Case Report 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Sylvian Aqueductal Web/ Diaphragm-A Case Report and Short Review of Imaging Techniques
*Corresponding author: Chithra Ram, Department of Radiology, University of Louisville, USA.
Received: February 10, 2020; Published: February 19, 2020
ORCID: 0000-0003-2712-4225
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2020.07.001167
Abstract
Aqueductal Web/Diaphragm (AW/D) causing Aqueductal stenosis is a known but uncommon entity [1]. Appropriate diagnosis helps in prompt and adequate patient care. We present a case report of a 48 YOF who was evaluated for acute mental status changes with severe headaches. Regular CT images demonstrated obstructive hydrocephalus at the level of the Sylvian aqueduct. When an additional 10 minutes was spent on post processing using CT 3D Multiple Plane Reconstruction (MPR) function on a McKesson PACS radiology station, it showed an AW/D as the cause of obstructive hydrocephalus. As the patient was confused and couldn’t hold still, conventional MRI with 3D CISS sequince contained motion artifact, but still confirmed the finding.
Keywords: Aqueduct stenosis, Sylvian Aqueduct web, Sylvian Aqueduct diaphragm, Obstructive hydrocephalus, CISS-Constructive Interference in Steady State, CSF-Cisternography, McKesson PACS radiology station, Severe headaches, Neuroendoscopic aqueductoplasty, Visualizing cranial nerves
Abbreviations: AW/D: Aqueductal Web/ Diaphragm, YOF: Year-Old Female, CT: Computerized Tomography, MRI: Magnetic Resonance Imaging, CISS: Constructive Interference in Steady State, FIESTA: Fast Imaging Employing Steady State Acquisition, PACS: Picture Art-Chivying and Communication System
Case Report
48 YOF came to the ER with acute mental status changes, severe headaches, nausea and vomiting. She had no significant past medical history. Regular CT images demon started obstructive hydrocephalus at the level of the Sylvian aqueduct. CT 3D sagittal reconstruction images demonstrated an AW/D. Extra Ventricular Drain (EVD) was placed in the ER and patient was admitted. MRI of the brain was performed with an additional CISS 3d sequence in a 3T Siemens Vireo magnet[2]. Sagittal and coronal reconstruction CISS images clearly demonstrated and confirmed the AW/D. EVD was Removed and endoscopic third ventriculostomy was performed with placement of a vein- triculoperitoneal shunt.
Imaging
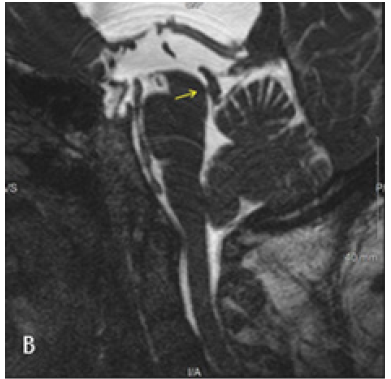
CT Brain was performed using a 128 slice Siemens Somtam Definition Edge scanner. Axial images were obtained with 5mm and 1mm slice thickness. Using the 3D MPR function on McKesson Radiology PACS station, reconstructions were performed. The sagittal reconstruction images demonstrated obstructive hydrocephalus with AW/D (Figure 1B).
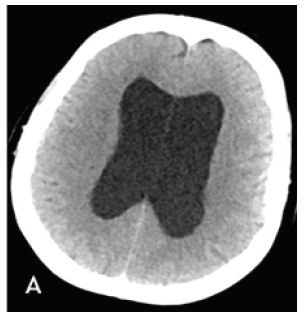
Figure 1A: Axial 1mm CT slices acquired on Siemens Somatom Definition Edge scanner. Dilated bilateral lateral ventricles.
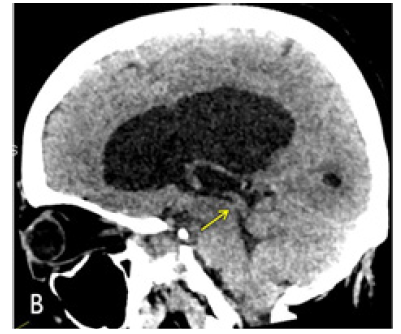
Figure 1B: Sagittal reconstruction from Axial 1 mm CT slices. Dilated lateral and third ventricles with normal appearing fourth ventricle. Yellow arrow points to the AW/D, best seen in this image 1B.
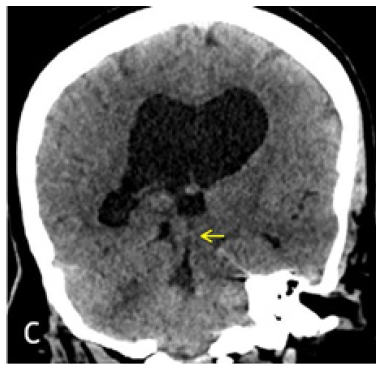
Figure 1C: Coronal reconstruction from Axial 1mm CT slices. Dilated lateral and third ventricles with normal appearing fourth ventricle. Yellow arrow points to the AW/D.
MRI brain was performed in a 3T Siemens Vireo magnet. The additional axial CISS 3D sequence was obtained with isotropic 0.6 x 0.6 x 0.6 voxels taking 7.18 minutes. Sagittal and Coronal reconstructions clearly demonstrated the AW/D Despite the Motion ArtiFact (Figure 2B) (Figure 2C).
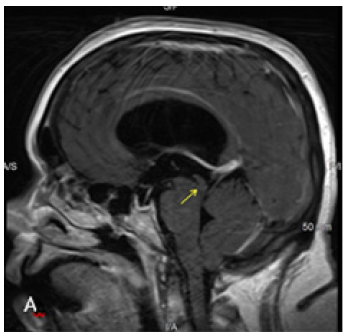
Figure 2A:Sagittal T1 post contrast sequence with 2640 TR, 9.4 TE. Dilated lateral and third ventricles with normal appearing fourth ventricle. Aqueduct is not clearly seen in the 4mm thick slice.
Discussion
An AW/D is a congenital abnormality. The web is a translucent membrane composed of ependymal cells and fibrillary neuroglia [3] . In patients with prior subarachnoid hemorrhages, the linear structure could represent adhesions. Recognition of this entity facilitates surgical resection and cure instead of longterm shunting with associated complications. Neuroendoscopic aqueductoplasty [4] can be considered for restoring physiologic CSF circulation in carefully selected patients with Aqueductal stenosis [5, 6]. The 3D-CISS (Constructive Interference in Steady State) sequence on Siemens and FIESTA C (modified FIESTA Fast Imaging Employing Steady State Acquisition) sequence on GE are similar pulse sequences [7] . Because of its high spatial resolution, high signal to noise ratio and better differentiation between CSF and brain parenchyma it’s the current sequence of choice for CSFCisternography, visualizing cranial nerves, cavernous sinuses, small extra-axial lesions and ventricular system [8] .
Due to perfectly balanced gradients, it has inherent flow compensations. 3D-CISS sequence in our study took 7.18 minutes for acquisition. It has no adverse effects of radiation or an invasive procedure. CSF cine flow study is also used to show the degree of obstruction along the CSF pathway in conditions like Arnold Chiari malformation and Aqueductal stenosis. Time-resolved 2D phase contrast technique with velocity encoding, which depends on location specific sequential application of a pair of phase encoding pulses in opposite directions, is predominantly used to acquire CSF flow studies. However, it does not demonstrate anatomy of the obstructive lesions clearly. In our case report, the CT sagittal reconstruction images post processed on a McKesson PACS itself, demonstrated the lesion clearly. MRI study confirmed the finding.In patients with contra indications for MRI, CT 3D MPR is a good alternative.
Conclusion
It is known that 3D MPR CT images and 3D-CISS (Constructive Interference in Steady State) sequence, demonstrate aqueduct web/diaphragm in patients in a reliable and reproducible way. If the patient cannot hold still, a shorter sagittal thin section T2 slice sequence can be considered. However, in patients who have contraindications to MRI, adequately reconstructed sagittal images from 1mm CT axial images can also be used effectively to demonstrate the lesion.
References
- Mcmillan JJ, Williams B (1977) Aqueduct stenosis. Case review and discussion. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 40(6): 521-532.
- Algin O, Hakyemez B, Parlak M (2010) Phase-contrast MRI and 3D-CISS versus contrast enhanced MR cisternography on the evaluation of the aqueduct stenosis. Neuroradiology 52: 99-108.
- Partington MD (2001) Congenital hydrocephalus. Neurosurg Clin N Am 12(4): 737-742.
- Schroeder HW, Gaab MR (1999) Endoscopic aqueductoplasty: technique and results. Neurosurgery 45(3): 508-518.
- Sankari SSE, Lehmann P, Jouet CG, Fichten A, Godefroy O, et al. (2009) Phase-contrast MR imaging support for the diagnosis of aqueductal stenosis. Am J Neuroradiol 30(1): 209-214.
- Miki T, Nakajima N, Wada J, Haraoka J (2005) Indications for neuroendoscopic aqueductoplasty without stenting for obstructive hydrocephalus due to aqueductal stenosis. Minim Invasive Neurosurg 48(3): 136-141.
- Parekh ND, Prabhu SP (2010) Aqueductal web causing obstructive hydrocephalus demonstrated on sagittal FIESTA sequence. Pediatric Radiology 40(1): 154.
- Hingwala D, Chatterjee S, Kesavadas C, Thomas B, Kapilamoorthy TR (2011) Applications of 3D CISS sequence for problem solving in neuroimaging. Indian J Radiol Imaging 21(2): 90-97.




 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.