Mini Review 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Protective Effect of Medicinal Plants on Neuron Degeneration Diseases and Controversial Predictive Diagnosis
*Corresponding author: Mahmoud M Elalfy, Forensic Medicine and Toxicology, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Mansoura University, Egypt.
Received: April 03, 2019; Published: April 23, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.02.000599
Abstract
Neuron degenerations resulted from chronic exposure of chemicals, environmental pollutions, drugs and pesticides. Many diseases of neuron degenerations prediction still so difficult as it occurs in advanced age in animal or human and even advanced technology and recent trial of biomarkers for diagnosis of neuron degenerations still controversial. Protective herbal plants help in prevention of neuron degeneration diseases or delay its occurrence through antioxidant mechanisms. Recently, tau and tubulin protein expression could explore the future occurrence of neurogenerative diseases in human.
Keywords: Neuron Degeneration, Biomarkers, Albino Rats
Introduction
Neuron degenerative diseases are more common in developed and developing countries and occur all over the world due to death of neurons [1-3]. The incidence of neuro-degenerative diseases expected to increase nearly 131.5 million in 2050 [1,2].
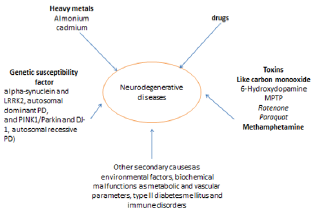
The etiological causes of neuron degenerative diseases were varied from heavy metals exposure like ammonium [4] drugs [5] or genetic susceptibility [6] and toxic agent like carbon monoxide [3]. Also, the scientist is investigating different possible causes of secondary neuron degeneration resulting from environmental factors, biochemical malfunctions as metabolic and vascular parameters, type II diabetes mellitus and immune disorders [7] (Figure 1).
The mechanism of neuron degeneration still obscure even there is one accepted theory about neurotoxicity of Acetylcholinesterase that may play a role in the development of neuronal degeneration observed in Alzheimer’s disease [8] and evidence by potential role of cholinesterase inhibitor (ChI) in improvement of cognitive function and decrease the risk of falls in patients with parkinsonism [9].
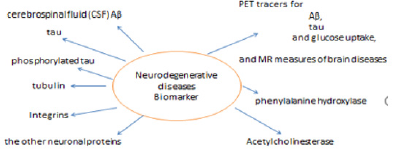
The incidence of neurodegenerative disease varied between individuals and there is no predictive measurable parameter except some trail about serum biomarkers like tau protein [10]. Also, integrins are play important role pathophysiology of many brain diseases, such as epilepsy, and consider a potential target for the discovery of new drugs for neurological disorders [11,12] different biomarkers are currently being studied in Alzheimer disease and other neurodegeneration diseases such as cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) Aβ, tau, phosphorylated tau and the other neuronal proteins, PET tracers for Aβ, tau and glucose uptake, and MR measures of brain diseases [3-15]. Interestingly, phenylalanine hydroxylase could also be a biomarker of neurodegenerative disease [16] (Figure 2).
The only promising in prevention and delay neurodegenerative diseases are many herbal plants that have been studied like Nigella sativa (Khazdair, 2015), moringa olifera [17] and many Plants-derived natural products used in the treatment of neurological diseases [8]. The ethanol extract of Alchemilla vulgaris and Filipendula ulmaria were used as acetylcholinesterase and tyrosinase inhibitor for treatment of neurodegenerative diseases in human [19]. Notably, there many medicinal plants have neuroprotective effects studied before like Ashwagandha, Baccopa monnieri, Centella asiatica, Ginseng, Ginkgo biloba, and active principals that extracted from plants as celastrol, curcumin , flavonoids, lycopene, resveratrol, sesamol, and trehalose characterized by antioxidant and antiapoptotic neuroprotection effects [20] (Figure 3).
Medicinal plants used in traditional medicine along with their extracted phytochemicals have various neuro-pharmacological pathways as modulation of transcription, transduction and intracellular signaling pathways including ERK and p38, with up regulation of anti-inflammatory cascades, anti-apoptosis and antoxidative stress associated pathways, all of them have essential role in the preventive and protection effects of the plants in neurodegenerative diseases [21,22].
Future Highlights
The causes of neurodegenerative diseases remain controversial. The use of plants medicine has enhanced a lot of interest for their therapeutic potential effects for many decades. In future, the benefit of phytochemicals on neurodegenerative diseases treatments due to their anti-apoptotic, anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidative and anticholinesterase activities. The rational of this review to investigate complex of predictive diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases and possible protective agents as medicinal plants.
References
- Awasthi M, Singh S, Pandey VP, Dwivedi UN (2016) Alzheimer’s disease: An overview of amyloid beta dependent pathogenesis and its therapeutic implications along with in silico approaches emphasizing the role of natural products. J Neurol Sci 361: 256-271.
- Prince M, Wimo A, Guerchet M, Ali GC, Wu YT, et al. (2015) World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia. Alzheimer’s Disease International London.
- Weintraub D, Comella CL, Horn S (2008) Parkinson’s disease--Part 1: Pathophysiology, symptoms, burden, diagnosis, and assessment. Am J Manag Care 14: S40-S48.
- Zhang Qinli, Li Meiqing, Jiao Xia, Xu Li, Guo Weili, et al. (2013) Necrostatin-1 inhibits the degeneration of neural cells induced by aluminum exposure. Restorative Neurology and Neuroscience 31(5): 543-555.
- Patrícia Batista, Anabela Pereira (2018) Impact and Prevention of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Society: Alzheimer and Parkinson.
- Shulman JM, De Jager PL, Feany MB (2011) Parkinson’s disease: genetics and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol 6: 193-222.
- Torrao AS, Cafe-Mendes CC, Real CC, Hernandes MS, Ferreira AF, et al. (2012) Different approaches, one target: understanding cellular mechanisms of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. Rev Bras Psiquiatr 34: S194-S205.
- Calderón FH, von Bernhardi R, De Ferrari G, Luza S, Aldunate R, Inestrosa NC (1998) Toxic effects of acetyl cholinesterase on neuronal and gliallike cells in vitro. Mol Psychiatry 3(3): 247-255.
- Pagano G, Rengo G, Pasqualetti G, Femminella GD, et al. (2014) Cholinesterase inhibitors for Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol Neuro surg Psychiatry 86(7): 767-773.
- Salama M, Shalash A, Magdy A, Makar M, Roushdy T, et al. (2018) Tubulin and Tau: Possible targets for diagnosis of Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s diseases. PLoS One 13(5): e0196436.
- Denda S, Reichardt LF (2007) Studies on integrins in the nervous system. Methods Enzymol 426: 203-221.
- Wu X, Reddy DS (2012) Integrins as receptor targets for neurological disorders. Pharmacol Ther 134(1): 68-81.
- Beach TG (2017) A Review of Biomarkers for Neurodegenerative Disease: Will They Swing Us Across the Valley? Neurol Ther 6(1): 5-13.
- Hoglund K, Kern S, Zettergren A, Skoog, Blennow K, et al. (2017) Preclinical amyloid pathology biomarker positivity: effects on tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Transl Psychiatry 7(1): e995.
- Villemagne VL, Dore V, Bourgeat P, Masters CL, Rowe CC, et al. (2017) Abeta-amyloid and Tau imaging in dementia. Semin Nucl Med 47: 75-88.
- Rawlings L, Turton L, Mitchell SC, Steventon GB Drug S-oxidation and phenylalanine hydroxylase: a biomarker for neurodegenerative susceptibility in Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
- Giacoppo S, Rajan TS, De Nicola GR, Iori R, Rollin P, et al. (2015) The Protective Effects of Nigella sativa and Its Constituents on Induced Neurotoxicity. J Toxicol 841823.
- Sengupta T, Vinayagam J, Singh R, Jai sankar P, Mohan Kumar KP (2016) Plant-Derived Natural Products for Parkinson’s Disease Therapy. Adv Neurobiol 12: 415-496.
- Neagu, E., Paun, G., Albu, C, Radu, GL (2015) Assessment of acetylcholinesterase and tyrosinase inhibitory and antioxidant activity of Alchemilla vulgaris and Filipendula ulmaria extracts. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers 52: 1-6.
- Ratheesh G, Tian L, Venugopal JR, et al. (2017) Biomanuf Rev 2: 2.
- Farzaei MH, Shahpiri Z, Mehri MR, Bahramsoltani R, et al. (2018) Medicinal Plants in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Perspective of Traditional Persian Medicine. Curr Drug Metab 19(5): 429-442.
- (2017) The Isothiocyanate Isolated from Moringa oleifera Shows Potent Anti-Inflammatory Activity in the Treatment of Murine Subacute Parkinson’s Disease. Rejuvenation Res 20(1): 50-63.




 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.