Mini Review 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Targeting Cancer Through Autophagy With Β-Elemene and Puerarin
*Corresponding author: Bashir Ahmad, College of Basic Medical Science, Dalian Medical University, 116044 Dalian, China.
Received: February 02, 2020; Published: March 12, 2020
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2020.08.001237
Abstract
Cancer remains the second foremost cause of mortality around the world; therefore immediate development of highly effective and safe therapy is important. Different therapies are used for cancer treatment, but natural products (NPs) are considered more effective and less toxic. β-elemene (ELE) and Puerarin are the important NPs for the treatment of different cancers. Recently, its anticancer mechanisms through autophagy have been reported, therefore we summarized its molecular mechanisms. This review may serve as the basis for the future research on these NPs against cancer through autophagy.
Keywords: Natural products; β-elemene; Puerarin; Autophagy
Introduction
Cancer remains the second foremost cause of mortality around the world; therefore immediate development of highly effective and safe therapy is important [1,2]. Natural products (NPs) are used widely in the effective treatment due to high success rate and low toxicity [1]. The vital source of NPs are medicinal plants [3,4] and these NP can cure cancer through regulation of different pathways, including cell cycle, intrinsic and extrinsic apoptosis, oxidative stress, inflammation, MEK-ERK, NF-kB PI3K/AKT/mTOR and autophagy [3]. Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) consist of a large group of plant secondary metabolite, and belong to the C15 terpenoids group. SLs have shown various biological activities including antitumor and anti-inflammatory activities [4]. ELE is a wellknown sesquiterpene lactone possess anticancer activities against different cancers [5]. ELE is an approved NP from the Chinese Ministry of health for the treatment of cancer [1]. It is derived from Rhizoma zedoairae, which is a dry rhizome formed from Curcuma phaeocaulis, Curcuma wenyujin and Curcuma khwangsiensis [1]. In different cancers ELE induces death through apoptosis and autophagy. Here, we will discuss it autophagy mechanisms in cancer. The next important NP is Pue, derived from different plants, including Pueraria thomsonii Benthi, Pueraria tuberosa (wild) and Pueraria lobata (Wild) ohwi [3]. Pue is an approved NP from Chinese ministry of health in 1993 for the treatment of different diseases, but later was found to have anticancer activities [3]. Although cure cancer through different pathways but here we will discuss about autophagy which is the most recent targeted pathway in cancer.
Autophagy and Cancer
Autophagy is a metabolic process and it has been reported that, there is a genetic and functional link exist between cancer and autophagy, which reveal that the autophagy is a mechanism of tumor suppression. In autophagy, the cell contents are packed in autophagosome and then attached with lysosome to degrade and recycle the contents [6]. In cancer, the case is different, because it is not only death process, but also survival process during cellular stress [7,8]. Autophagy death and survival nature maybe related to the stage, sustaining and type of cancer, but different studies shows that the autophagy inhibition increases the rate of apoptosis [9,10]. It is obvious, in normal cells autophagy help in suppressing tumor growth, but as the tumor forms, this unbalance in autophagy help in tumor growth. As autophagy is a complex process and different pathways, including PI3K/MAPK, ERK/MAPK and other pathways play important role in its complexity [11]. Next, the autophagy protein 5 (atg-5) and light chain-3 (LC3) are the essential marker of autophagy [12]. The NP modulates autophagy in different diseases, including cancer [13].
Targeting Cancer Through Autophagy With ELE and PUE
ELE is SL compound and induces autophagy in a variety of cancer cells, including SGC7901, MGC803, A549, HepG-2, SPC-A-1/DDP and human breast cancer cells [14-18]. In molecular mechanisms, in these cells, ELE increase the LC3I conversion to LC3II, as a result Beclin1 become activated, Atg5-atg12 complex become formed, LC3 punctate dots formation start and lead to autophagy in these cells [14-18]. Further mechanisms are summarized in Figure 1A. Another important NP is Pue which induces autophagy in NCL-H441 cells through PI3K/Akt/ERK pathways via downregulation the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK, which was further inhibited by a PI3K/Akt inhibitor BEZ235. With further activation of PI3K/Akt pathways also increase the Atg5 activation but having no obvious effect on the conversion of LC3I to LC3II [19] as depicted in Figure 1B.
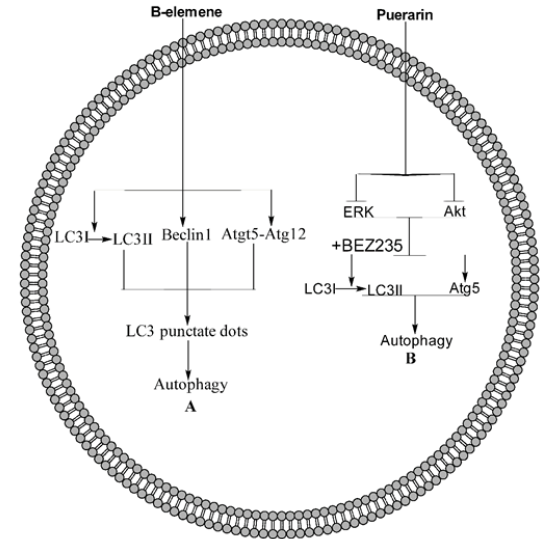
Figure 1: Molecular Mechanism of autophagy A) ELE increase the LC3I conversion to LC3II, as a result Beclin1 become activated, Atg5-atg12 complex become formed, LC3 punctate dots formation start and lead to autophagy in these cells. B) Pue which induces autophagy in through PI3K/Akt/ERK pathways via downregulation the phosphorylation of Akt and ERK, which was further inhibited by a PI3K/Akt inhibitor BEZ235. With further activation of PI3K/Akt pathways also increase the Atg5 activation but having no obvious effect on the conversion of LC3I to LC3II.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree to be published.
References
- Pengyu S AB, Bashir Ahmad, Zou Lijuan (2018) Natural β-Elemene:Advances in Targeting Cancer Through Different Molecular Pathways. North American Journal of Acedamic Research 1: 27.
- Ahmad B, Khan S, Nabi G, Gamallat Y, Su P, et al. (2019) Natural gypenosides: targeting cancer through different molecular pathways. Cancer management and research 11: 2287-2297.
- Ahmad B, Khan S, Liu Y, Xue M, Nabi G, et al. (2020) Molecular Mechanisms of Anticancer Activities of Puerarin. Cancer management and research 12: 79-90.
- Jalal S, Ahmad B, Zhang T, Guo L, Huang L, et al. (2020) SANTAMARINE: Mechanistic Studies on Multiple Diseases. Chem Biol Drug.
- Jiang Z, Jacob JA, Loganathachetti DS, Nainangu P, Chen B, et al. (2017) beta-Elemene: Mechanistic Studies on Cancer Cell Interaction and Its Chemosensitization Effect. Front Pharmacol 8:105.
- Sato K, Tsuchihara K, Fujii S, Sugiyama M, Goya T, et al. (2007) Autophagy is activated in colorectal cancer cells and contributes to the tolerance to nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res 67: 9677-9684.
- Hour TC, Chen J, Huang CY, Guan JY, Lu SH, et al. (2000) Characterization of chemoresistance mechanisms in a series of cisplatin-resistant transitional carcinoma cell lines. Anticancer research 20(5A): 3221-3225.
- Yu HJ, Tsai TC, Hsieh TS, Chiu TY (1992) Characterization of a newly established human bladder carcinoma cell line, NTUB1. Journal of the Formosan Medical Association 91(6): 608-613.
- Huang KH, Kuo KL, Ho IL, Chang HC, Chuang YT, et al. (2013) Celecoxib-induced cytotoxic effect is potentiated by inhibition of autophagy in human urothelial carcinoma cells. PloS One 8(12): e82034.
- Huang S, Sinicrope FA (2010) Celecoxib-induced apoptosis is enhanced by ABT-737 and by inhibition of autophagy in human colorectal cancer cells. Autophagy 6(2): 256-269.
- Liu L, Liao JZ, He XX, Li PY (2017) The role of autophagy in hepatocellular carcinoma: friend or foe. Oncotarget 8(34): 57707-577022.
- Arakawa S, Honda S, Yamaguchi H, Shimizu S (2017) Molecular mechanisms and physiological roles of Atg5/Atg7-independent alternative autophagy. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci 93(6): 378-385.
- Wang P, Zhu L, Sun D, Gan F, Gao S, et al. (2017) Natural products as modulator of autophagy with potential clinical prospects. Apoptosis 22(3): 325-356.
- Liu J, Zhang Y, Qu J, Xu L, Hou K, et al. (2011) beta-Elemene-induced autophagy protects human gastric cancer cells from undergoing apoptosis. BMC cancer 11:183.
- Liu J, Hu XJ, Jin B, Qu XJ, Hou KZ, et al. (2012) beta-Elemene induces apoptosis as well as protective autophagy in human non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 64: 146-153.
- Guan C, Liu W, Yue Y, Jin H, Wang X, et al. (2014) Inhibitory effect of beta-elemene on human breast cancer cells. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7(7): 3948-3956.
- Lin Y, Wang K, Hu C, Lin L, Qin S, et al. (2014) Elemene injection induced autophagy protects human hepatoma cancer cells from starvation and undergoing apoptosis. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 637528.
- Mu L, Wang T, Chen Y, Tang X, Yuan Y, et al. (2016) beta-Elemene enhances the efficacy of gefitinib on glioblastoma multiforme cells through the inhibition of the EGFR signaling pathway. Int J Oncol 49: 1427-1436
- Hu Y, Li X, Lin L, Liang S, Yan J, et al. (2018) Puerarin inhibits non-small cell lung cancer cell growth via the induction of apoptosis. Oncol Rep 39(4):1731-1738.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.