Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Block Diagram of an Electro Elastic Drive for Nanobiomedicine
*Corresponding author: SM Afonin, National Research University of Electronic Technology, MIET, Moscow, Russia.
Received: June 02, 2025; Published: June 12, 2025
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2025.27.003556
Abstract
In the work the block diagram of an electro elastic drive is calculated for nanobiomedicine. An electro elastic drive is used for nanobiomedicine in scanning microscopy, DNA research, adaptive optics, XYZ micropositioning system, compensation of gravitational and temperature displacements. By using method of mathematical physics, the block diagram of an electro elastic drive is determined for nano biomedicine.
Keywords: Electro elastic drive, Piezo drive, Block diagram, Nanobiomedicine
Introduction
An electro elastic drive is used for nanobiomedicine in nanoposition, DNA research, scanning microscopy, adaptive optics, XYZ micropositioning system, damping vibration [1-21]. The block diagram of an electro elastic drive is constructed for nanobiomedicine [22-59].
Method
The method of mathematical physics is used to determine the of the electroelastic drive using the equation of electroelasticity and the ordinary differential equation. The equation electroelasticity an electro elastic drive [3-43] is written in the general form
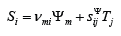
here 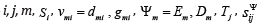 are the indexes,
the relative displacement, the electroelasticity coefficient for the
voltage or current control, the control parameter in the form the
electric field strength or the electric induction, the mechanical field
strength and the elastic compliance.
are the indexes,
the relative displacement, the electroelasticity coefficient for the
voltage or current control, the control parameter in the form the
electric field strength or the electric induction, the mechanical field
strength and the elastic compliance.
The ordinary differential equation [11-57] for an electro elastic drive
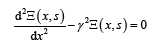
here Ξ(x, s) ,γ , x , s, are the Laplace transform displacement, the propagation coefficient, the coordinate, and the transform parameter.
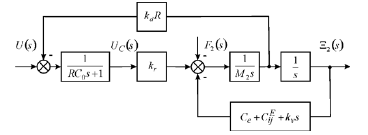
Block Diagram
For the ordinary differential equation for an electro elastic drive its boundary conditions are determined
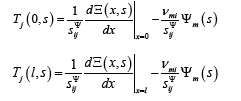
here l = { δ , h, b for the longitudinal, transverse, shift piezo drives.
The Laplace transform general force
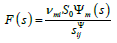
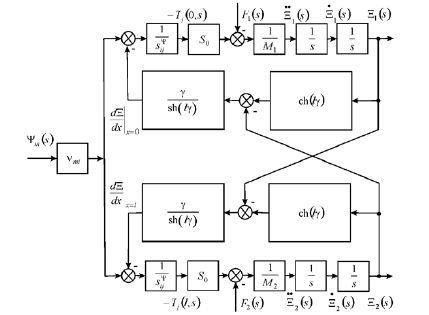
Than the general block diagram for distributed parameters of an electro elastic drive with on (Figure 1) is calculated for nanobiomedicine
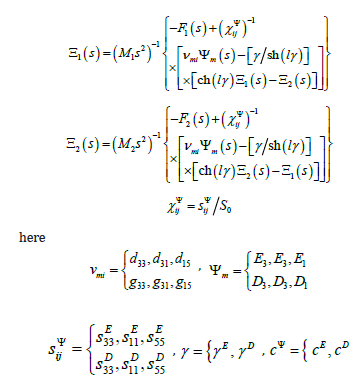
The general block diagram of an electro elastic drive with distributed parameters on (Figure 1) is used for nanobiomedicine.
Than displacement matrix
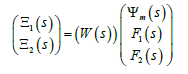
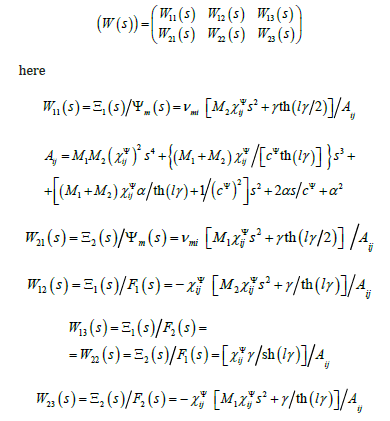
Than displacements two ends of the longitudinal piezo drive
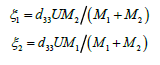
At PZT drive  this displacements are determined
this displacements are determined 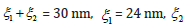 = 6 nm.
Let us consider the block diagram of the piezo drive with first
fixed end and elastic inertial load at the voltage control.
The equation direct piezo effect [3-43]
= 6 nm.
Let us consider the block diagram of the piezo drive with first
fixed end and elastic inertial load at the voltage control.
The equation direct piezo effect [3-43]
Let us consider the block diagram of the piezo drive with first fixed end and elastic inertial load at the voltage control.
The equation direct piezo effect [3-43]
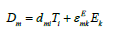
here 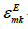 - the permittivity.
- the permittivity.
Than 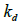 direct coefficients
direct coefficients
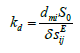
The Laplace transform voltage for first feedback is obtained
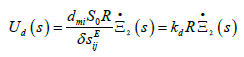
The equation of the reverse piezo effect [3-43]
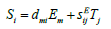
Than Laplace transform general force of drive
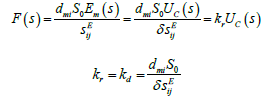
The Laplace transform force for second feedback at the voltage control
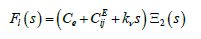
here kν - the coefficient of viscous friction.
Than block diagram for lumped parameters the piezo drive and fixed end, elastic inertial load and the voltage control is determined on (Figure 2)
Than its transfer function
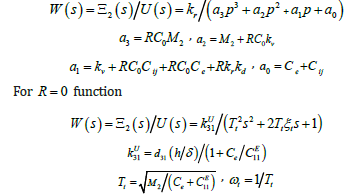
Discussion
In the work the method of mathematical physics is used to determine the block diagram of the electro elastic drive using the equation of electro elasticity and the ordinary differential equation. The displacement matrix drive is determined.
Conclusions
The general block diagram for distributed parameters an electro elastic drive is calculated for nanobiomedicine. The displacements two ends of the longitudinal PZT drive are determined. The block diagram for lumped parameters the piezo drive and the voltage control is obtained. The parameters PZT drive are founded.
Conflict of Interest
None.
Acknowledgement
None.
References
- Uchino K (1997) Piezoelectric Actuator and Ultrasonic Motors. Boston, MA, Kluwer Academic Publisher: 350.
- Zhao C (2011) Ultrasonic Motors Technologies and Applications. Springer, Berlin, Germany: 494.
- Afonin SM (2006) Absolute stability conditions for a system controlling the deformation of an elecromagnetoelastic transduser. Doklady Mathematics 74(3): 943-948.
- Bhushan B (2004) Springer Handbook of Nanotechnology. New York, Springer: 1222.
- Shevtsov SN, Soloviev AN, Parinov IA, Cherpakov AV, Chebanenko VA (2018) Piezoelectric Actuators and Generators for Energy Harvesting: Research and Development. Springer, Switzerland, Cham: 182.
- Spanner K, Koc B (2016) Piezoelectric motors, an overview. Actuators 5(1): 6.
- Belfiore NP (2018) Micromanipulation: A challenge for actuation. Actuators 7(4): 85.
- Toledo J, Ruiz Díez V, Hernando García J, Sánchez Rojas JL (2020) Piezoelectric actuators for tactile and elasticity sensing. Actuators 9(1): 21.
- Afonin SM (2020) Optimal control of a multilayer electroelastic engine with a longitudinal piezoeffect for nanomechatronics systems. Applied System Innovation 3(4): 53.
- Afonin SM (2021) Coded control of a sectional electroelastic engine for nanomechatronics systems. Applied System Innovation 4(3): 47.
- Afonin SM (2018) Structural-parametric model of electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics. Actuators 7(1): 6.
- Afonin SM (2019) Structural-parametric model and diagram of a multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechanics. Actuators 8(3): 52.
- Mason W (1964) Physical Acoustics: Principles and Methods. Vol. 1. Part A. Methods and Devices. Academic Press, New York: 515.
- Liu Y, Zhang S, Yan P, Li H (2022) Finite element modeling and test of piezo disk with local ring electrodes for micro displacement. Micromachines 13(6): 951.
- Jang Seonmin, Yang Su Chul (2018) Highly piezoelectric BaTiO3 nanorod bundle arrays using epitaxially grown TiO2 Nanotechnology 29(23): 235602.
- Akpinar M, Uzun B, Yayli MO (2024) Dynamics of a piezoelectric restrained nanowire in an elactic matrix. Mechanics of Solids 59(5): 2936-2959.
- Kodakkal A, Pentek M, Bletzinger KU, Wuchner R, et al. (2025) Systematic and quantitative assessment of redused model resolution on the transient structural response under wind load. Applied sciences 15(3): 1588.
- Afonin SM (2015) Structural-parametric model and transfer functions of electroelastic actuator for nano- and microdisplacement. Chapter 9 in Piezoelectrics and Nanomaterials: Fundamentals, Developments and Applications. Ed. Parinov IA. Nova Science, New York: 225-242.
- Afonin SM (2017) Structural-parametric model electromagnetoelastic actuator nanodisplacement for mechatronics. International Journal of Physics 5(1): 9-15.
- Afonin SM (2019) Structural-parametric model multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanomechatronics. International Journal of Physics 7(2): 50-57.
- Afonin SM (2021) Rigidity of a multilayer piezoelectric actuator for the nano and micro range. Russian Engineering Research 41(4): 285-288.
- Afonin SM (2024) Structural scheme of an electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanotechnology research. Chapter 45 in Physics and Mechanics of New Materials and Their Applications. PHENMA 2023. Springer Proceedings in Materials. Vol.41. Editors Parinov IA, Chang SH, Putri EP. Springer, Cham: 486-501.
- Ferrara Bello A, Vargas Chable P, Vera Dimas G, Vargas Bernal, et al. (2021) XYZ micropositioning system based on compliance mechanisms fabricated by additive manufacturing. Actuators 10(4): 68.
- Afonin SM (2024) A multi-layer electro elastic drive for micro and nano robotics. International Robotics & Automation Journal 10(2):73-76.
- Afonin SM (2024) Correction of characteristics compound longitudinal piezodrive at elastic inertial load for nanorobotics research. International Robotics & Automation Journal 10(3): 103-106.
- Afonin SM (2022) Nano drive for biomedical science and research. American Journal of Biomedical Science and Research 15(3): 260-263.
- Afonin SM (2024) Structural model of a nano drive for biomedical science 21(2): 188-193.
- Afonin SM (2023) Condition absolute stability of system with nano piezoactuator for astrophysics research. Aeronautics and Aerospace Open Access Journal 7(3): 99-102.
- Limpichaipanit A, Ngamjarurojana A (2023) Strain characteristics of PLZT-based ceramics for actuator applications. Actuators 12(2): 74.
- Afonin SM (2024) System with nano piezoengine under randomly influences for biomechanics. MOJ Applied Bionics and Biomechanics 8(1): 1-3.
- Afonin SM (2024) DAC electro elastic engine for nanomedicine. MOJ Applied Bionics and Biomechanics 8(1): 38-40.
- Afonin SM (2025) Structural scheme of electroelastic engine micro and nano displacement for applied bionics and biomechanics. MOJ Applied Bionics and Biomechanics 9(1): 1-4.
- Afonin SM (2021) Characteristics of an electroelastic actuator nano- and microdisplacement for nanotechnology. Chapter 8 in Advances in Nanotechnology. 25. Eds. Bartul Z, Trenor J, Nova Science, New York: 251-266.
- Afonin SM (2023) Structural model of nano piezoengine for applied biomechanics and biosciencess. MOJ Applied Bionics and Biomechanics 7(1): 21-25.
- Zhao C, Li Z, Fangchao Xu, Zhang H, Sun F, et al. (2024) Design of a novel three-degree-of-freedom piezoelectric-driven micro-positioning platform with compact structure. Actuators 13(7): 248.
- Cui F, Li Y, Qian J (2021) Development of a 3-DOF flexible micro-motion platform based on a new compound lever amplification mechanism. Micromachines 12(6): 686.
- Huang W, Lian J, Chen M, Dawei An (2021) Bidirectional active piezoelectric actuator based on optimized bridge-type amplifier. Micromachines 12(9): 1013.
- Ma W (2024) Open STM: A low-cost scanning tunneling microscope with a fast approach method. HardwareX 17: e00504.
- Hu G, Xin W, Zhang M, Chen G, et al. (2024) Development of a fast positioning platform with a large stroke based on a piezoelectric actuator for precision machining. Micromachines (Basel) 15(8): 1050.
- Afonin SM (2023) Nanopiezoactuator for astrophysics equipment. Physics & Astronomy International Journal 7(2): 153-155.
- Afonin SM (2024) Structural scheme of piezoactuator for astrophysics. Physics & Astronomy International Journal 8(1): 32-
- Afonin SM (2023) Electroelastic actuator of nanomechatronics systems for nanoscience. Chapter 2 in Recent Progress in Chemical Science Research. Volume 6. Ed. Min HS, B P International, India, UK. London: 15-27.
- Afonin SM (2020) Structural scheme of electroelastic actuator for nanomechatronics, Chapter 40 in Advanced Materials. Proceedings of the International Conference on “Physics and Mechanics of New Materials and Their Applications”, PHENMA 2019. Editors: Ivan A. Parinov, Shun-Hsyung Chang, Banh Tien Long. Springer Nature, Switzerland, Cham: 487-502.
- Afonin SM (2021) Absolute stability of control system for deformation of electromagnetoelastic actuator under random impacts in nanoresearch. Chapter 43 in Physics and Mechanics of New Materials and Their Applications. PHENMA 2020. Springer Proceedings in Materials. Volume 10. Eds. Parinov I.A., Chang S.H., Kim Y.H., Noda N.A. Springer, Switzerland, Cham: 519-531.
- Afonin SM (2023) Harmonious linearization of hysteresis characteristic of an electroelastic actuator for nanomechatronics systems. Chapter 34 in Physics and Mechanics of New Materials and Their Applications. Proceedings of the International Conference PHENMA 2021-2022, Springer Proceedings in Materials series. Vol. 20. Eds. Parinov IA, Chang SH, Soloviev AN. Springer, Cham: 419-428.
- Afonin SM (2023) Structural parametric model and diagram of electromagnetoelastic actuator for nanodisplacement in chemistry and biochemistry research. Chapter 7 in Current Topics on Chemistry and Biochemistry. Vol. 9. Ed. Baena O.J.R., B P International, India, UK: 77-95.
- Afonin SM (2018) Multilayer electromagnetoelastic actuator for robotics systems of nanotechnology. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus) Moscow and St. Petersburg, Russia: 1698-1701.
- Afonin SM (2020) Digital analog electro elastic converter actuator for nanoresearch. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference of Russian Young Researchers in Electrical and Electronic Engineering (EIConRus), St. Petersburg and Moscow, Russia: 2332-2335.
- Afonin SM (2024) Frequency method for determination self-oscillations in control systems with a piezo actuator for astrophysical research. Aeronautics and Aerospace Open Access Journal 8(2): 115-117.
- Afonin SM (2024) Structural model and scheme of a piezoengine for aeronautics and aerospace. Aeronautics and Aerospace Open Access Journal 8(4): 212-217.
- Afonin SM (2024) Parallel and coded control of multi layered longitudinal piezo engine for nano biomedical research. MOJ Applied Bionics and Biomechanics 8(1): 62-65.
- Afonin SM (2024) Structural model of a nano piezoelectric actuator for nanotechnology. Russian Engineering Research 44(1): 14-19.
- Afonin SM (2018) Electroelastic actuators for nano- and microdisplacement. SCIREA Journal of Physics 3(2): 81-91.
- Afonin SM (2016) Structural-parametric models of electromagnetoelastic actuators for nano- and micromanipulators of mechatronic systems. SCIREA Journal of Mechanics 1(2): 64-80.
- Afonin SM (2018) Electroelastic actuator nano- and microdisplacement for precision mechanics. American Journal of Mechanics and Applications 6(1): 17-22.
- Afonin SM (2016) Structural-parametric models and transfer functions of electromagnetoelastic actuators nano- and microdisplacement for mechatronic systems. International Journal of Theoretical and Applied Mathematics 2(2): 52-59.
- Afonin SM (2016) Decision wave equation and block diagram of electro magneto elastic actuator nano - and micro displacement for communications systems. International Journal of Information and Communication Sciences 1(2): 22-29.
- Schultz J, Ueda J, Asada H (2017) Cellular Actuators. Butterworth-Heinemann Publisher, Oxford: 382.
- Nalwa HS (2019) Encyclopedia of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology. Los Angeles: American Scientific Publishers 30.

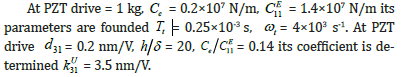


 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.