Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Healthful, Eatable and Vitaminous Plant Species in the Area of Township Visoko
*Corresponding author: Alma Juko Mostic, Department of Biology, University of Sarajevo, Natural mathematics faculty, Bosnia and Herzegovina.
Received: December 13, 2019; Published: January 08, 2020
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2020.06.001085
Abstract
The aim of this research is to determine the significance of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species in meadow and forest ecosystems in the area of 232 km², Municipality of Visoko, Bosnia and Herzegovina in September, October and November 2016. The phases of field and laboratory studies were applied as well as the numerical classification methods and ordination of the ecosystem. Studies on the natural potentials of plant species with beneficial properties have shown that families of Asteraceae and Rosaceae occupy the most important places; the most prominent life-form are hemicryptophytes; the most common floristic element is Submediterranean; out of the total number of 261 plant species determined, 148 species have healing properties, 125 are edible and 80 plant species are vitaminous. We conclude that the natural resources of the researched area are not sufficiently used and known. It is necessary to undertake some activities to raise awareness and knowledge about natural potentials.
Keywords: Classification, Ecological system, Life form, Floristic elements, Visoko
Introduction
One of the most important issues today is the food shortage. According to the World Health Organization (WHO) estimation, more than one third of the human population suffers from hunger or severe malnutrition [1] . On the other hand, there has been an increase in the trend of food contamination by various types of toxic compounds (pesticides, fertilizers, all kinds of environmental pollutants) that affect human health. The wilderness in many parts of the world is rich in self-seeded, vitaminous plant species and herbs that could be a solid basis for solving these problems. Although these reserves are not an adequate basis for human nutrition, they could be an important source of supplementary food, as well as a dietary substitute for populations consuming unhealthy food daily [2] . Today, intensive research is being conducted all over the world with the aim of discovering the healing effects of different types of plants. In the world of limited financial resources, it is currently impossible to explore the biological activity of unexplored species’ compounds [3] .With about 6,340 different plant species, the Balkans, compared to 10,500 species accepted in Flora Europaea, is one of the most important centers of biodiversity in Europe. Despite its small area, Bosnia and Herzegovina has about 3,600 species of vascular plants. In accordance with the conditions of the external environment and the human influence on the territory of Bosnia and Herzegovina, there are many phytocenoses, which are typical only of certain regions and abundant with significant natural resources recognizable by their healing properties [4] .
Characteristics of the Area Explored
Municipality of Visoko is in central Bosnia, at the mouth of the Fojnica and Bosna rivers and it administratively belongs to the Zenica- Doboj Canton. The city is situated at 43° 59ˈ latitude N, at longitude 18° 10ˈ E. The municipality area reaches relatively low altitude ranges from 399 to 1050 m above sea level [5] . The mild continental climate is characterized by hot summers and cold winters with moderate amounts and precipitation ranges. The mountain climate is characterized by somewhat cooler and humid summer periods, while the winters are harsh with plentiful precipitation [6] .
Material and Methods
The research included two phases:
Phase 1: Field Research
Phase 2: Laboratory Research
Field Research Phase
Field research phase was conducted at various sites in the Municipality of Visoko area. The fieldwork was carried out in September, October and November 2016. 20 phytocenological recordings were analyzed, using the phytocenological method (Braun-Blanqet). After choosing the surface we determined the stratification: the layer of the trees up to 25 m, the layer of trees 5-10 m, the layer of trees and the rocks up to 5 m and the layer of the herbaceous plants.The analysis of forests and meadows was carried out, whereby 6 phytocenological recordings were analyzed in the phytocenosis of forests. The remaining 14 recordings were made in arable land, in orchards, beside the roads, rough grazing areas, pastures and meadows in populated places. The method of phytocenological recording included the following procedures:
a. Choosing the surface where the recording will take place
b. Determining the size of the selected surface,
c. Determining the structure of phytocenosis,
d. Collection of plant material.
Laboratory Research Phase
During the laboratory phase, the results of the fieldwork were synthesized in order to define the phytocenological position of the stands recorded. Laboratory research on the structure of plant communities in the area of Visoko took place through the following segments:
a. Making the herbarium
b. Determining the plant species
c. Sorting recordings
d. Preparing the synthetic table
After listing the plants in the table, the names of the plants were verified according to The Plant List. The data on medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species were attached in order to study the degree of their representation in the Municipality of Visoko area. The determination of medicinal, edible and vitaminous species in the investigated areas was based on the analysis of published scientific papers [7, 8, 9]. Also, by the analysis of the scientific papers, the folk names of plants were entered in the synthetic table and the literature such as [10, 11, 12] was used as well. For the analysis of life forms and floristic elements, classification according to [13] was used. Statistical data processing was carried out at the laboratory phase to determine the presence of useful plants. The analysis of spectrum of medicinal, edible and vitaminous species according to systematic position was conducted. The total number of plants from the aspect of healing, edible and vitaminous properties was determined. The analysis of life forms and floristic elements was conducted as well. Differentiation of habitat types according to the representation of useful plants was carried out, and the methods of numerical classification (cluster analysis) and ecological systems (CA) were applied.
Results and Discussion
Research on plants with healing, edible and vitaminous properties was carried out in the area of Visoko in September, October and November 2016 in the ecosystems of forests and meadows. 20 phytocenological recordings were analyzed, carried out at different localities, with 261 plant species determined, some of which are shown in (Figure 1a) (Figure 1b) (Figure 1c) (Figure 1d) .
The altitude ranged from 456 to 692 m and the size of the recording was 20 - 50 m². Coverage amounted to 20-100%. The geological substratum on all localities is consisted of conglomerates, sandstones, and marl (Conglomerates of Lašva). The type of soil at all sites is represented by the composite of rendzina, distric cambisol, stagnosol on flysch-like sediments.
The Spectrum of Medicinal, Edible and Vitaminous Plant Species by Systematic Classification
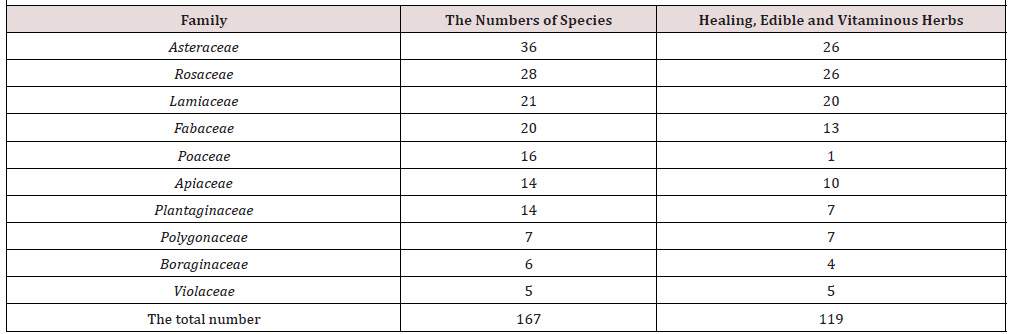
Based on the analysis conducted in forest and meadow ecosystems, in the Visoko Municipality area, 51 families with 261 plant species were determined. Of the total number, 46 families have medicinal, edible and/or vitaminous properties. Asteraceae and Rosaceae have the largest number of plants with beneficial herbs (26 plant species), then, Lamiaceae family with 20 plant species and the rest of the families shown in the table, Table 1. The smallest number of herbs with beneficial properties has Poaceae family with 1 plant species (Table 1).
The Spectrum of Representation of Medicinal, Edible and Vitaminous Plant Species According to Life-Form-
Based on the data presented graphically, Figure 2, the total number of plant species with established life- form is 247 of which 181 plant species with beneficial properties. The most prominent form of life is hemicryptophytes (H) with 109 species having beneficial properties. Phanerophytes (P) are following with 37 plant species, therophytes (T) with 15 species, geophytes (G) with 12 plant species. The least represented life-form are chamaephytes (Ch) with 8 species containing beneficial properties (Figure 2).
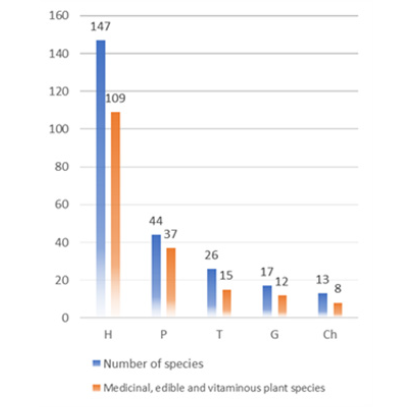
Figure 2: The representation of life-forms in medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species. *H – hemicryptophytes, P - phanerophytes, T – therophytes, G – geophytes, Ch – chamaephytes.
The Spectrum of Representation of Medicinal, Edible and Vitaminous Plant Species by Floristic Elements
on the data presented graphically in (Figure 3), the total number of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species with the determined floristic element is 172. The most widely used floristic element is smed with 52 plant species with beneficial properties. Then there is subatl with 31 species and eurassubozean with 20 plant species. Other flora elements with a small number of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species are presented graphically.
Differentiation of Habitat Types Based on The Representation of Healing, Edible and Vitaminous Species
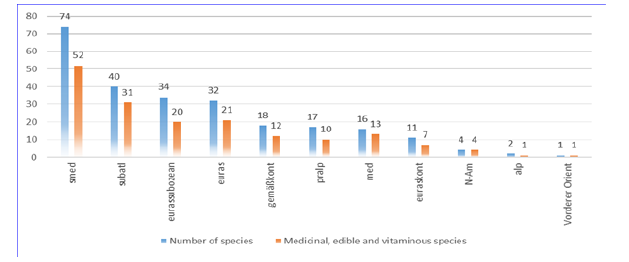
Figure 3: The representation of floristic elements in medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species.
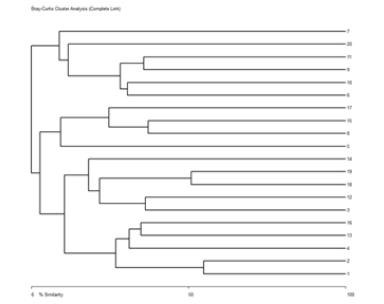
For the purpose of grouping vegetation and floristic data, methods of numerical classification, i.e. cluster analysis techniques were used. (Figure 4) shows the differentiation of the identified habitat types. The two main groups identified are forest (7, 20, 11, 9, 10, 6) and open ecosystems (all other localities). With the further differentiation we can classify open habitat type into three smaller groups: thermophilic meadows and carts terrains (16, 13, 4, 2, 1), tertiary ecosystems (14, 19, 18, 12, 3) and wet meadows (17,15, 8,5). Thus, the cluster analysis method yields the differentiation of habitat types in ecological groups, which are easily recognized in natural conditions (Figure 3)&(Figure 4).
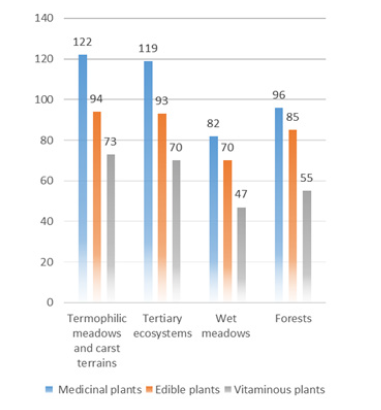
Figure 5: Comparative overview of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plants in forests and meadows ecosystems.
For the purpose of community differentiation within the gradient of ecological factors, the methods of ordination, i.e. the technique of correspondence analysis, were used. The analysis of the numerical representations of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species in the habitats of groups was carried out. The groups were identified by cluster analysis. In the habitats of thermophilic meadows and carts terrains the largest number of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species was found, (Figure 5) .
The Relation Between Medicinal, Edible and Vitaminous Plant Species in Different Habitat Types
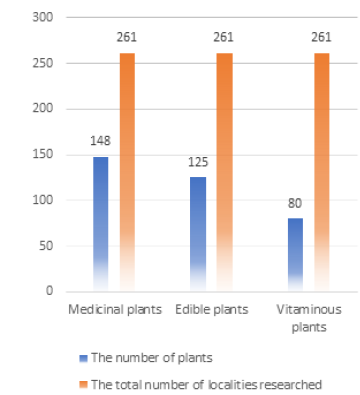
Figure 6: Comparative overview of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plants in different habitat types.
Based on the data presented in (Figure 6), we can determine the presence of natural potentials of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species in different habitat types in the Municipality of Visoko area. 20 phytocenological recordings were analyzed, with 261 plant species determined. Among them, the most common are medicinal plants with 148 plant species. These are followed by edible plants with 125 plant species. The least represented are vitaminous plants with 80 plant species (Figure 6).
Conclusion
The studies of the natural potentials of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species in different habitat types in Municipality of Visoko have demonstrated that:
a. Out of 51 families present, 46 families have healing, edible and / or vitaminous properties. It was found that families of Asteraceae and Rosaceae occupy the most significant places for these properties (with 26.
b. species). Twenty species from Lamiaceae family have these properties. The smallest number of useful species belongs to Poaceae family (1 out of 26 species).
c. The most represented life-form are hemicryptophytes, which have 109 medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species. A smaller number of species has a form of phanerophytes, therophytes and geophytes. The smallest number of species with useful properties (8) has a form of chamaephytes.
The most represented floristic element is Submediterranean, with 52 useful plant species. Subatlantic floristic element is also significantly
a. Present (31 plant species), while 29 species belong to Eurasian floristic element. The least represented are oriental and mountain species.
b. Based on the research carried out in different habitat types, it is found that of total number of 261 species, 148 species have healing properties, 125 are edible plants of 125 species. Vitaminous properties have 80 plant species.
c. The analysis clearly shows that the natural resources of the explored area are not sufficiently used and known. In this regard, it is necessary to undertake activities to raise awareness and knowledge about natural resources in the Municipality of Visoko area, but also about the possibilities of sustainable use of the recognized natural resources.
d. It is also necessary to undertake activities of documenting traditional local skills regarding the use of plant species, especially in folk medicine and nutrition.
e. From the aspect of preservation, it is necessary to udertake the active management of thermophilic meadows and carst ecosytems, where the largest number of medicinal, edible and vitaminous plant species was found.
References
- (1993) Second report on the world nutrition situation- volume 1: Global and regional results.
- Agrahar Murugkar, A Subbulakshmi G (2005) Nutritive values of wild edible fruits, berries, nuts, roots and species consumed by the Khasi tribes of India. Ecology Food and Nutrition 44(3): 207-223.
- Gillani A H, Rahman AU (2005) Trends in ethnopharmacology. J Ethnopharmacol 100(1-2):43-49.
- Redžić S (2007) The Ecological Aspect of Ethnobotany and Ethnopharmacology of Population in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Coll Antropol 31(3): 869-890.
- (2015) Development strategy of the Municipality of Visoko 2015-2021.
- (2016) FBIH Climate Atlas, Federal Meteorological Institute.
- Redžić S (2006) Wild edible plants and their traditional use in the human nutrition in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Ecology of Food and Nutrition 45(3): 189-232.
- Redžić S (2007) The Ecological Aspect of Ethnobotany and Ethnopharmacology of Population in Bosnia and Herzegovina. Coll Antropol 31(3): 869-890.
- Redžić S (2010) Use of Wild and Semi-Wild Edible Plants in Nutrition and Survival of People in 1430 Days of Siege of Sarajevo during the War in Bosnia and Herzegovina (1992-1995). Coll Antropol 34(2): 551-570.
- Tucakov J (1984) Herbs treatment, phytotherapy. Publishing work organization Rad Beograd.
- Pelagić V (1940) Pelagic's national teacher. Freedom Belgrade.
- Domac R (1989) Small flora of Croatia and neighboring areas. Schoolbook. Zagreb printing press, Zagreb.
- Oberdorfer E (1983) Plant sociological excursions flora. Eugen Ulmer asked. Stuttgart.







 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.