Review Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
The Concurrence of Human Episodic Memory with Linked Lists ADT and Block Chain Technologies
*Corresponding author: S Vidhusha, Department of Computer Science and Engineering School of Engineering Shiv Nadar University Chennai, India.
Received: October 21, 2024; Published: October 28, 2024
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2024.24.003220
Abstract
The human brain comprises of millions of neurons that contribute to memory, work, and recall. It stores a chain of disjoint episodes in a decentralized manner. It can be related to similar kind of experience which maps human conscious and working memory to the concepts of blockchain technology and data structures. Data Structures is a branch of computer science which relates to the way of storing and retrieval of information represented through arrays and linked lists in a fundamental way. Specifically, the concepts of episodic memory can be related to linked lists while long-term recall could be related with working principles of arrays. Digging more about the fundamental data structures and their relation to brain computing could lead ways to put forth contribution of block chain technologies to Cognitive Neuroscience. In turn, such mapping could provoke interesting results or findings which could help in diagnosis of numerous cognitive disorders at an earlier stage.
Keywords: Episodic memory, Cognitive neuroscience, Block chain technologies, Data structures, Disorder studies, Brain mapping
Introduction
The human brain comprises of a network which joins multiple neurons that wire together to perform a particular task [1]. Brain disorders occur due to the improper wiring patterns or over wiring patterns of the neurons. Numerous research works have concentrated to understanding these patterns of the neurons to decode the brain network [2]. Neuro disorders such as autism, Alzheimer’s disease, dementia primarily arise due to the underwiring of neurons. While on the other hand, Attention Deficient Hypersensitivity Disorder (ADHD), High Functioning Autism (HFA) occur due to the over wiring of the neurons [3]. Therefore, if there is a possibility to involve the use of the technology to support the decoding of the brain network, it can facilitate the treatment interventions for the affected individuals.
Episodic memory relates to action of involving a person to encounter a series of interrelated events that are associated to each other [4]. This paper focusses on applying the concepts of block chain technology and data structures to decode the neuronal patterns of the brain and suggests the similarity and concurrence in the network of block chain and data structures. Hence, this work proposes and suggests the mechanisms of fixing the neuronal wirings in the appropriate way that could help in the treatment interventions of the individuals who suffer from brain disorders.
Review of Related Work
Jakub Hort, et al,. have done the survey of existing publications, projects, and platforms on the use of blockchain in Medicine and Neurology. These researchers have highlighted that use of having a register using blockchain technology could help doctors in performing patient management, monitoring treatments, and tuning clinical trials. They have also highlighted that the use of probable blockchain technology and understanding can lead to substantial improvements in the field of neuroscience.
Hamed Taherdoost has tried to relate the neuroscience and blockchain principles by picking up hashing techniques used in blockchain principles for secure transactions with respect to how brain stores and retrieves information. Cho SH, et al,. [2] have explored the utility of blockchain as an analogy for understanding the brain mechanisms. They have concluded their research by referring the illogical analogies done on neuroscience and have called for global researchers to relate the concepts of neuroscience with state of art technologies and concepts. These research works mentioned here have motivated the need to perform a correlation between cognitive neuroscience, data structure concepts and block chain technologies for the use in relevant fields which has been attempted in this paper.
Data Structures
Data structures is a branch of computer science that relates to efficient organization, storing, and retrieval of information. Fundamental data structures which include arrays and linked lists vary in their implementation strategy [5]. While arrays represent elements in a consecutive/contiguous manner, linked lists on the other hand can relate to distorted grouping of elements. Therefore, to implement applications that involve contiguous/distorted representation of data, the choice of the respective data structure can be useful [6].
Cognitive Neuroscience & Data Structures
The human brain consists of millions of neurons. They get wired when a human is involved in a task or remain unwired during rest. When a person gets involved in a specific task/action, certain neurons collaborate with each other by getting themselves wired [7]. Episodic memory is a brain cognition process which can be observed based on the collection of events that happened to a person at a particular time [8]. Recall is a kind of memory related activity that is done to recollect a specific incident or series of incidents. Long-term recall is a brain cognition task which involves a series of associated events that happened over a period [9].
While conventional data structures can help in efficient storage and retrieval of data in computing principles. Incorporating the concepts of data structures towards cognitive neuroscience can decipher neuronal wirings. This can help in figuring out the inner engineering of the brain. For instance, episodic memory relates to memory of interim events which need not necessarily have an association with the current state a person currently experiences. Whereas long-term memory can relate to reminiscing of events with a related sequence [10]. As depicted in figure 1 (Figure 1).
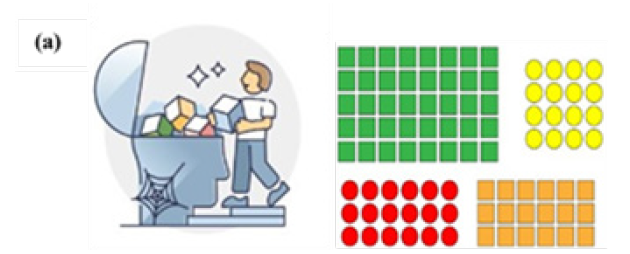
Figure 1: Representation of how long-term memory and recall can relate to concept of arrays. (a) relates to how specific events get stored as memory in the human brain. (b) relates to how array data structure gets represented to signify memory components. Recall of long-term memory leads to access all the related occurrences which are dependent on each other.
Block Chain Technology
The block chain technology is a buzz word in the recent era. It is because of its ease of use that it offers as a part of its working mechanism. A Block chain is a collection of records in a ledger format which can be stored in a distributed and decentralized system [11]. Such a technology can help the end user in maintaining the information in a ledger format which could be accessed remotely on demand [12]. Security is a major concern when we are storing ledgers at a decentralized repository. However, data structure concepts such as hashing can offer lookup mechanisms that can help in accessing information in a secure manner.
Block Chain & Cognitive Neuroscience
As mentioned in Section II, the human brain involves wiring numerous neurons for an activity. Be it a memory recall or accounting episodic memory, these neurons need to wire to do that task [13]. While in concurrence with the concepts of data structures, using arrays and linked lists - the wiring pattern of the neurons relate themselves for long term recall and episodic memory respectively [14]. Likewise, the working principle of block chain technologies can be related with brain cognition for relating the similarity for building solutions for many research problems that help in addressing disorder studies. A block chain consists of several nodes involved in a process, which is connected as a network [15].
Hypothesizing this, a formulation to relate a group of neurons of the brain that wire against each other to perform a particular task related like block chain technologies. A node can be accessed in block chain network which performs similar or interrelated tasks [16]. Similarly, a group of neurons get wired for a particular task. In block chain, a particular network can be accessed based on the requirement. A group of nodes can be focused for information processing and retrieval. For a task of long-term memory recall, the neurons which were wired already for that task, need to be rewired (Figure 2a,2b).
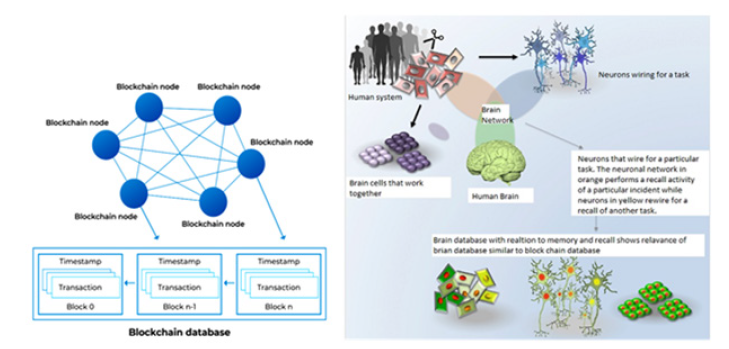
Figure 2: Representation of how the concepts of block chain technology and cognitive neuroscience work similarly. (a) Explains the block chain network (Source: https://unova.io/blockchain) (b) Explains the working of human brain network. The hypothesis of relating block chain and human brain can help in understanding the process of the neural rewiring.
Conclusion
This article highlights the similarity between the working of the human brain for long term memory and recall tasks against the concepts of data structures and block chain technology. This understanding and hypothesizing can help in brain mapping studies which can contribute to especially figuring out the logic of underwiring of neurons for the patients suffering with memory related brain disorders such as Dementia, Alzheimer’s and so on. Specific schemes on employing the concurrence of human episodic memory with related data structure concepts and blockchain technologies can be helpful for providing customised treatment interventions for affected individuals. This hypothesis can be helpful for treating neurological disorders like autism, ADHD, dementia by understanding the patient’s neuronal pathway by providing them an episodic memory task and observe their neuronal patterns and simulate the observations through linked lists ADT concepts and blockchain concepts. As they undergo the treatment, the improvements in their neuronal wirings can be observed by simulation parallelly. If the simulated pathways through linked list ADT and blockchain gives encouraging results, such customised treatment interventions can help the therapist in providing similar treatments to the patient. This can facilitate by giving a preview of how the treatment methodology can help in the betterment of the patient since relying on the evidence of symptomatic improvements in neuro disordered individuals is difficult to observe. If a proper understanding of neuronal wiring of such affected patients can be decoded, specific mechanisms can be employed in concentrating on the neural region and simulating the rewiring of neurons could possibly benefit the patient and improve their lifestyle.
Acknowledgement
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Taherdoost Hamed (2022) Neuroscience and Blockchain. Hamed Taherdoost. Neuroscience and Blockchain. Arch Neurol & Neurosci.
- Cho SH, Cushing CA, Patel K, Kothari A, Lan R, et al., (2018) Blockchain and human episodic memory.
- Celesti A, Ruggeri A, Fazio M, Galletta A, Villari M, et al., (2020) Blockchain-based healthcare workflow for tele-medical laboratory in federated hospital IoT clouds. Sensors 20(9): 2590.
- Veritx (2021) Trusted B2B Marketplace for Industry 4.0.R.
- Nichola Cooper (2022) Editorial: Blockchain in Health Care. Frontiers in Blockchain 4.
- Srinivasan, Vidhusha N Udayakumar, Kavitha Anandan (2020) Influence of primary auditory cortex in the characterization of autism Spectrum in young adults using brain connectivity parameters and deep belief networks: An fMRI study. Current Medical Imaging 16(9): 1059-1073.
- Srinivasan, Vidhusha, N Udayakumar, Hualou Liang, Kavitha Anandan, et al., (2022) A hybrid approach for analysis of brain lateralisation in autistic children using graph theory techniques and deep belief networks. International Journal of Biomedical Engineering and Technology 39: 40-64.
- Vidhusha S, Kavitha Anandan (2016) Inter-hemispherical investigations on the functional connectivity of Autistic resting state fMRI. International Journal of Cognitive Informatics and Natural Intelligence (IJCINI) 10(2): 95-108.
- Vidhusha S, Kavitha Anandhan (2015) Analysis and evaluation of autistic brain MR images using learning vector quantization and support vector machines. International Conference on Industrial Instrumentation and Control (ICIC): 911-916.
- Ezzyat, Youssef, Lila Davachi (2011) What Constitutes an Episode in Episodic Memory? Psychological Science 22(2): 243-252.
- Lisman John, Katherine Cooper, Megha Sehgal, Alcino J Silva (2018) Memory Formation Depends on Both Synapse-Specific Modifications of Synaptic Strength and Cell-Specific Increases in Excitability. Nature Neuroscience 21(3): 309-314.
- Zheng Z, S Xie, H Dai, X Chen, H Wang, et al., (2017) An Overview of Blockchain Technology: Architecture, Consensus, and Future Trends. In 2017 IEEE International Congress on Big Data (BigData Congress): 557-564.
- Raghavendra M (2019) Can blockchain technologies help tackle the opioid epidemic: a narrative review. Pain Med 20: 1884-1889.
- Bell L, Buchanan WJ, Cameron J, Lo O (2018) Applications of Blockchain Within Healthcare. Stamford, CT: Blockchain in Healthcare Today.
- Angeletti F, Chatzigiannakis I, Vitaletti A (2017) The role of blockchain and IoT in recruiting participants for digital clinical trials, in Proceedings of the 2017 25th International Conference on Software, Telecommunications and Computer Networks, SoftCOM.
- Paglialonga A, Keshavjee K (2019) Use of alternative currencies, blockchain technology, and predictive analytics for chronic disease prevention: a conceptual model. Stud. Health Technol Inform 264: 1872-1873.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.