Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Ameliorative Effects of Dried and Germinated Fenugreek Seeds on Kidney Failure Induced by Gentamicin in Male Mice
*Corresponding author: Marwa M Darwish, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Egypt
Received: March 13, 2020; Published: August 12, 2020
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2020.09.001452
Abstract
Gentamicin is an aminoglycoside antibiotic widely used against Gram-negative microorganisms. Nephrotoxicity is the main limitation to its therapeutic efficacy. The aim of work was to investigate the role of dried and germinated fenugreek seeds as a potent antioxidant against the nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in the kidney. Male Swiss albino mice were divided into
- The animals were injected intraperitoneally with distilled water.
- The animals were intraperitoneally injected with gentamicin.
- The animals were orally received fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum)
- The animals were orally received germinated fenugreek.
- The animals were intraperitoneally injected with gentamicin simultaneously with fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum).
- The animals were intraperitoneally injected with gentamicin simultaneously with germinated fenugreek.
All the treatments of gentamicin were given as (100mg/kg) and all treatments of dried and germinated fenugreek were given as (500mg/kg) a single daily dose for five days. Physiological studies were investigated using by kidney function, oxidative stress and histopathological examination. Results showed Administration of gentamicin caused significant blood urea, serum creatinine, uric acid, glutathione s- transferases and Lipid peroxidase levels were raised significantly, while reduction of reduced glutathione, glutathione reductase, super oxide dismutase, and catalase as compared to control. Renal damage was confirmed with histopathological studies. The primary site of damage was the tubules especially proximal convoluted tubules. Co-administration of dried and germinated fenugreek along with gentamicin led to significant restoration of blood urea, uric acid, serum creatinine MDA, GSH, GR, GST, SOD, and CAT levels. We concluded that nephrotoxicity due to gentamicin is associated with oxidative stress. The primary site of damage was renal proximal convoluted tubules. Co-administration of dried and germinated fenugreek seeds along with gentamicin significantly prevented nephrotoxicity by virtue of its antioxidant effect.
Keywords: Gentamicin; Nephrotoxicity; Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum); Germinated fenugreek; Antioxidant Stresses; Mice
Abbreviations: BUN: Blood Urea Nitrogen; CAT: Catalase; SOD: Superoxide Dismutase; GPX: Glutathione Peroxidase; ROS: Reactive Oxygen Species; GST: Glutathione s- Transferases; MDA: Lipid Peroxidation; GR: Glutathione Reductase; MDA: Lipid Peroxidation; GR: Glutathione Reductase
Introduction
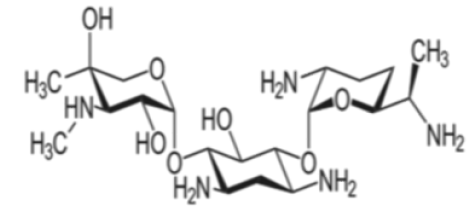
Aminoglycoside antibiotics are the most commonly used antibiotics in the treatment of gram-negative bacterial infections [1]. Gentamicin, (Figure 1) an aminoglycoside antibiotic known by its rapid bactericidal effect, a lower incidence of bacterial resistance than the other different antibiotics [2, 3]. One serious limitation to the use of this antibiotic is that it can cause ototoxicity and nephrotoxicity and up to 30% of patients treated with GM for more than 7 days show some signs of renal impairment [4]. Treatment of experimental animals with gentamicin produces apoptosis [5]. As well as necrosis [6]. Tubular epithelial cells in vivo and also in cultured cells [7]. Although the exact mechanism involved in GM induced nephrotoxicity is not elucidated completely, oxidative stress is considered as one of the key factors which play a central role in pathophysiology of GM-induced nephrotoxicity [8]. The accumulation of GM in renal proximal convoluted tubules was responsible for its nephrotoxicity and leads to network damage in brush border cells, reduction in glomerular filtration rate, acute tubular necrosis etc. [9]. Oxidative stress is responsible for the development of toxic free radicals, increased cellular Lipid peroxidation, insufficiency in cellular antioxidants and finally cellular necrosis in renal tubules. Nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin is a complex situation characterized by an increase in blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine concentration, tubular necrosis and also histological damage by reducing The activity of antioxidant enzymes such as catalase (CAT), superoxide dismutase(SOD), and glutathione peroxidase (GPX) in the kidneys [10,11].
In recent years, there has been a considerable interest in finding natural antioxidants from plant materials. The antioxidant phytochemicals from plants, particularly flavonoids and other polyphenols have been reported to inhibit the propagation of free radical reactions, to protect the human body from disease. Natural antioxidants show a comprehensive range of biochemical activities, including inhibition of ROS generation, direct or indirect free radicals scavenging activity, and changing intracellular redox potential [12]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) belongs to Fabaceae family; it was named, Trigonella, from Latin language that means ‘‘little triangle” due to its yellowish-white triangular flowers [13]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) is well known for its use as an edible species and spice herb, as well as medicinal plant because of its medicinal, nutraceutical, and pharmaceutical features [14]. It is considered as rich source of protein (25%), lysine (5.7 g/116 g N), soluble (20%) and insoluble (28%) dietary fibers, alkaloid (trigoneline) (36%), flavonoids like ornithine, viticsine and quercetin that have anti-cancer properties. In addition, the seeds of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) contain fix oil, essential nutrients (Calcium, iron and beta-carotene), as well as different steroid saponins such as diosgenin, ticogenine and neoticogenine [15]. Various components of the seeds have a varying steroidal sapogenin peptide ester has hypoglycemic properties. Plant phenolics are another component have potential health benefits mainly due to their antioxidant properties such as reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging and inhibition, electrophile scavenging and metal chelation [16]. Supplementation of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seed powder in the diet leads to a reduction in biomarkers of oxidative damage in alloxan-diabetic rats [17].
Number of studies regarding that fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) used as antibacterial [18], anticarcinogenic [19], antidiabetic [20], anti-inflammatory [21], and antioxidant [22]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) contains phenolic and flavonoid compounds which help to enhance its antioxidant capacity [23]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) been used in alleviating high oxidative damage [24]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) also tonifies kidneys without any side effects [25,26]. Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) has protective effect on lipid peroxidation and on enzymatic antioxidants. Compounds isolated from fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) have remarkable biological activities including protection against cancer, malaria, allergies, bacteria and viruses [27,28]. We aimed in this study to evaluate the antioxidant and beneficial effect of natural antioxidant plant used in our daily life fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seeds and germinated Fenugreek seeds on kidney failure caused by the effect of common antibiotic drug gentamicin in male Swiss albino mice.
Materials and Methods
Experimental Design
Experimental Animals: Thirty-six Male Swiss albino mice aged 9 -12 weeks and weighing 25-30gm. were used in this study. Animals were obtained from animal house of National Organization for Drug Control and Research (NODCAR) in Giza, Egypt. Animals were supplied with standard commercial diet pellets and water Ad-labium, kept in plastic cages for 7 days to be accommodated with our laboratory conditions before treatment. Animals were housed at room temperature (22-250C) and photoperiod of 12hrs. Light/dark cycle. The present experimental procedures were conducted, in accordance with the general international guide lines principles on the use of living laboratory animals in scientific research and approved by the Ethical Committee of Cairo University, Faculty of Sciences, Cairo, Egypt. (Reference number (CU/I/S/48/17).
Chemicals
Gentamicin: Gentamicin: Dose 100 mg/kg, ip for 5 days, as described in a standard protocol by [29].
Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum): Trigonella seeds, purchased from the local market Giza, Egypt were finely powdered to prepare solution according to [30].
Germinated Fenugreek: Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seeds were soaked in water and germinated for 24h. Then they were kept at 4°C for 2 days, dried in the shade and powdered. 1g powder was weighed and added to 10mL of distilled water. This solution was stirred on a magnetic stirrer for 1 h and for boiled aqueous extract the solution was boiled in a boiling water bath for 30min. These preparations corresponded to their use as natural remedies and in cooking. They were then centrifuged, and the supernatants were stored at -20°C until use [31].
Experimental Design
Thirty-six mice were equally divided into six groups (6 mice/group) as followed:
- Control Group: The animals were injected intraperitoneally with distilled water.
- Gentamicin Group: The animals were intraperitoneally injected with gentamicin (100 mg / kg body weight / day) for 5 days.
- Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) Group: the animals were orally received fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seed powder (500mg/kg body weight/day) for five days according to [32].
- Germinated Fenugreek Group: the animals were orally received germinated fenugreek seed powder (500mg/ kgbody weight/day) for five days.
- Gentamicin + Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) Group: The animals were daily intraperitoneally injected with gentamicin (100mg/kg body weight/day) for 5 days simultaneously withfenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seed powder (500mg/ kg body weight/day) for five days.
- Gentamicin + germinated Fenugreek Group: The animals were intraperitoneally injected with gentamicin (100mg / kg body weight / day) for 5 days simultaneously with germinated fenugreek seed powder (500mg/kg body weight/day) for five days.
Sampling
Serum Biochemistry: Blood samples were individually collected from rats of the different groups at the time of killing (24 hours after the last dose), left to coagulate at room temperature. The serum was separated by centrifugation using (universal 16), maintained at -40C and run at a speed of 10000rpm for 10 min. urea was determined using kits provided by Bio-diagnostic according [33]. Creatinine was determined using kits provided by Bio Med Diagnostics Company according to [34]. Uric acid was determined using kits provided by Vitro scient. According to [35] urea, creatinine and uric acid were expressed as (mg/dL).
Kidney: A known weight of the kidney tissue homogenates was prepared with 0.1M Tris-HCl buffer (pH4), and supernatant of homogenates was employed to estimate oxidative stress parameters glutathione s- transferases (GST) was determined according to [36]. Levels were expressed as (U/g.tissue), lipid peroxidation (MDA) was determined according to [37, 38]. Levels were expressed as (nmol/g.tissue), reduced glutathione (GSH) was determined according to [39]. Levels were expressed as (mg/g.tissue), glutathione reductase (GR) was determined according to [40]. Levels were expressed as (U/L) superoxide dismutase (SOD) was determined according to [41]. Levels were expressed as (U/g tissue) and catalase (CAT) was determined according to [42,43]. Levels were expressed as (U/g tissue) all antioxidant parameters were assayed using Biodiagnostic kits, Giza, Egypt. And were measured by a spectrophotometer (UV-Visible spectrophotometer, RIELE Photometer 5010 V5+)
Histological Evaluation: For light microscopic examinations, renal samples were fixed in 10% neutral buffered formalin. The tissue samples were embedded in paraffin. After being embedded in paraffin, several 5-μm-thick transverse sections were obtained from the kidney and stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological evaluation. All sections of kidney samples were examined for characteristic histological changes and another kidney section stained with Masson's trichrome stain. Masson trichrome is most useful to differentiate collagen from other fibers. All sections of kidney samples were examined for characteristic histological changes like kidney pathologies (glomerular fibrosis) or collagen deposition in kidney tissues.
Statistical Analysis
Statistical analyses were performed using a software program (SPSS version 23). The comparisons between groups were performed using one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey post hoc test. P< 0.05 was considered statistically significant. The results are presented in the form of mean+- standard error of the mean (SEM).
Results
Effects of Gentamicin Dried and Germinated Fenugreek Seeds Treatments on Levels of Kidney Function Parameters of Treated Mice
Table 1 showed that, the male mice treated with fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) alone or germinated fenugreek alone did not show any significant changes in all kidney function parameters that were measured in the serum, as compared with the control group (P>0.05). However, gentamicin treated mice showed a significant increase (P<0.001) in Urea, creatinine and uric acid levels compared with the control group. On the other hand, the co- administrations of gentamicin with fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) or with germinated fenugreek showed a significant decrease (P<0.001) in the creatinine level when compared with gentamicin group. But germinated fenugreek showed ameliorative effect in reduction of urea levels (P<0.001) than fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) (P=0.01) when compared with gentamicin group. Also germinated fenugreek showed ameliorative reduction in uric acid level (P<0.001) than Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum - graecum) (P=0.014).
Effect of Gentamicin, Dried and Germinated Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum -Graecum) Seeds on Oxidative Stress Parameters in Kidney of Treated Mice
Table 2 showed that, the male mice treated with fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) alone or germinated fenugreek alone did not show any significant changes in all oxidative stress parameters that were measured in the kidney, as compared with the control group. A significant increase in glutathione s- transferases (GST) and the lipid peroxidation (MDA) levels of gentamicin treated mice (P<0.001) compared with control group. But co- administrations of gentamicin with germinated fenugreek improved level of glutathione s- transferases (GST) and lipid peroxidation (MDA) levels down (P<0.001) compared with gentamicin group. While in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) group did not record any significance in levels of (GST) and (MDA) (P< 0.005). The data in table 2 indicated also significant decrease in kidney levels of glutathione reduced (GSH) glutathione reductase (GR), superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities in gentamicin group (P<0.001) compared with control group. Simultaneous treatment of germinated fenugreek caused significant ameliorative restoration in levels of (GSH), (GR) and (CAT) to their normal values (P<0.001) but the significance value of (SOD) was (P<0.005) compared with control group. On the other hand, simultaneous administration of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) along with gentamicin revealed a significant reduction in levels of (GSH), (GR), (SOD) and (CAT)(P=0.001, P<0.029, P<0.023 and P<0.001) respectively compared with the control group.
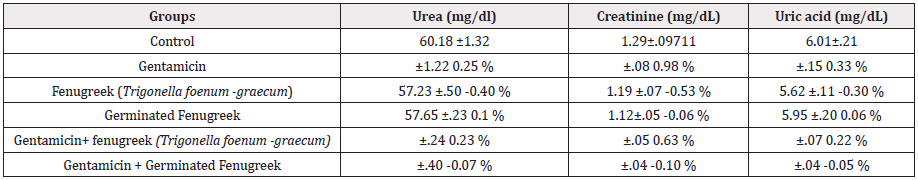
Table 1: Effects of dried and germinated fenugreek (Trigonella foenum- graecum) seeds on serum biochemical parameters of mice treated with gentamicin.
Note: Values were expressed as mean ± SD., the significance level is expressed as; b: P<0.01, d: P<0.001 and number of each group=6.
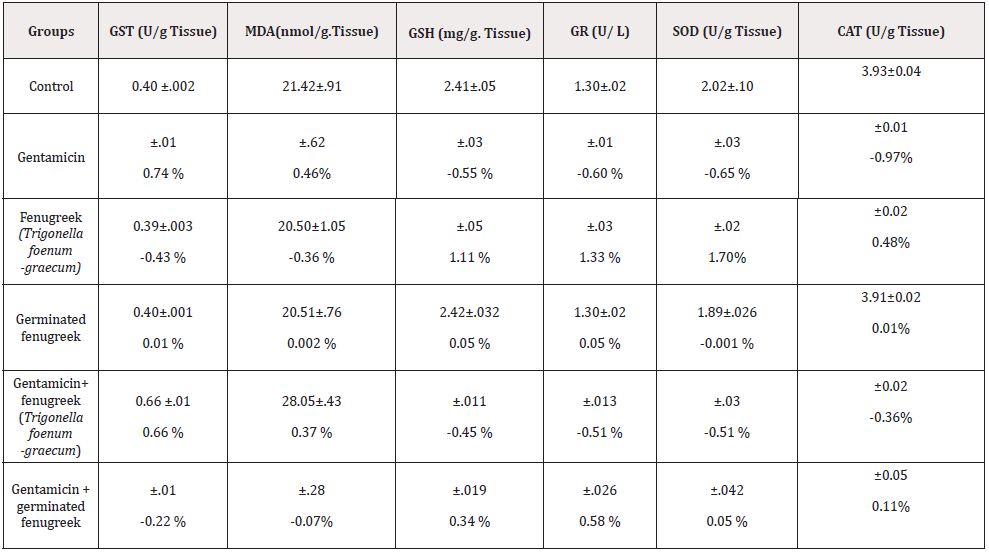
Table 2: effects of dried and germinated fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seeds on renal antioxidant activity of mice treated with gentamicin.
Note: Values were expressed as mean ± SD., the significance level is expressed as; a: P<0.05, c: P<0.005, d: P<0.001 and number of each group = 6
Histopathological Examination
Haematoxylin and Eosin stain
Control Group: Histopathologic examination of kidney showed that there were no pathologic findings in control group (Figure 2a).
Gentamicin Group: After administration of gentamicin revealed variable degrees of pathological alterations they were severe aggregations of inflammatory cells in the interstitial tissues, segmented glomerular tuft also showed hyaline casts in the lumen of renal tubule and hemosiderin deposited. Wide areas of diffused extravasated (RBCs) of the epithelial cells lining some renal tubules. were observed. In addition to Bowman's space filled with a cellular eosinophilic material (Figure 2b).
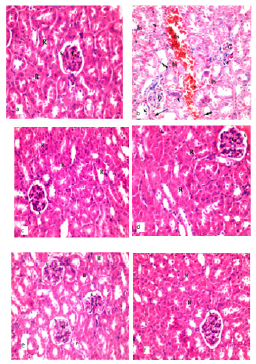
Figure 2: Photomicrographs of kidney sections of mice stained with hematoxylin and eosin. a) Control group showing normal appearance of renal tubules (R) and glomerulus (G). b) Gentamicin group showing Bowman’s space filled with a cellular eosinophilic material (arrow), pyknotic nuclei (two arrow head), Vacuolation cytoplasm (arrow head) and diffused extravasated RBCs (bs), c) Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) group showing normal histological structure of glomerular tuft (G) with Bowman’s space (S) and intact renal tubules (R). d) Germinated fenugreek group showing intact glomerular tuft (G) with good sized Bowman’s space (S). e) Gentamicin + Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) group showing glomerular tuft (g) still showed mild to moderate reduction in size, moderate degenerative changes in epithelial cells lining few renal tubules (r) and f) Gentamicin+germinated fenugreek group showing return normal histological structures of the glomerular tuft (G) bowman’s space (S) and intact renal tubules (R). (H&E 400x)
Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum -Graecum) Group Only and Germinated Fenugreek Only Group: Normal appearance of kidney tissues of these groups (Figures 2c-2d).
Gentamicin+Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) Group: Showed most glomerular tuft, bowman's space and renal tubules within normal appearance, but others glomerular tuft still showed mild to moderate reduction in size, and mild dilated bowman's space, moderate degenerative changes in epithelial cells lining of few renal tubules so, there a reduction in pathogenic changes when compared with control group (Figure 2e).
Gentamicin Group + Germinated Fenugreek Group: Showed return of normal histological structures of glomerular tuft with normal sized bowman's space and normal appearance of renal tubules so the degenerations were recovered in the kidney by germinated fenugreek administration (Figure 2f).
Masson Trichrome Stain: The degree of renal fibrosis was determined by Masson.
- Control Group: Control group showed normal distribution of collagen fibers, in the glomerulus and renal tubules.
- Gentamicin Group: Gentamicin group showed increases in collagen deposition in interstitial tissues, artery and brush border of the epithelial cells lining renal tubules (Figures 3a&3b).
- Fenugreek (Trigonella Foenum- Graecum) Only Group and Germinated Fenugreek Only Groups: Showed no fibrosis (Figures 3c-3d).
- Gentamicin+fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) group: Showed moderate collagen deposition in interstitial tissues. The damage to the kidney tissue was minimal (Figures 3e&3f).
- Gentamicin + Germinated Fenugreek Group: Showed normal distribution of collagen fibers in the glomeruli, and around the tubules.
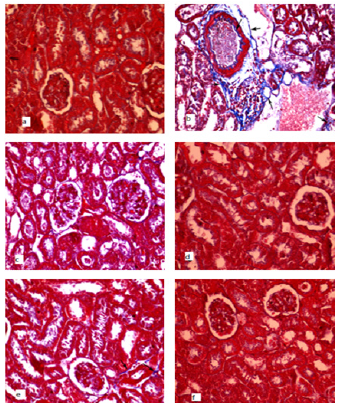
Figure 3: Photomicrographs of kidney sections of mice stained with Masson’s trichrome 400x a)Control group showed normal distribution of collagen fibers in the glomerulus and renal tubules. b)Gentamicin group showed increases in collagen deposition in interstitial tissues, artery and brush border of the epithelial cells lining renal tubules (arrow). c)Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) group showed no fibrosis. d)Germinated fenugreek group showed no fibrosis. e)Gentamicin + fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) group showed moderate collagen deposition in interstitial tissues (arrow) in some areas still seen And f)Gentamicin +germinated fenugreek group showed normal distribution of collagen fibers in the glomeruli and surrounding the tubules.
Discussion
The Kidney is very sensitive to the adverse effects of drugs and chemicals. Walker and Duggin [44] proved that even low concentrations of any chemical or its metabolites could generate a certain degree of nephrotoxicity. Acute kidney injury (AKI) is a major kidney disease characterized by rapid loss of renal function, resulting in accumulation of metabolic waste and imbalanced electrolytes and bodily fluid [45] we aimed in our experiment to observe the nephrotoxic effect of gentamicin on kidney which caused reduction in the renal function, oxidative stress and also histopathologic changes in kidney tissues. and to detect the potential protective role of dried and germinated fenugreek seeds against these lesions, in order to gain new insights into the treatment modality of gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Gentamicin is an effective and widely used antibiotic against serious and life-threatening infections caused by gram-negative aerobes in clinical practice [46]. Gentamicin is the most common nephrotoxic aminoglycoside [47]. A relationship between nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress has been detected by many investigations.
The impairment in kidney functions was accompanied by either increase in serum creatinine and urea levels or kidney tissue MDA levels that indicated lipid peroxidation [48,49]. In addition, uric acid might be a true mediator of renal disease and progression [50,51] Was also observed in one earlier study that gentamicin caused a significant decrease in GSH, SOD, catalase and GST levels in the kidney tissue. In present study, Gentamicin administration at the dose of 100 mg/kg (I.p.) for 5 consecutive days produced a significant increase of urea, creatinine, uric acid, MDA, GST levels and significantly decreased levels of reduced glutathione, glutathione reductase, superoxide dismutase, and catalase as compared to control. Because of the obvious responsibility of ROS in GEN induced renal damage, several antioxidant agents have been used to prevent GEN nephrotoxicity [52]. in present study we used dried and germinated fenugreek seeds which considered a potent antioxidant agent, like other studies confirmed that fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) is a well-known plant in traditional medicine and although all related research was limited to its antidiabetic and hypocholesterolemic effects, it has been found recently that the secondary metabolites of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seeds have a powerful antioxidant and antiradicalaire capacity in vivo and in vitro [53,54]. against oxidative stress induced by several toxins [55-57]. A central aspect of gentamicin nephrotoxicity is its tubular effect, which may range from a mere loss of the brush border in epithelial cells to an overt tubular necrosis [58]. The microscopic observation of the kidneys of control group in our study showed a normal morphology of renal glomeruli and tubules. On the other hand, gentamicin group showed tubular necrosis increased bowman's capsule space and glomeruli atrophy.
And also Masson stain showed increase in collagen deposition in interstitial tissues, artery and brush border of the epithelial cells lining renal tubules. The specificity of gentamicin for renal toxicity is apparently related to its preferential accumulation in the renal proximal convoluted tubules (50 to 100 times greater than serum) and gentamicin's effect on biological membranes appears to be critical in the pathogenetic sequence [59]. These histopathognic alteration restored by administration of germinated fenugreek more obviously than fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum). These findings correspond with [60] who reported concomitant increase in antioxidant activity of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) seeds with germination due to increase in phenolic content. Our results disagreed with [61-63] who found GEN-induced nephrotoxicity is characterized by direct tubular necrosis, without morphological changes in glomerular structures. But our results illustrated that some lobulated atrophy in the glomerular tufts.
Conclusion
we concluded that gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity. Its administration induced several histological lesions, reduced antioxidant markers as well as elevated oxidative stress in the kidney tissues. The treatment with germinated fenugreek more effective than fenugreek (Trigonella foenum -graecum) in the contract the histopathological changes, and restored antioxidant / oxidant balance kidney tissue induced by gentamicin.
Acknowledgements
The completion of this research wouldn’t have been possible without the unconditional help and support of many people. Thus I would like to express my gratitude to: Dr. Hanan Salah Ebead Associated professor, Department of Zoology, Faculty of Science, Cairo University. Sahar Mohamed Ibrahim Mohamed Lecturer assistant, center of the basic science, Misr University for Science and Technology.
References
- Aygün FÖ, Akçam, FZ, Kaya O, Ceyhan BM, Sütçü, R (2012) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester modulates gentamicin-induced oxidative nephrotoxicity in kidney of rats. Biological trace element research 145(2): 211-216.
- Martinez Salgado C, FJ Lopez Hernandez, JM Lopez Novoa, (2007) Glomerular nephrotoxicity of aminoglycosides. Toxicol Applied Pharmacol 223(1): 86-98.
- Ali BH, M Al Za'abi, G Blunden, A Nemmar (2011) Experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity and agents that modify it: A mini-review of recent research. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 109(4): 225-232.
- Ali BH (2003) Agents ameliorating or augmenting experimental gentamicin nephrotoxicity: some recent research Food ChemToxicol 41(11): 1447-1452.
- Li J, Li Q X, Xie XF, Ao Y, Tie CR, Song RJ (2009a) Differential roles of dihydropyridine calcium antagonist nifedipine, nitrendipine and amlodipine on gentamicin-induced renal tubular toxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 620(1): 97-104.
- Edwards JR, Diamantakos EA, Peuler JD, Lamar PC, Prozialeck WC (2007) A novel method for the cellular necrosis in the cellular necrosis in the evaluation of proximal tubule epithelial intact rat kidney using ethidium homodimer. BMC Physiol 7:1.
- Pessoa EA, Convento MB, Silva RG, Oliveira AS, Borges FT, et al. (2009) Gentamicin induced preconditioning of proximal tubular LLC-PK1 cells stimulates nitric oxide production but not the synthesis of heat shock protein. Braz J Med Biol Res 42(7): 614-620.
- M Tavafi, H Ahmadvand, P Toolabi (2012) Inhibitory effect of olive leaf extract on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Iran J Kidney Dis 6(1): 25-32.
- P Randjelovic, S Veljkovic, N Stojiljkovic, L Velickovic, D Sokolovic, et al. (2012) Protective effect of selenium on gentamicin-induced oxidative stress and nephrotoxicity in rats, Drug Chem Toxicol 35(2): 141-148.
- Parlakpinar H, Tasdemir S, Polat A (2005) Protective role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) on gentamycin-induced acute renal toxicity in rats. Toxicology 207(2): 169-177.
- El-Razek FHA, Kamel EA (2011) Ameliorative effect of POMENGRANATE peel water extract against folic acid-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int J Acad Res 3(4): 554-559.
- Sharma HK, Gogoi B, Nainwal LM (2016) A review on some antioxidant plant species growing in North East India 37(1): 224-229.
- Flammang A, Cifone M, Erexson G, Stankowski L (2004) Genotoxicity testing of a fenugreek extract. Food Chem Toxicol 42(11): 1769-1775.
- Acharya SN, Thomas JE, Basu SK (2008) Fenugreek an alternative crop for semiarid regions of North America. Crop Sci 48(3): 841–853.
- Hanafy, Rania, Akladious, Samia (2018) Physiological and molecular studies on the effect of gamma radiation in fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum L.) plants. Journal of Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology 16(2): 683-692.
- Mullaicharam AR, Geetali Deori, Uma Maheswari R (2013) Medicinal Values of Fenugreek- A Review Research Journal of Pharmaceutical, Biological and Chemical Sciences 4(1): 1304-1313.
- Anuradha CV, Ravikumar P (2001) Restoration on tissue antioxidants by fenugreek seeds (Trigonella Foenum Graecum) in alloxan-diabetic rats Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 45(4): 408-420.
- Alkofahi A, Batshoun R, Owais W, Najib N (1996) Biological activity of some Jordanian medicinal plant extracts. Fitoterapia 67(5): 435-442.
- Shabbeer S, Sobolewski M, Kachhap S, Hidalgo M, Jimeno A, et al. (2009) Fenugreek : a naturally occurring edible spice as an anticancer agent. Cancer Biol Ther 8(3): 272-278.
- Victoria V Konopelniuk, Ievgenii I Goloborodko, Tetyana V Ishchuk, Tetyana B Synelnyk, Ludmila I Ostapchenko, Mykola Ya Spivak, Rostyslav V Bubnov EPMA J 8(4): 377-390.
- Piao CH, Bui TT, Song CH, Shin HS, Shon DH, Chai OH (2017) Trigonella foenum-graecum alleviates airway inflammation of allergic asthma in ovalbumin-induced mouse model. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 482(4): 1284-1288.
- Ktari N, Feki A, Trabeisi I, Tirik M, Hana M, et al. (2017) Structure, functional and antioxidant properties in Tunisian beefsausage of a novel polysaccharide from Trigonella foenum-graecum Int J BiolMacromol 98: 169-181.
- Dixit P, Ghaskadbi S, Mohan H, Devasagayam TP (2005) Antioxidant properties of germinated fenugreek seeds. Phytother Res 19(11): 977-983.
- S Kaviarasan GH, Naik R, Gangabhagirathi, CV Anuradha, KI Priyadarsini (2007) In vitro studies on antiradical and antioxidant activities of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seeds. Food Chemistry 103(1): 31-37.
- Sharma RD, Sarkar A, Hazra DK, Misra B, Singh JB, et al. (1996) Toxicological evaluation of fenugreek seeds: a long term feeding experiment in diabetic patients. Phytother. Res. 10(6): 519-520.
- Warrier PK, Nambiar VPK, Ramankutty C, (1995) Indian Medicinal Plants. eds13; Orient Longman. New York, India.
- Bhatia, K., Kaur, M., Atif, F., Ali, M., Rehman, H., Rahman, S., (2006) Aqueous extract of ameliorates additive urotoxicity of buthioninesulfoximine and cyclophosphamide in mice. Food Chem Toxicol 44(10): 1744-1750.
- Naidu MM, Shyamala B, Naik JP, Sulochanamma G, Srinivas P (2011) Chemical composition and antioxidant activity of the husk and endosperm of fenugreek LWT-Food Sci Techno 44(2): 451-456.
- Amrit Pal Singh, Arunachalam Muthuraman, Amteshwar Singh Jaggil, Nirmal Singh, Kuldeep Grover, et al. (2012) Animal models of acute renal failure. Pharmacological Reports 64(1): 31-44.
- Seema Z (2014) Protective effect of Fenugreek on thioacetamide induced hepatotoxicity in rats. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 21(2): 139-145.
- Priyanjali Dixit, Saroj Ghaskadbi, Hari Mohan, Thomas PA Devasagayam (2005) Antioxidant Properties of Germinated Fenugreek Seeds. Phytotherapy Research19(11): 977-983.
- Pallavi Deshpande, Vishwaraman Mohan, Prasad Thakurdesai (2016) Preclinical Safety Evaluation of Low Molecular Weight Galactomannans Based Standardized Fenugreek Seeds Extract 15: 446-459.
- Fawcett JK, Scott JE (1960) J Clin Path 13(2): 156-159.
- Young DS (1975) Clin Chem 21(286).
- Young Ds (1990) Effects of Drugs on Clinical Laboratory Tests. (3rd Edn) 3: 6-12.
- Habig W, Pabst M Jakoby WJ (1974) Biol Chem 249(22): 7130-7139.
- Satoh K (1978) Clinica Chimica Acta 15 90(1): 37-43.
- Ohkawa H, Ohishi W, Yagi K Anal (1979) Biochem 95(2): 351-358.
- Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly MB J (1963) Lab Clin Med 61: 882-888.
- Goldberg DM, Spooner RJ, Verlog Chemie, Deerfiled Beach (1983) in Methods of Enzymatic Analysis (Bergmeyer HV Eds) (3rd Edn) 3: 258-265.
- Nishikimi M, Roa NA, Yogi K (1972) Biochem Bioph Res Common 46(2): 849-854.
- Aebi H (1984) Methods Enzymol 105: 121-126.
- Fossati P (1980) Clin Chem 26: 227- 231.
- Walker RJ, Duggin GG (1992) Cellular mechanism of drug nephrotoxicity. In: The Kidney: Physiology and Pathophysiology. Seldin, DW, Giebisch G (Eds) pp. 3571-3595. Raven Press, USA.
- Jiang, M et al. (2012) Autophagy in proximal tubules protects against acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 82(12): 1271-1283 .
- Bledsoe G, Crickman S, Mao J, Xia C, Murakami H, et al. (2006) Kallikrein/kinin protects against gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity by inhibition of inflammation and apoptosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21(3): 624-633.
- Luft FC, Bloch R, Sloan RS, YumMN, Costello R, Maxwell DR (1978) Comparative nephrotoxicity of aminoglycoside antibiotics in rats. J Infect Dis 138(4): 541-545.
- Atessahin A, Yilmaz S, Karahan I, Ceribasi AO, Aziz Karaoglu (2005) Effects of lycopene against cisplatin-induce nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Toxicology 212 (2): 116-123.
- Salvatore Cuzzocrea, Emanuela Mazzon, Laura Dugo, Ivana Serraino, Rosanna Di Paola, et al. (2002) A role for superoxide in gentamicin-mediated nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 450(1): 67-76.
- Kang DH, Nakagawa T, Feng L, Watanabe S, Han L, et al. (2002) A role for uric acid in the progression of renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol13(12): 2888-2897.
- Ozbek E, Turkoz Y, Sahna E, Ozugurlu F, Mizrak B, et al. (2000) Melatonin administration prevents the nephrotoxicity induced by gentamicin BJU Int 85(6): 742-746.
- Simmons CF Jr, Bogusky RT, Humes HD (1980) Inhibitory effects of gentamicin on renal mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 214(3): 709-715.
- S Kaviarasan, CV Anuradha (2007) Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seed polyphenols protect liver from alcohol toxicity: a role on hepatic detoxification system and apoptosis. Pharmazie 62(41) 299-304.
- S Kaviarasan (2006) Fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seed extract prevents ethanol-induced toxicity and apoptosis in chang liver cells. Alcohol 41(3): 267-273.
- Y Belaïd-Nouira, H Bakhta, Z Haouas, I Flehi Slim, H Ben Cheikh (2013) Fenugreek seeds reduce aluminum toxicity associated with renal failure in rats. Nutr Res Pract 7(6): 466-474.
- MO Albasha, ESA Azab, (2014) Effect of cadmium on the liver and amelioration by aqueous extracts of Fenugreek seeds, rosemary, and cinnamon in Guinea pigs: histological and biochemical study, Cell Biol 2(2): 34-44.
- S Kaviarasan, R Sundarapandiyan, CV Anuradha (2008) Protective action of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum graecum) seed polyphenols against alcohol-induced protein and lipid damage in rat liver. Cell Bio Toxicol 24(5): 391-400.
- Yaremi Quiros, Laura Vicente-Vicente, Ana I Morales, José M López-Novoa, Francisco J López-Hernández (2011) An Integrative Overview on the Mechanisms Underlying the Renal Tubular Cytotoxicity of Gentamicin, Toxicological Sciences 119(2): 245-256.
- Humes HD Weinberg Jhl: Toxic Nephropathies. In: BM Brennar, J Rector FC (Eds.): The Kidney, 2, 3‘d. Philadelphia WB Saunders Company pp. 1491-1532.
- Pandey H, Awasthi P (2013) Effect of processing techniques on nutritional composition and antioxidant activity of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graceum) seed flour. Journal of Food Science and Technology 52(2):1054-1060.
- Cuzzocrea S, Mazzon E, Dugo L, Serraino I, Di Paola R, et al. (2002) A role for superoxide in gentamicin-mediated nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 450(1): 67-76.
- Eisenberg JM, Koffer H, Glick HA, Connell ML, Loss LE, et al. (1987) What is the cost of nephrotoxicity associated with aminoglycosides? Ann Intern Med 107(6): 900-909.
- Pedraza Chaverri J, Gonzalez Orozco AE, Maldonado PD, Barrera D, Medina Campos ON, et al. (2003) Diallyl disulfide ameliorates gentamicin-induced oxidative stress and nephropathy in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 473 (1): 71-78.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.