Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Effects of a Novel Composition of Traditional Chinese Herbal Plants and Modern Functional Ingredients on the Welfares of Chinese Male Individuals regarding their Sexual Performance, Renal Protection and Sleep Quality
*Corresponding author: Yan Li, Product Innovation Center, Qingdao Hai Zhi Sheng Biological Engineering Co., Ltd, China.
Received: December 09, 2025; Published: December 18, 2025
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2025.29.003824
Abstract
Objective: In the context of holistic male health management, there is growing interest in formulations that simultaneously support multiple physiological domains. This study evaluates a novel composite, developed under the guidance of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) theory and modern nutritional science, for its potential benefits on key aspects of male well-being, including physiological vitality, sleep quality, and renal resilience.
Methods: A multi-faceted assessment was conducted in adult male zebrafish models. The intervention was a composite powder comprising core TCM botanicals—Cistanche, American Ginseng, Polygonatum, Angelica, and Oyster—orchestrated according to the Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi principle. The zebrafish were administered the formulation at low, medium, and high concentrations. Evaluations encompassed indicators of physiological vitality (e.g., mating behavior frequency, testis weight, sperm count, and testosterone levels), sleep parameters (total awakening time and activity during rest), and renal protection (incidence of edema in a nephrotoxicity model).
Results: The composite powder significantly enhanced core markers of male physiological vitality. It promoted natural mating behavior, supported reproductive organ health, and contributed to the maintenance of healthy testosterone levels. A distinct dose-response relationship was observed, with the medium dose consistently yielding the most favorable outcomes. Furthermore, the formulation demonstrated significant sleep-supporting activity by reducing restlessness and improving sleep continuity. It also exhibited notable renal protective effects, significantly mitigating pathological edema.
Conclusion: This integrative formulation, synergizing TCM wisdom with modern nutritional concepts, demonstrates comprehensive benefits for supporting male health. Its multi-domain efficacy in promoting physiological vitality, sleep quality, and renal resilience aligns with a proactive, “preventive treatment” approach to wellness. The findings underscore the value of blending traditional herbal strategies with contemporary science to advance men’s health. Further research in human cohorts is merited.
Introduction
Male health encompasses a broad spectrum of physiological and psychological well-being, with sexual health representing a crucial component that significantly influences quality of life and interpersonal relationships. Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is defined as the persistent inability to achieve or maintain a penile erection sufficient for satisfactory sexual performance [1]. Beyond its adverse effects on quality of life and interpersonal relationships, ED is increasingly recognized as an indicator of underlying physical and physiological deterioration, potentially serving as an early marker for life-threatening conditions such as coronary artery and peripheral vascular diseases [2].
ED arises from a complex interplay of psychological and organic factors. Psychogenic ED, mediated by noradrenergicor sympathetic pathways, is frequently associated with stress, depression, and anxiety [3]. In contrast, organic ED is commonly linked to modifiable risk factors including tobacco use, obesity, physical inactivity, and chronic alcohol consumption, which disrupt hormonal balance by reducing testosterone levels and impairing endothelial function [4]. Chronic inflammation, characterized by elevated circulating inflammatory markers such as C-Reactive Protein (CRP), intercellular adhesion molecule-1, interleukins (IL- 6, IL-10, IL-1β), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), further exacerbates endothelial dysfunction and contributes to the onset and severity of ED [4].
Large-scale epidemiological studies have reported substantial variation in ED prevalence worldwide, with rates as high as 76.5% in certain regions [5]. In mainland China, the prevalence of ED exhibits considerable geographic disparity, ranging from 17.1% in several provinces and metropolitan areas (e.g., Beijing, Guangzhou) to 92.3% in Gansu Province [6]. Moreover, the incidence of ED increases markedly with age, affecting 20.86% of men under 30 years and rising to 93.72% among those aged 70 and above [7]. Notably, a growing proportion of younger men are reporting EDrelated concerns, highlighting an emerging public health issue.
Pharmacotherapy remains the cornerstone of ED management. The market for ED drugs in China is projected to reach US$179.3 million by 2030, with a compound annual growth rate of 9.9% from 2025 to 2030. Sildenafil citrate (Viagra) was the top revenuegenerating product in 2024 [8]. However, despite their efficacy and widespread use, the misuse of ED medications is increasingly documented [9]. Such practices may lead to risky sexual behaviors, including unprotected intercourse with multiple partners, and elevate the incidence of sexually transmitted infections. Furthermore, psychological dependence on these drugs can exacerbate anxiety and undermine self-confidence in maintaining erectile function without pharmacological aid [10].
Given these limitations of conventional pharmacotherapy, there has been a growing interest in complementary and alternative approaches, particularly Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM). TCM offers a holistic framework for understanding and treating ED, often attributing it to patterns such as Kidney Yang deficiency, Qi stagnation, and Blood stasis [11]. Numerous herbal compounds, such as the classic formulation Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan, have been historically utilized and investigated for their potential benefits on male reproductive health [12]. However, many traditional formulations lack rigorous validation through modern scientific methodologies, and their mechanisms of action often remain partially characterized, limiting their acceptance and application in evidence-based practice. On the other hand, phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibition is an established mechanism for treating ED by enhancing erectile function. Studies in sexually exhausted rat models have shown that Turnera diffusa (80 mg/kg) improves ejaculatory performance and shortens the post-ejaculatory interval [13]. Its active components, including apigenin-7-glucoside and Z-echinacin, exhibit anti-aromatase and estrogenic activities, with an IC₅₀ of 63.1 μg/ml for aromatase inhibition [14]. In addition, Turnera diffusa was incorporated for its aphrodisiac properties. Pelvic Floor Muscle (PFM) function is another critical factor in ED. Normal PFM activity supports penile rigidity by maintaining intracorporeal pressure. Postbiotic component that upregulates androgen receptor and α-actin expression in the levator ani muscle can strengthen PFM and aid functional recovery [15].
To bridge this gap between traditional wisdom and contemporary scientific standards, we developed a novel composite that strategically integrates well-established TCM herbs with modern functional ingredients. This study aims to systematically evaluate the effects of this composite on multiple fronts—sexual performance, sleep quality, and renal protection—using a zebrafish model. The zebrafish model was selected for its high genetic and physiological homology to mammals, particularly in drug metabolism and organ function, making it a robust platform for preliminary efficacy and safety screening. We hypothesize that this integrated formulation will not only ameliorate ED symptoms by leveraging the synergistic effects of its components but also confer broader health benefits, thereby offering a comprehensive, multitargeted strategy for managing male health and well-being.
Materials and Methods
Tested Formulation and Preparation
The investigational composite powder utilized in this study was a precisely formulated mixture of standardized botanical extracts, designed based on the principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) to warm and tonify Kidney Yang, replenish essence, and benefit Qi. The core composition consisted of the following five key ingredients, all administered in their extracted forms to ensure consistent bioactivity and dosage:
Cistanche deserticola (Cistanche, Rou Cong Rong) Extract
Panax quinquefolius (American ginseng, Xi Yang Shen) Extract
Polygonatum sibiricum (Huang Jing, Huang Jing) Extract
Angelica sinensis (Angelica, Dang Gui) Extract
Ostreidae (Oysters, Mu Li) Extract
These constituents were meticulously blended in fixed proportions according to the TCM Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi (Chief, Deputy, Assistant, Envoy) formulation strategy. In this framework, Cistanche served as the Jun (Chief) herb to primarily tonify Kidney Yang; American Ginseng and Polygonatum acted as the Chen (Deputy) to reinforce the chief herb and replenish Qi; Angelica functioned as Zuo (Assistants) to nourish essence and blood, respectively; and Oyster acted as the Shi (Envoy) to guide the actions of the other herbs to the kidney meridian and consolidate essence. The final composite powder was dissolved in the aquarium water to the specified test concentrations (e.g., 3.90625, 7.8125, and 15.625 μg/mL for the sexual function assay) for administration to the zebrafish.
Animals and Housing
Adult male zebrafish (AB strain) were maintained in a standardized aquaculture system under a 14/10-hour light/ dark cycle at 28.5°C. The zebrafish were randomly divided into six groups (n=10-15 per group): a normal control group, a model control group, a positive control group (administered either clomiphene citrate tablets or Wu Zi Yan Zong Wan, a classic TCM formula for tonifying the kidney and reinforcing essence [16]), and three experimental groups receiving the test composite powder at the Maximum Tolerated Concentration (MTC), 1/2 MTC, and 1/4 MTC. The MTC was predetermined as the highest concentration that did not induce mortality or significant adverse effects beyond transient intestinal abnormalities.
Evaluation of Male Sexual Function Enhancement
A model of impaired male sexual function was established by exposure to cyclophosphamide, an alkylating agent known to selectively deplete differentiating spermatogonia, leading to oligospermia or asthenozoospermia in zebrafish [17]. Sexual performance was assessed by quantifying the frequency of “rear-end collisions,” a well-documented mating behavior where the male pursues and makes contact with the female’s genital region, culminating in egg release and sperm ejaculation [18]. A significant reduction in this behavior confirmed successful model establishment.
Following the induction period, the cyclophosphamide was withdrawn. The positive control drugs and the composite powder were administered via aqueous solution. The following endpoints were measured: (1) body weight and testis weight; (2) frequency of rear-end collisions; (3) sperm count using a hemocytometer; and (4) serum levels of testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), and luteinizing hormone (LH) using commercial enzymelinked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits.
The improvement rate in male health efficacy(%)
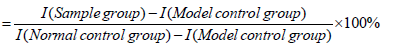
Evaluation of Sleep Quality Improvement
An insomnia model was induced with Penty Lenetetra Zole (PTZ), a GABA_A receptor antagonist that reduces inhibitory neurotransmission and reliably induces hyperarousal and sleep disturbances in zebrafish [19,20]. Except for the normal control group, all fish were pre-exposed to hydrochloride adrenaline to establish a model of Qi stagnation and blood stasis, a TCM syndrome often associated with sleep disorders. After model induction, the test sample was delivered as a water-soluble solution. Behavioral tracking was performed to quantify the total awakening time and locomotor activity levels during the designated sleep period.
The improvement rate in sleep quality (%)
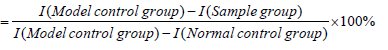
Evaluation of Renal Protective Efficacy
The zebrafish model was employed for nephrotoxicity studies due to its high degree of conservation with mammals in renal development, function, and response to nephron toxicants [21]. Aristolochic Acid (AA) was used to induce acute kidney injury, as it causes specific damage to renal tubular epithelial cells, leading to interstitial fibrosis, atrophy, and the characteristic syndrome known as Aristolochic Acid Nephropathy (AAN) [22]. The model was validated by observing significant renal edema and morphological abnormalities. After AA exposure, zebrafish were treated with water-soluble samples. The primary outcome was the incidence of renal edema, determined by visual inspection under a microscope.
The improvement renal protection efficacy (%)
Results
Composite Powder Ameliorates Cyclophosphamide- Induced Impairments in Male Sexual Function
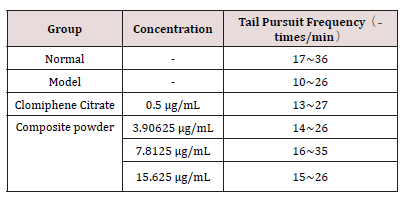
To evaluate the effects of the composite powder on male sexual function, a zebrafish model of reproductive impairment was established using cyclophosphamide. As summarized in Table 1, the frequency of tail pursuit, a key indicator of sexual motivation and performance, was significantly reduced in the model control group compared to the normal group. Treatment with the composite powder, particularly at the medium concentration (7.8125 μg/ mL), markedly increased the pursuit frequency, demonstrating a restorative effect on this core mating behavior.
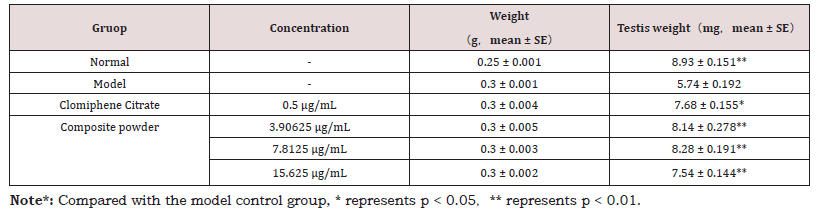
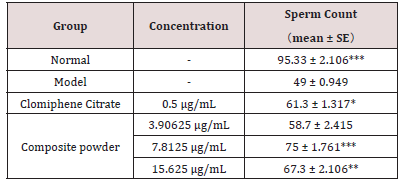
The impact on reproductive organ morphology and function was further investigated. As shown in Table 2, while the composite powder did not significantly alter the overall body weight of zebrafish, it induced a significant increase in testis weight across all treatment concentrations compared to the model control group. This suggests a specific trophic effect on the male gonad. Consistent with this finding, sperm count, which was severely depleted in the model group, was significantly enhanced at the medium and high concentrations of the composite powder (Table 3). The improvement in male reproductive health, calculated based on a composite efficacy formula, reached 75.18%, 79.67%, and 56.41% at the low, medium, and high concentrations, respectively, for testicular health, and 20.86%, 56.12%, and 39.57% for sperm count.
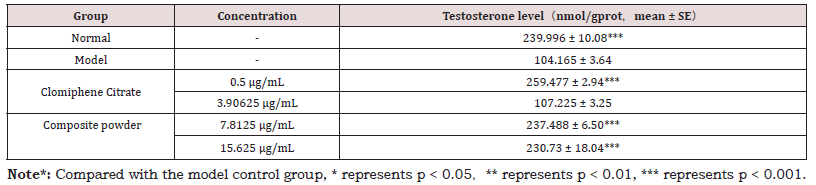
Furthermore, the composite powder exhibited a potent effect on the endocrine axis. Testosterone levels, which were drastically lowered in the model group, were restored to near-normal levels following treatment with the medium and high concentrations of the composite powder (Table 4). The calculated improvement in testosterone content was 98.15% and 93.18% for these two concentrations, respectively, indicating a strong androgen-boosting capacity (Table 1-4).
Composite Powder Mitigates Pentylene Tetrazole- Induced Sleep Disturbances
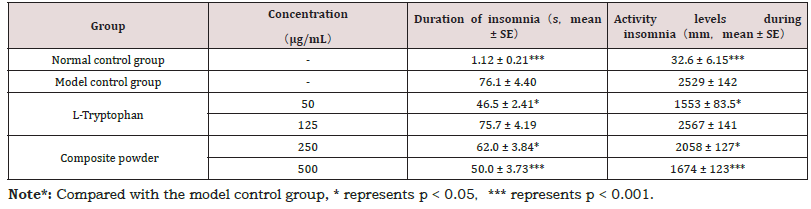
The efficacy of the composite powder in improving sleep quality was assessed in a zebrafish insomnia model induced by PTZ. The model control group exhibited a pronounced increase in both the duration of insomnia and locomotor activity during the sleep period. As detailed in Table 5, treatment with the composite powder at 250μg/mL and 500 μg/mL significantly reduced these parameters in a dose-dependent manner. The high concentration (500 μg/mL) produced effects comparable to the positive control, L-Tryptophan, confirming the formulation’s potent sleep-aid properties. A representative behavioral trajectory (Figure 1) visually corroborates the reduction in hyperactive, insomnia-like movement following treatment (Table 5) (Figure 1).
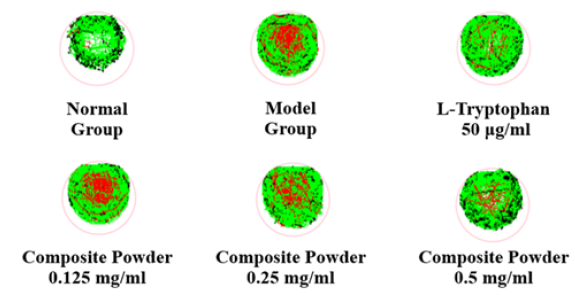
Figure 1: Typical behavioral trajectory of zebrafish after treatment with composite powder (black lineslow motion; green line: medium speed motion; red line: fast motion).
Composite Powder Confers Protection against Aristolochic Acid-Induced Nephrotoxicity
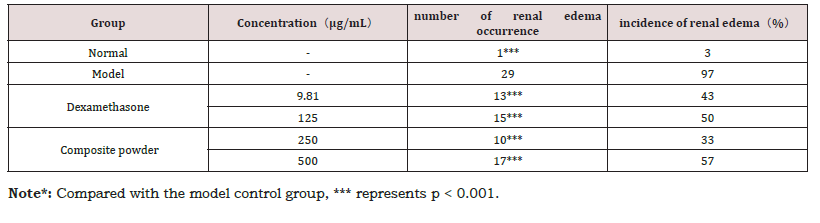
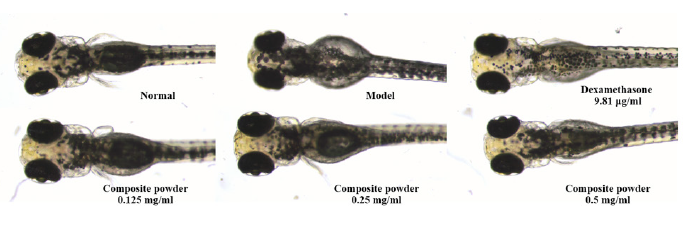
The renal protective potential of the composite powder was evaluated in an Aristolochic Acid (AA)-induced acute kidney injury model. AA administration resulted in a high incidence of renal edema (97%) in the model control group. As presented in Table 6, treatment with the composite powder significantly reduced the occurrence of renal edema at all tested concentrations. The most pronounced protective effect was observed at 250 μg/mL, which reduced the incidence to 33%, outperforming the positive control, dexamethasone (43%). A typical image of renal edema is provided in Figure 2 for morphological reference (Table 6) (Figure 2).
Discussion and Conclusion
The pursuit of holistic male health encompasses the optimization of multiple physiological domains, including sustained vitality, restorative sleep, and robust organ function. Contemporary lifestyle challenges often simultaneously impact these interconnected systems, necessitating integrated approaches that extend beyond single-symptom management. This study demonstrates that a novel composite formulation, developed by synergizing Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) principles with modern functional ingredients, confers significant, multi-faceted benefits on key aspects of male well-being—specifically sexual performance, sleep quality, and renal protection—in established zebrafish models.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a multifactorial condition that significantly impairs quality of life and acts as a potential sentinel for systemic vascular disease. While phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE-5) inhibitors provide effective symptomatic relief, concerns regarding their long-term use, potential for psychological dependency, and limited ability to address the underlying pathophysiology highlight the urgent need for alternative, holistic strategies [11]. This study demonstrates that a novel composite formulation, which integrates the principles of Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) with modern functional ingredients, confers multi-faceted benefits on male sexual performance, sleep quality, and renal protection in wellestablished zebrafish models.
Our findings on male sexual function reveal a comprehensive restorative effect. The composite powder significantly enhanced zebrafish chasing behavior, a direct indicator of sexual motivation and performance [21]. This behavioral improvement was corroborated by fundamental physiological changes: a marked increase in testis weight and a significant recovery of sperm count at medium and high concentrations, indicating a robust enhancement of reproductive organ vitality and spermatogenesis. Crucially, the formulation restored testosterone levels to near-physiological ranges in a dose-dependent manner. The efficacy at the medium concentration (7.8125μg/mL) was particularly pronounced, often surpassing the effect of the higher dose, suggesting the existence of an optimal therapeutic window. This coordinated enhancement across behavior, organ morphology, and endocrine function strongly validates the TCM principle of tonifying the kidney to bolster reproductive health [12,19], an effect attributable to the synergistic action of core ingredients like Cistanche, ginseng, and Polygonatum.
The therapeutic mechanism of our formulation extends beyond mere hormonal modulation, embodying a multi-targeted strategy. The inclusion of Turnera diffusa, supported by its documented aphrodisiac properties [15], introduces a targeted mechanism. Its active compounds, such as apigenin, function as natural aromatase inhibitors [23,24], potentially reducing the conversion of testosterone to estrogen and thereby increasing bioactive androgen levels—a key factor for sustaining libido.
Furthermore, the postbiotics in our formulation represent a novel approach to targeting Pelvic Floor Muscle (PFM) health. Given the PFM’s critical role in maintaining penile rigidity by preventing venous outflow [ 25], our formulation, by potentially enhancing the expression of Androgen Receptor (AR) and α-actin, may strengthen PFM contractility. This offers a mechanical improvement of erectile function that is distinct from, yet complementary to, the vascular effects of PDE5 inhibitors.
The benefits of the formulation are not confined to sexual health. It exhibited significant sedative effects in a PTZ-induced insomnia model, substantially reducing both insomnia duration and associated hyper-locomotor activity. This aligns with the TCM concept that sleep disturbances (Shen imbalance) often stem from heart-kidney disharmony due to kidney essence deficiency [26]. Ingredients such as Polygonatum and Danggui, with their nourishing and blood-tonifying properties, likely contribute to calming the Shen, thereby improving sleep quality. This crosssystem efficacy underscores the holistic advantage of a TCM-based approach.
Similarly, the significant renal protective effects observed in an aristolochic acid-induced nephropathy model underscore the formulation’s systemic value. The reduction in renal edema incidence suggests potent anti-inflammatory and/or anti-fibrotic properties [27], aligning with the TCM tenet that strengthening the kidney, the foundation of innate constitution, enhances resistance to pathological insults.
The observation that the medium dose frequently yielded optimal results is particularly noteworthy. This non-linear, biphasic dose-response is characteristic of complex botanical formulations and suggests a carefully balanced synergistic interaction among the constituents, masterfully guided by the Jun-Chen-Zuo-Shi principle [28]. This principle provides a sophisticated framework for formulation: Cistanche (Jun) directs the primary Yang-tonifying action; American Ginseng and Polygonatum (Chen) synergistically reinforces this effect; Danggui (Zuo) assists by improving blood circulation to the genitalia; Ostreidae and modern ingredients like postbiotics can be seen as a contemporary interpretation of the Shi role, targeting ancillary pathways like PFM function. An overdose may disrupt this delicate herbal synergy, attenuating efficacy.
By presenting products through the lens of “TCM Theory + Precision Nutrition,” consumers can grasp the traditional logic of “nourishing the kidneys” while simultaneously understanding and appreciating the scientific efficacy of novel technological ingredients through evidence-based data. This dual approach builds trust through familiar traditional concepts and then introduces and validates new scientific components, fostering a more profound and educated acceptance of integrated health solutions.
In conclusion, this study provides robust preclinical evidence for the efficacy of our novel TCM-modern composite formulation. It operates through a multi-targeted mechanism that integrates endocrine modulation (testosterone restoration), potential enzymatic inhibition (aromatase), structural and functional improvement (spermatogenesis, PFM strength), and systemic protection (sleep, renal health). This integrative strategy, which seamlessly merges the holistic framework of TCM with the precision of modern nutritional science, represents a promising and comprehensive paradigm for male health management. It moves beyond mere symptom relief to foster foundational wellness, aligning with the “preventive treatment” model and potentially mitigating the future risk of chronic diseases for which ED is an early warning sign. Future clinical trials are warranted to translate these promising findings into tangible human health benefits.
Acknowledgements
None.
Conflict of Interest
None.
References
- Lizza EF, Rosen RC (1999) Definition and classification of erectile dysfunction: Report of the Nomenclature Committee of the International Society of Impotence Research. International Journal of Impotence Research 11(3): 141-143.
- Salonia A, Bettocchi C, Boeri L, Capogrosso P, Carvalho J, et al. (2021) European Association of Urology guidelines on sexual and reproductive health-2021 update: Male sexual dysfunction. European Urology 80(3): 333-357.
- Mirone V, Napolitano L, D Emmanuele di Villa Bianca R, Mitidieri E, Sorrentino R, et al. (2021) A new original nutraceutical formulation ameliorates the effect of Tadalafil on clinical score and cGMP accumulation. Archivio Italiano di Urologia, Andrologia 93(2): 221-226.
- Barone B, Napolitano L, Abate M, Cirillo L, Reccia P, et al. (2022) The role of testosterone in the elderly: What do we know? International Journal of Molecular Sciences 23(7): 3535.
- Kessler A, Sollie S, Challacombe B, Briggs K, Van Hemelrijck M, et al. (2019) The global prevalence of erectile dysfunction: A review. BJU International 124(4): 587-599.
- Hao Z Y, Li H J, Wang Z P, Xing J P, Hu W L, et al. (2011) The prevalence of erectile dysfunction and its relation to chronic prostatitis in Chinese men. Journal of Andrology 32(5): 496-501.
- Wang W, Fan J, Huang G, Zhu X, Tian Y, et al. (2017) Meta-analysis of prevalence of erectile dysfunction in mainland China: Evidence based on epidemiological surveys. Sexual Medicine 5(1): e19-e30.
- Grand View Research (2025) China erectile dysfunction drugs market size & outlook.
- Cachay E, Mar Tang M, Mathews W C (2004) Screening for potentially transmitting sexual risk behaviors, urethral sexually transmitted infection, and sildenafil use among males entering care for HIV infection. AIDS Patient Care and STDs 18(6): 349-354.
- Harte C B, Meston C M (2012) Recreational use of erectile dysfunction medications and its adverse effects on erectile function in young healthy men: The mediating role of confidence in erectile ability. The Journal of Sexual Medicine 9(7): 1852-1859.
- Chauhan N S, Sharma V, Dixit V K, Thakur M (2014) A review on plants used for improvement of sexual performance and virility. BioMed Research International 2014: 868062.
- Li H, Jiang H, Liu J (2017) Traditional Chinese medical therapy for erectile dysfunction. Translational Andrology and Urology 6(2): 192-198.
- Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Ioakeimidis N, Rokkas K, Vasiliadou C, et al. (2006) Unfavourable endothelial and inflammatory state in erectile dysfunction patients with or without coronary artery disease. European Heart Journal 27(22): 2640-2648.
- Estrada Reyes R, Ortiz López P, Gutiérrez Ortíz J, Martínez Mota L (2009) Turnera diffusa Wild (Turneraceae) recovers sexual behavior in sexually exhausted males. Journal of Ethnopharmacology 123(3): 423-429.
- Cohen D, Gonzalez J, Goldstein I (2016) The role of pelvic floor muscles in male sexual dysfunction and pelvic pain. Sexual Medicine Reviews 4(1): 53-62.
- McCampbell KK, Wingert R A (2014) Renal stem cells: Fact or science fiction? Biochemical Journal 459(1): 41-51.
- Rihel J, Prober D A, Arvanites A, Lam K, Zimmerman S, et al. (2010). Zebrafish behavioral profiling links drugs to biological targets and rest/wake regulation. Science 327(5963): 348-351.
- Siegel A L (2014) Pelvic floor muscle training in males: Practical applications. Urology 84(1): 1-7.
- Wang Y, Li Z, Xu P, Li J (2021) A novel and high-throughput method for quantifying mating behavior in zebrafish. Biology of Reproduction 104(1): 208-217.
- Zhao J, Dasmahapatra A K, Khan S I, Khan I A (2008) Anti-aromatase activity of the constituents from damiana (Turnera diffusa). Journal of Ethnopharmacology 120(3): 387-393.
- Zhou J (2009) New understanding of the basic theory of traditional Chinese medicine. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine 15(1): 7-12.
- Zhou R, Yu X, Liao Y, Chen Z, Liang F, et al. (2020) Cyclophosphamide induced impairment of sperm and sexual function in zebrafish. Environmental Toxicology 35(4): 506-515.
- Cosyns J P (2003) Aristolochic acid and 'Chinese herbs nephropathy': A review of the evidence to date. Drug Safety 26(1): 33-48.
- Santen R J, Brodie H, Simpson E R, Siiteri P K, Brodie A, et al. (2009) History of aromatase: Saga of an important biological mediator and therapeutic target. Endocrine Reviews 30(4): 343-375.
- Dorey G, Speakman M, Feneley R, Swinkels A, Dunn C, et al. (2005) Randomised controlled trial of pelvic floor muscle exercises and manometric biofeedback for erectile dysfunction. British Journal of General Practice 55(517): 572-578.
- Lee J, Jang H, Park S, Kim H (2021) The heart-kidney axis in traditional Chinese medicine and the neuroendocrine mechanisms of sleep regulation. Integrative Medicine Research 10(Suppl.): 100677.
- Kokel D, Cheung C Y, Mills R, Coutinho Budd J, Huang L, et al. (2013) Rapid behavior-based identification of neuroactive small molecules in the zebrafish. Nature Chemical Biology 9(11): 716-724.
- Marshall A C (2020) Traditional Chinese medicine and clinical pharmacology. In M. H. G. G. (Ed.), Drug discovery and evaluation: Methods in clinical pharmacology. Springer International Publishing: 455-482.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.