Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Facial Adipostructuring, the Intelligent Rejuvenation. Presentation of Clinical Case with Histopathological Analysis
*Corresponding author: Gladys Velazco, building attached to the rector’s office of the Universidad de Los Andes Merida Venezuela.
Received: December 21, 2024; Published: January 07, 2025
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2025.25.003319
Abstract
With age, one of the first compartments that are lost and sagging is the middle fat compartment, which accentuates the dark circles and the nasolabial fold and in turn gives a tired appearance to the face. Skin aging is not the same for everyone; many factors influence it, including age, sex, lifestyle, diet, pollution and genetics. On the face, we have several adipose panicles and it has been shown by studies that each panicle ages differently and has a tendency to contract, forming the lipodystrophies, flaccidity, deflation and lipoatrophies that we observe in older people, this, without taking into account the damage extrinsic of the skin given by the sun and lifestyle and diet. In recent studies, the medical community has established that deep subcutaneous tissue gives the face its position, contour and youthful dimensions, and therefore is critical to slowing down the morphological changes that occur in our face over time: when we lose tissue, we begin to look haggard and aged. Currently and by tradition, filler materials or collagen inducers are used (hyaluronic acid and calcium hydroxyapatite among others...), in order to achieve a more rested and natural appearance, redefining the cheekbone and improving sagging in that middle third of the cheek. face. It is not about changing the face, but about ensuring that, being the same and with its own characteristics and personality, we can improve it as much as possible, always taking into account what it was like a few years ago. In this study we demonstrate with biopsies and histological preparations that adipostructure can be a vital tool in facial rejuvenation based on cellular and structural change.
Keywords: Facial adipostructure, Intelligent rejuvenation, Collagen fibers, Senolitics
Introduction
A case is presented in which, a new technique, the facial adipostructuring, was used as a facial rejuvenation technique, supported by the histopathological analysis of the skin before and after the treatments, in search of the changes that the treated skin presents at the level of the dermis in relation to collagen, reticular fibers and elastic fibers. The treatment was with 3 sessions, one every 20 days.
Facial adipostructuring is an innovative technique that uses senolytic chemical compounds, whose application for many years has been for skin rejuvenation through mesotherapy to stimulate cells and fibroblasts, so that they change from senescent mode to rejuvenation mode. It is born from years of study and research of evidence-based science [1].
It consists of the panniculopathic reorganization of the adipose panicles in the skin of the face. It is already recognized, through clinical studies and research, that it is the source of youth of the face, preventing bone resorption and reversing sagging or deflation, glycation and lipomatosis of the skin, improving its physical appearance and at the same time the texture. and thickness thereof, increasing its turgor. It is a combination of lipocarving with a cannula and a biochemical reaction, which occurs in the adipocytes, when the senolytic compounds are applied to them [1-4].
Medical Record
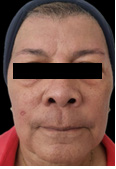
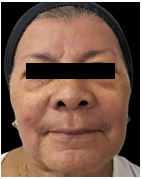
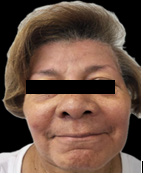
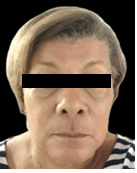
This is a 72-year-old female patient with symptoms of deflation, lipomatosis and glycation on physical examination, who comes because she wants to improve the appearance of her skin and its sagging. She has not had any rejuvenating treatments and uses hyaluronic acid creams and sunscreen to maintain herself and has never had fillers or threads in her face. The patient underwent surgery for nodular basal cell carcinoma on the right cheek 3 months before the first session (February 2024), with a scar observed on said cheek.
A physical examination and medical history were performed to look for chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus and high blood pressure and cancers, which the patient denied. Control photos are taken from the front, 45 degrees and 90 degrees on both sides before and after 20 days of each session. Topical anesthesia is placed at the entry points of the cannula. The adipose panicles are marked on the skin of both cheeks and the temple with the direction of insertion of each one. And then we proceed to carve each panicle separately, respecting its limits.
Materials and Method
A skin biopsy was taken with punch 3 of untreated skin. And Hematoxylin and eosin stains, and special stains were performed.
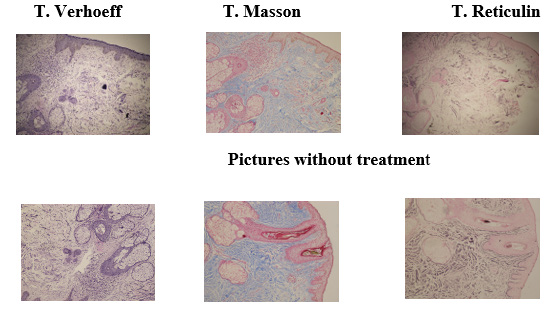
Stains
a) Verhoeff: allows you to visualize fine structures such as elastic fibres with a black-stained nucleus and red collagen. The cytoplasmic elements are yellow.
b) Masson’s Trichrome: allows differentiation between collagen and muscle fibers in tissues. Collagen type I, blue, red muscle, red erythrocytes and black nuclei.
c) Reticulin: visualization of extracellular matrix fibers of connective tissue, especially type III collagen.
It is part of the dermis, being 0.4% of the dry tissue. It is dyed black with silver nitrate.
Then, cannulation of each cheek adipose tissue was performed and left in the same active ingredients.
Senolytic compounds such as Centella Asiatica, L-Carnitine and Dimethylaminoethanol (DMAE) and Hexapeptide #38, among others, were used combined with an acceptable pH and the individual carving technique, with cannulas ranging from 22g x 38 mm to 27 G x 38 mm, of each panicle respecting the limits of the same and subsequently the product is left in the panicle. Each session is carried out with different chemical compounds since fat has memory. (There is already in the market, a formulated presentation with these products combined called Face structure, to perform the same treatment.) [1,2]
Then, substances that will stimulate the nerve receptors of the ligaments were applied at the level of the interseptal spaces, between the panicles, substances among which are Silicon, DMAE combined with an acceptable pH to cause their contraction, closing these spaces, thus allowing the flaccid skin to be raised and the panicles to be rearranged.
Subsequently, supplementation with oral active ingredients is given to reinforce the treatment and use of sunscreen. Three adipose structuring sessions were performed, one every 20 to 30 days. After the recovery period of the 3rd session, another skin biopsy was taken again with punch 3 and the same stains were performed [5] (Figures: 1-5).
Analysis
A marked progressive improvement is clearly observed in the patient’s physical appearance at the skin level, in relation to the density and volume of the facial contour. The skin acquired a glow and a hydrated and rejuvenated appearance. In addition, the patient’s scar on the right cheek has improved its appearance and is almost imperceptible, due to the remodelling of the skin. There is improvement in sagging, glycation, and even a lightening of skin tone is noted.
At the Histopathological Level it is Observed
Patient without Treatment: Epidermis with mild to moderate hypotrophy, discrete mild to moderate intercellular edema, mild focal spongiosis. At the level of the papillary and reticular dermis, areas of mild to moderate intercellular edema, focal solar elastosis, discrete dilation of blood vessels, and mild and focal inflammatory infiltrate are observed. In the stains, a decrease in type collagen fibers and elastic fibers is observed.
Patient Post Treatment: Epidermis with mild focal acanthosis, with thickening of previously hypotrophic areas. Mild to moderate edema at the level of the papillary dermis.
In the stains, a moderate increase in collagen fibers type I and 3 and elastic fibers is observed. Compared to other studies, [6-8] the results are really encouraging both hydrologically and morphologically.
Conclusion
Facial adipostructuring, intelligent rejuvenation, can be considered an innovative and safe technique for skin rejuvenation, without having to resort to the use of fillers and threads, which, in some cases, can cause complications in patients. The changes found in patients are progressive and can last up to 2 years (depending on the patient’s lifestyle), unlike fillers and threads that add weight and volume to the face and last for months and when reabsorbed leave a dead space that is not reabsorbed.
It is a simple technique that is performed in the office with topical anaesthesia and is minimally invasive and, above all, does not involve work disability. Adipostructuring of different areas of the face can be performed such as rhinoplasty without surgery, lips, eyes, forehead and neck without having to undergo surgery, which is excellent for people who are afraid of surgeries.
The patient begins to see improvement instantly in the thickness, shine and sagging of the skin, which increases progressively each day up to a maximum of 15 days. In the stains, changes are found at the level of the dermis, where an increase in the number of type 1 and 3 collagen fiber as well as elastic fibers.
Acknowledgements
None.
References
- Velazco Viloira G (2020) Adipoestructuración facial. Acta Bioclionica 10(20) Julio Diciembre.
- Ibarra L, Camacho R (2023) Adipoestructuración facialuna nueva herramienta para la armonización orofacial. Secuencia de casos. Acta Bioclínica 13(26)95-115.
- Garcia Guevara V, Velazco Viloria G (2023) Evaluando la eficacia y seguridad de la técnica de adipoestructuración facial: a propósito de una serie de casos. Acta Bioclinica 13: 25.
- Velazco Viloria GSíndrome de Sobrellenado Facial Vs Adipoestructuración facial, ficción o realidad. Acta Bioclinica15(29).
- Katta R, Huang S (2019) Skin, Hair and Nail Supplements: An Evidence-Based Approach. Skin therapy letter 24(5): 7-13.
- Gierloff M, Storing C, Buder T, Gasssling V, Ail WiltfangJ (2017) Aging changes of the midfacial fat compartments: A computed tomographic study. Plastic Reconstruct Surg 129: 263-373.
- Eugenia Murawska Cialowicz (2017) Adipose tissue-morphological and biochemical characteristic of different depots. Pstepy Hig Med Dosw (online) 71: 466-484.
- Uwe Wollina Reinhard Wetzker, Mohamed Badawy Abdel N, Ilja L Kruglikov (2017) Role of adipose tissue in facial aging. Clin Interv Aging 12: 2069-2076.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.