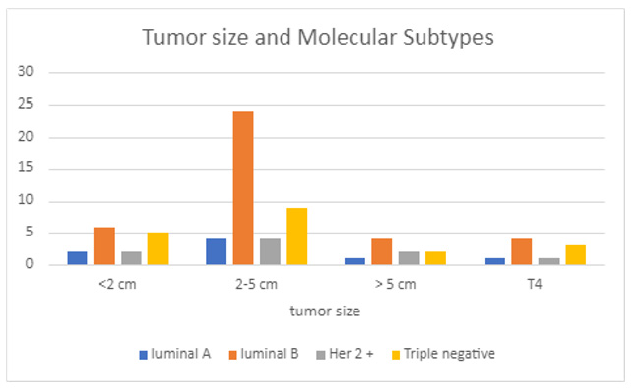
Tumor size in relation to the four subtypes were as follows described in Figure 2.
Multicentricity was noted in correlation with the molecular subtypes as in Table 4.
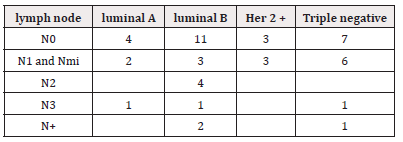
Correlation with Lymph node stage was as follows described In Table 5.
Distant Metastasis among the various Molecular subtypes was as depicted in Figure 3.
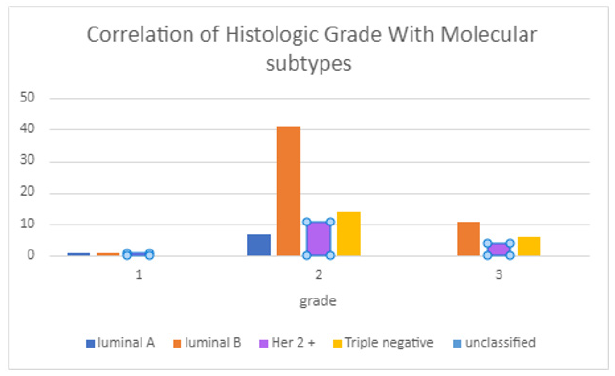
Correlation of the various subtypes with histologic grade is as in Figure 4.
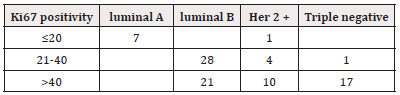
The various subtypes in relation to Ki67 percentage positivity (proliferation index) are as in Table 6.
Post Treatment follow-up
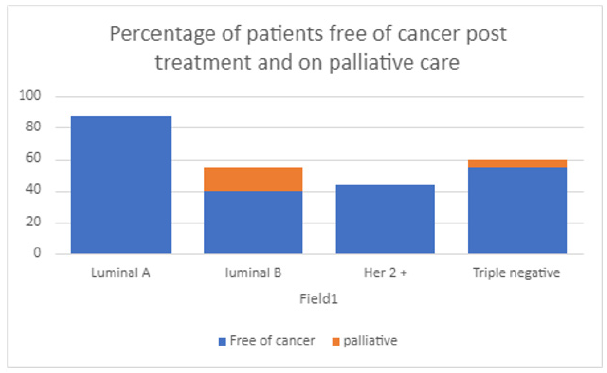
The percentage of patients cured of cancer on follow-up during the period of study and those on palliative care, in correlation with the various molecular subtypes are depicted in Figure 5.
Discussion
Patients of 15 nationalities were included in the study, which is representative of the diverse population of this country and region. The prevalence of the four molecular subtypes showed luminal B as the most common subtypes. In previous 9 studies carried out in various geographic regions in the period from 1993 to 2018, Luminal A was found to be the most common subtype [5]. However a few other studies have found Luminal B to be the most common subtype [6-10]. The higher prevalence of Luminal B subtype in the present study is indicative of more aggressive presentation of cancer in women of this region. In relation to the age of patients, the prevalence of more aggressive subtypes such as Luminal B, Her 2 + and Triple negative was seen in the age group 40 to 50, however the result was not statistically significant with a p value of 0.32 in the Chi square test. A few other studies have also not found statistically significant correlation between age and molecular subtype [11,12]. Multicentricity was seen in 5 of luminal B, 4 of triple negative, which are aggressive types, however also in 2 of Luminal A, which is the less aggressive subtype, indicating that this may be a different attribute of the tumor not related to its proliferation index or aggressive behavior. This is somewhat in correlation with previous studies, one of which significantly increased chances of multicentricity in patients with HER2-expression, Luminal A, and Luminal B groups compared to basal-like group or triple negative [13].
Lymph node positive status was more often seen with the known aggressive tumor types - Luminal B, Her2 + and Triple negative cases, however the correlation was not seen to be statistically significant with P value of 0.97. Some other studies have found similar patterns, one study concluding that Her2-enriched breast cancer was associated with 1.53 times faster lymph node spread than luminal A cancer [14]. Distant metastasis was most often seen in the Luminal B subtype in present study, followed by Triple negative and Her 2 positive tumors. Other studies have found similar results. In a study including 260 patients over a period of 5 years, the following incidence of distant metastasis were -Luminal B (61.5%), HER2+ (21.5%), TNBC (14.6%) and luminal A (2.3%) [15]. Another study found that Triple negative and HER2 subtypes of breast cancer were associated with significantly poorer overall survival and prone to earlier recurrence and metastases [16].
Histologic Grade of tumor in correlation with molecular subtypes was analyzed. As expected, Grade 3 cancer was found in more aggressive tumor types Notably Luminal B, Her2 + and Triple negative, however the correlation between histologic grade and molecular subtypes was not statistically significant with p value of 0.76. Other studies have analyzed this aspect and have found similar results, notably a study involving 247 patients, in which it was concluded that Grade I was associated with Luminal A, while Grade III was associated with Luminal B, HER2 and TNBC subtypes [17]. Ki67 percentage positivity was assessed in correlation with molecular classification. As expected, Higher Ki67 percentage greater than 40 % was observed in more aggressive subtypes such as Luminal B, Her 2 + and Triple negative. Similar findings have been observed in other studies, one of which had studied this association in 107 cases [18]. As regards to post treatment follow-up during the course of the study, Luminal A had the best response to treatment, with 80 % of the patients for whom data was available achieving complete cure. Other three subtypes had more or less similar cure rates. Patients with advanced metastatic disease on palliative care belonged to subtypes Luminal B and triple negative types. A few other studies have noted a similar pattern of response to treatment [19].
Conclusion
Luminal B was found to be the most common subtype, indicating more aggressive presentation of cancer in many women in this region. Advanced tumor stage, Lymph node positivity and higher histologic grade was more often seen in Her2 + and Triple negative cancers, in keeping with their known aggressive potential. Multicentricity was most frequently seen in Luminal A subtype, indicating that this maybe a different aspect of these type of tumors apart from their usual favorable prognosis and low stage presentation. Distant metastasis was seen more in the aggressive subtypes and absent in Luminal A type. Suvival rate was highest in Luminal A and Least in Luminal B type. Even though molecular classification of breast cancer into 4 types is oversimplified in reflecting the genetic complexity of the tumor, it forms a foundation for further exploration of prognostic and predictive molecular assays facilitating better treatment outcomes.
Acknowledgements
Gratitude to the Management of Prime Healthcare Group for facilitating this study Sincere Thanks to Dr. Verushka Mukesh Mansukhani (General Surgeon, Prime Hospital) and Dr. Arun Karanwal (Medical Oncologist, Prime Hospital) for referring cases to us which contributed to the study.
Conflict of Interest
We have No conflict of interests to declare.
References
- Humaid O Al-Shamsi, Nadia Abdelwahed, Aydah Al-Awadhi, Mohamed Albashir, Amin M Abyad, et al. (2023) Breast Cancer in the United Arab Emirates. JCO Glob Oncol 9: e2200247.
- Al-Thoubaity FK (2019) Molecular classification of breast cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Ann Med Surg (Lond) 49: 44-48.
- Orrantia-Borunda E, Anchondo-Nunez P, Acuna-Aguilar LE, Francisco Octavio Gomez-Valles, Claudia Adriana Ramirez-Valdespino, et al. (2022) Subtypes of Breast Cancer. Breast Cancer [Internet]. Brisbane (AU): Exon Publications.
- Renan Gomes do Nascimento, Kaleu Mormino Otoni (2020) Histological and molecular classification of breast cancer: what do we know?
- Fatma Khinaifis Al-thoubaity (2020) Molecular classification of breast cancer: A retrospective cohort study. Annals of Medicine and Surgery 49: 44-48.
- Batra A, Marwah N, Marwah S, Gupta S, Dharembra D, et al. (2016) Gallen’s molecular subtypes in primary breast carcinoma in Indian population. Clin Cancer Investig J 5(05): 416-423 24.
- Vasconcelos I, Hussainzada A, Berger S, Ellen Fietze, Jörg Linke, et al. (2016) The St. Gallen surrogate classification for breast cancer subtypes successfully predicts tumor presenting features, nodal involvement, recurrence patterns and disease free survival. Breast 29: 181-185.
- Harish S, Anand S, PrasharM, Lohia N, Singh S, et al. (2020) Intrinsic subtyping of breast cancer and its relevance with clinicopathological features and outcomes in patients from North India: a single center experience. J NTR Univ Health Sci 9(03): 164-171.
- Park S, Koo JS, Kim MS, Hyung Seok Park, Jun Sang Lee, et al. (2012) Characteristics and outcomes according to molecular subtypes of breast cancer as classified by a panel of four biomarkers using immunohistochemistry. Breast 21(01): 50-57.
- Ayad Ahmad Mohammed (2021) The clinical behavior of different molecular subtypes of breast cancer. Cancer Treat Res Commun 29: 100469.
- Devadass CW, Royal AB, Saxena P, Devraj D, Gouri M, et al. (2023) Breast Carcinoma: Correlation of Molecular Subtypes with Histopathologic Characteristics. J Med Sci Health 9(3): 281-287.
- Joute, Zothangsung; Debnath, Maharshi; Pukhrambam, Gayatri Devi; Khuraijam, Sushma; Sarangthem, Babina. Molecular subtypes of breast carcinoma and its relation with clinicopathological features: A single-center initial experience. J Med Soc 35(3): 103-107.
- Baradaran A, Derakhshan M, Raeisi S, Neshat S, Raeisi S, et al. (2023) Multicentricity in Different Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer: A Cross-sectional Study in Isfahan. Adv Biomed Res 12: 9.
- Gabriel Isheden, Felix Grassmann, Kamila Czene, Keith Humphreys, (2021) Lymph node metastases in breast cancer: Investigating associations with tumor characteristics, molecular subtypes and polygenic risk score using a continuous growth model. International Journal of Cancer 149(6): 1348-1357.
- Ahmad Fakhrozi Helmi, Daan Khambri, Rony Rustam (2021) The Relationship of Breast Cancer Subtypes with the Event of Metastasis in Dr. M. Djamil Hospital Padang. Bioscientia Medicina: J BioTrans Res 5 (4).
- Wu X, Baig A, Kasymjanova G, Kafi K, Holcroft C (2016) Pattern of Local Recurrence and Distant Metastasis in Breast Cancer By Molecular Subtype. Cureus 8(12): e924.
- Setyawati Y, Rahmawati Y, Widodo I, Ghozali A, Purnomosari D, et al. (2018) The Association between Molecular Subtypes of Breast Cancer with Histological Grade and Lymph Node Metastases in Indonesian Woman. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 19(5): 1263-1268.
- Soliman NA, Yussif SM (2016) Ki-67 as a prognostic marker according to breast cancer molecular subtype. Cancer Biol Med 13(4): 496-504.
- Ayad Ahmad Mohammed (2021) The clinical behavior of different molecular subtypes of breast cancer, Cancer Res Commun 29:100469.






 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.