Mini Review 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Targeting Cancer through PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway with Selected Natural Products (β-Elemene, Puerarin and Gypenosides)
*Corresponding author: Bashir Ahmad, College of Basic Medical Science, Dalian Medical University, PR China.
Received: March 17, 2020; Published: April 20, 2020
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2020.08.001298
Abstract
The second foremost cause of mortality around the world is cancer; therefore correct therapy for its treatment is important. A number of therapies are in practice for the treatment of cancer, but the highly effective and less toxic treatments for cancer are natural products (NPs). These NPs cure the cancer through regulation of different pathways; such are PI3K/AKT/mTOR, NF-kB, autophagy, MEK-ERK, inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis. A group of natural product is sesquiterpene lactone (SLs) among which β-elemene (ELE) and Puerarin (Pue) are well known due to its anticancer activities. Other NPs, Gypenosides (Gyp) also possessed potent anticancer effect. Although these NPs have possess potential effect against cancer, but its anti-cancer mechanism through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway are need to be summarized. Therefore, we summarize it and hope this review will provide a baseline for further research on these compounds via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Keywords: Sesquiterpenelactone , β-elemene, Puerarin, Gypenosides
Introduction
The second foremost cause of mortality around the world is cancer; therefore correct therapy for its treatment is important [1,2]. The highly effective and less toxic treatment for cancer are natural products (NPs),[1] its vital source is medicinal plants [3,4]. These NPs cure the cancer through regulation of different pathways, such are PI3K/AKT/mTOR, NF-kB, autophagy, MEK-ERK, inflammation, oxidative stress and apoptosis [3]. A group of NPs is sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) and belong to the C15 terpenoids group. SLs possess different biological and pharmacological activities including antiinflammatory and anti-cancer [4].
Among SLs, ELE is well known due to its anti-cancer effect against a variety of cancers [5]. ELE is derived from Rhizoma Zedoaire, which is a dry rhizome consist of Curcuma phaeocaulis, Curcuma khangsiensis and Curcuma wenyujin. (1) It is approved by the Chinese ministry of health for cancer treatment [1]. In a variety of cancers, ELE induces apoptosis through different mechanism including PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Another important and approved NP from the Chinese Ministry of Health is Puerarin for the treatment of different diseases [3]. Pue is derived from a number of plants, such are Puerarialobata
(Wild) ohwi, Pueraria tuberosa (Wild) and Pueraria thomsonii Benthi [3]. Pue cure cancer through different mechanisms but here we will summarize its activities against cancer through PI3K/ AKT/mTOR pathway. Gypenosides (Gyp) are another group of triterpenesaponins, derived from Gynostemmapenthaphyllum (GpM), possess anticancer activities in vitro and in vivo. A number of clinical trials have also reported that the Gyp possess the potential effect against cancer [6]. The Gyp is popular folk medicine in China and used for the treatment of different diseases including, hepatitis [7], hyper-lipoproteinemia [8] and cardiovascular diseases [9]. Furthermore, in a number of cancer cell lines including, oral cancer SAS cells [10] SW620, [2,11] and cervical epidermoidcarcinoma cells have been reported [12]. Gyp inhibits the migration, invasion, metastasis, proliferation and induces apoptosis in a variety of cancers, including lung, hepatocellular, oral, colorectal and leukemic cancer through different mechanisms including PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [2].
PI3K/AKT/mTOR Pathway and Cancer
Phosphtidylinositol-3-Kinase, Protein Kinase B and mammalian Target-of-Rapamycin signaling pathway increases the cell growth and survival by different mechanisms [13,14]. A plethora of research has reported that, this pathway overexpressed in a variety of cancers [15-18]. For example, the AKT is activated, when its two residues including serine 473 (Sr 473) and threonine (Thr 308) become phosphorylated [19]. After activation, AKT enter into the nucleus, where they change the functions of transcription regulating factors. PI3K/AKT signaling increases the mTOR expression which leads to a poor prognosis. NPs reportedly inhibit the PI3K/AKT/ mTOR pathway in cancer cells [20] .The highly effective and less toxic treatment for cancer are natural products (NPs), [1] its vital source is medicinal plants [3,4] . These NPs cure the cancer through regulation of different pathways, including PI3K/AKT/mTOR [3].
Targeting cancer through Autophagy with ELE, PUE and Gyp
Phosphtidylinositol-3-Kinase, Protein Kinase B and mammalian Target-of-Rapamycin signaling pathway increases the cell growth and survival by different mechanisms [13,14]. Among NPs, ELE induces apoptosis in cancer cells through different mechanisms including PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. In different cancer cell lines including, FTC-133, human breast cancer cells (MDA-MB-468 and MCF-7) and human gastric cancer cells (SGC7901 and MGC803) ELE regulate the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway [21-24]. ELE regulate this pathway through inhibition of PI3K, which further inhibit AKT, mTOR and p70S6K1 respectively and lead the cells to apoptosis [21-24]. The effect of ELE on PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway is further summarized in Figure 1. Another, well know natural product is Pue [3] which induces apoptosis in different cancer cell lines including human-mental lymphoma Z138, [25] bladder cancer T24 and EJ cells through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. [25,26] In this pathway, Pue down-regulate PI3K [25], Akt [26], p-mTOR [26], and p-p70S6K [25,26]. This pathway is further summarized in Figure 1.
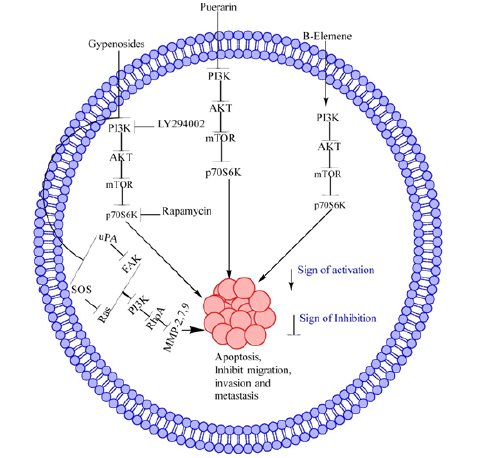
Figure 1: Anticancer effect of selected NP through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. ELE, Pue and Gyp target cancer through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. These NPs target PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through inhibition of PI3K, which further inhibit AKT, mTOR and p70S6K1 respectively and lead the cells toward apoptosis. Furthermore, Gyp target PI3/AKT/mTOR pathway through inhibition of son of seveless (SOS), RAS, uPA and FAK, which further inhibit PI3K and Rho-A. As a result, they inhibit MMP-2,7,9 and ultimately inhibit cell migration, metastasis and invasion.
Gyp is also a potential NP, inhibit the proliferation in a number of cell lines. Gyp inhibits the SCC-4, SAS and PDGF-induced rat hepatic cell proliferation through regulation of PI3/AKT/mTOR pathway via inhibition PI3K, AKT, and P70SK phosphorylation [10,27,28]. Next in SSC-4 and SAS cells, Gyp target PI3/AKT/mTOR pathway through inhibition of son of seveless (SOS), RAS, uPA and FAK, which further inhibit PI3K and Rho-A. As a result, they inhibit MMP-2,7,9 and ultimately inhibit cell migration, metastasis and invasion as shown in Figure 1 [10,28].
Conclusion
NPs play important role in cancer therapy through different mechanisms, including PI3/AKT/mTOR pathway. Among NPs, ELE, Pue and Gyp target cancer through PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. These NPs target PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway through inhibition of PI3K, which further inhibit AKT, mTOR and p70S6K1 respectively and lead the cells to apoptosis. Furthermore, Gyp target PI3/AKT/ mTOR pathway through inhibition of son of seveless (SOS), RAS, uPA and FAK, which further inhibit PI3K and Rho-A. As a result, they inhibit MMP-2,7,9 and ultimately inhibit cell migration, metastasis and invasion as shown in Figure 1.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Consent for Publication
All authors agree to be published.
References
- Pengyu S AB, Lijuan Z (2018) Natural β-Elemene:Advances in Targeting Cancer Through DifferentMolecular Pathways. North American Journal of Acedamic Research 1: 27.
- Ahmad B, Khan S, Nabi G, Gamallat Y, Su P, et al. (2019) Natural gypenosides: targeting cancer through different molecular pathways. Cancer management and research 11: 2287-2297.
- Ahmad B, Khan S, Liu Y, Xue M, Nabi G, et al. (2020) Molecular Mechanisms of Anticancer Activities of Puerarin. Cancer Manag Res 12: 79-90.
- Jalal S, Ahmad B, Zhang T, Guo L, Huang L, et al. (2020) SANTAMARINE: Mechanistic Studies on Multiple Diseases.
Chem Biol Drug Des 95(4): 427-434. - Jiang Z, Jacob JA, Loganathachetti DS, Nainangu P, Chen B, et al. (2017) Beta-Elemene: Mechanistic Studies on Cancer Cell Interaction and Its Chemosensitization Effect. Front Pharmacol 8: 105.
- Li Y, Lin W, Huang J, Xie Y, Ma W, et al. (2016) Anti-cancer effects of Gynostemma pentaphyllum (Thunb.) Makino (Jiaogulan). Chinese medicine 11: 43.
- Chen MH, Wang QF, Chen LG, Shee JJ, Chen JC, et al. (2009) The inhibitory effect of Gynostemma pentaphyllum on MCP-1 and type I procollagen expression in rat hepatic stellate cells. J Ethnopharmacol 126(1): 42-49.
- Yang YH, Yang J, Jiang QH (2013) Hypolipidemic effect of gypenosides in experimentally induced hypercholesterolemic rats. Lipids Health Dis 12: 154.
- Yu H, Guan Q, Guo L, Zhang H, Pang X, et al. (2016) Gypenosides alleviate myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury via attenuation of oxidative stress and preservation of mitochondrial function in rat heart. Cell Stress Chaperones 21(3): 429-437.
- Lu KW, Chen JC, Lai TY, Yang JS, Weng SW, et al. (2011) Gypenosides inhibits migration and invasion of human oral cancer SAS cells through the inhibition of matrix metalloproteinase-2 -9 and urokinase-plasminogen by ERK1/2 and NF-kappa B signaling pathways. Human & experimental toxicology 30: 406-415.
- Yan H, Wang X, Wang Y, Wang P, Xiao Y, et al. (2014) Antiproliferation and anti-migration induced by gypenosides in human colon cancer SW620 and esophageal cancer Eca-109 cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 33(5): 522-533.
- Chiu TH, Chen JC, Chung JG (2003) N-acetyltransferase is involved in gypenosides-induced N-acetylation of 2-aminofluorene and DNA adduct formation in human cervix epidermoid carcinoma cells (Ca Ski). In vivo 17: 281-288.
- Courtney KD, Corcoran RB, Engelman JA (2010) The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. Journal of clinical oncology: official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 28: 1075-1083.
- Steelman LS, Chappell WH, Abrams SL, Kempf RC, Long J, et al. (2011) Roles of the Raf/MEK/ERK and PI3K/PTEN/Akt/mTOR pathways in controlling growth and sensitivity to therapy-implications for cancer and aging. Aging 3: 192-222.
- Wong KK, Engelman JA, Cantley LC (2010) Targeting the PI3K signaling pathway in cancer. Current opinion in genetics & development 20: 87-90.
- Samuels Y, Wang Z, Bardelli A, Silliman N, Ptak J, et al. (2004) High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science (New York, N.Y.) 304(5670): 554.
- Samuels Y, Velculescu VE, (2004) Oncogenic mutations of PIK3CA in human cancers. Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) 3: 1221-124.
- Kang S, Denley A, Vanhaesebroeck B, Vogt PK (2006) Oncogenic transformation induced by the p110beta, -gamma, and -delta isoforms of class I phosphoinositide 3-kinase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103: 1289-1294.
- Vincent EE, Elder DJ, Thomas EC, Phillips L, Morgan C, et al. (2011) Akt phosphorylation on Thr308 but not on Ser473 correlates with Akt protein kinase activity in human non-small cell lung cancer. British journal of cancer 104: 1755-1761.
- Moselhy J, Srinivasan S, Ankem MK, Damodaran C (2015) Natural Products That Target Cancer Stem Cells. Anticancer Res 35: 5773-5788.
- Liu J, Zhang Y, Qu J, Xu L, Hou K, et al. (2011) beta-Elemene-induced autophagy protects human gastric cancer cells from undergoing apoptosis. BMC cancer 11: 183.
- Zou K, Tong E, Xu Y, Deng X, Zou L, et al. (2014) Down regulation of mammalian target of rapamycin decreases HIF-1alpha and survivin expression in anoxic lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell to elemene and/or irradiation. Tumour Biol: the journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 35(10): 9735-9741.
- Tong E, Xu Y, Li G, Zou K, Zou L, et al. (2013) The effects of beta-elemene on the expression of mTOR, HIF-1A, survivin in lung adenocarcinoma A549 cell. African journal of traditional, complementary, and alternative medicines : AJTCAM 10:18-23.
- Liu J, Hu XJ, Jin B, Qu XJ, Hou KZ, et al. (2012) beta-Elemene induces apoptosis as well as protective autophagy in human non-small-cell lung cancer A549 cells. J Pharm Pharmacol 64: 146-153.
- Gan M, Yin X (2015) Puerarin induced in mantle cell lymphoma apoptosis and its possible mechanisms involving multi-signaling pathway. Cell Biochem Biophys 71(1): 367-373.
- Jiang K, Chen H, Tang K, Guan W, Zhou H, et al. (2018) Puerarin inhibits bladder cancer cell proliferation through the mTOR/p70S6K signaling pathway. Oncology letters 15: 167-174.
- Chen MH, Chen SH, Wang QF, Chen JC, Chang DC, et al. (2008) The molecular mechanism of gypenosides-induced G1 growth arrest of rat hepatic stellate cells. J Ethnopharmacol 117: 309-317.
- Lu KW, Tsai ML, Chen JC, Hsu SC, Hsia TC, et al. (2008) Gypenosides inhibited invasion and migration of human tongue cancer SCC4 cells through down-regulation of NFkappaB and matrix metalloproteinase-9. Anticancer Res 28(2A): 1093-1099.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.