Short Communication 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Personalized Approach in the Diagnostic and Treatment of Tinnitus
*Corresponding author: Lisotskaya VV, The establishment of the Ministry of Health of the Republic of Belarus, State Institution “The Republican Center for Research and Practice in Otolaryngology”, The city of Minsk, Republic of Belarus, Belarus.
Received: June 27, 2019; Published: July 05, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.03.000712
Abstract
Tinnitus is a disease that affects millions of people. However, there is still no standard for diagnosing and treating this disease. What necessitates a lot of new research in this area?
The object: 40 patients with Tinnitus studied at Audiology department of the State Institution “The Republican Center for Research and Practice in Otolaryngology”, from 2018 to 2019 year.
The aim: To determine the most effective method of management patients with Tinnitus.
The methodology: Mathematical statistics, Student t-test, Fisher test. All patients underwent DPOAE, TEOAE, tympanometry and acoustic reflexes, Auditory Brainstem Response, high-frequency audiometry, Word Recognition test.
The results: The study involved 40 individuals an equal man (N=23) and women (N=17) in the middle age at 32,31 ± 10 years (95% CI 18- 55 years). All patients (N=40) were divided into 2 groups: 1 group (соntrol) - patients with tinnitus with standard diagnostic and treatment plus white noise masking, 2 group (experience) –patients with tinnitus who were managed with personalized approach. It was found that statistically significant difference was observed between the both groups diagnosed with DPOAE and TEOAE. All patients successfully passed the TEOAE-test from 2 groups. But all patients showed lower results at 1501, 2002, 6000, 8000 Hz frequencies by the distortion-product otoacoustic emissions. It was significantly revealed an elongation or the shortening of the peak of I wave (t≥ 0,95) with an increase in the amplitude and an increase in the latency. Speech intelligibility was 80±5% (t≥ 0,95in both groups. Based on the characteristics of the peak of I wave, drug treatment was prescribed to stimulate or inhibit the functioning of the auditory nerve in the experience group for 2 weeks. Additionally, in the group of experience group, listening to delta waves at a frequency of 5kHz was assigned for three months. Significant difference was achieved in the experiment group and was accompanied by the restoration of the amplitude of the peak of I wave to 61,3 ± 5.8 % to normal and completely passing DPOEA during 6 months.
Conclusion: Personalized approach increases the effectiveness of treatment of tinnitus and the quality of life this kind of patients.
Keywords: Tinnitus; Hearing threshold; Distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAE); Transient otoacoustic emissions (TEOAE); Pure-Tone Audiometry (PTA); Auditory Brainstem Response (ABR)
Introduction
Tinnitus is the perception of sound without an external source [1]. According to most information portals; tinnitus affects a huge number of people. Tinnitus can also affect otological healthy individuals and people with different otologic pathology. Tinnitus is found in diseases of the temporomandibular joint, pathology of the nervous system and other organs and systems [2].
Due to American Academy of Audiology, some 30 million Americans have tinnitus. Of those with tinnitus, almost 40 percent experience tinnitus during 80 percent of their day. Approximately 1 in 4 tinnitus sufferers report their tinnitus as loud, 1 in 5 report their tinnitus is disabling or nearly disabling [3-5].
Such a high frequency of distribution and impact on the quality of life, as well as the absence of a comprehensive multidisciplinary approach, necessitates new research in this field.
Methods
A prospective chart review was performed for patients who are diagnosed with Tinnitus at “The Republican Center For Research and Practice in Otolaryngology” of Republic of Belarus for 2018 year. Eligibility criteria includes the age of patients elder than 18 to 50 years old, otological health people, absence of hemodynamically significant cerebrovascular, brachiocephalic circulatory disorders. Rull out structural pathology was excluded for all patients: the absence of concomitant pathology of the endocrine, digestive, nervous, immune, musculoskeletal, respiratory, urinary systems, lack of cancer. All patients had no pathology of violations of the circulatory and blood. All studied people with tinnitus underwent a standard battery of tests: DPOAE, TEOAE, acoustic tympanometry, auditory brainstem response, pure-tone audiometry, word recognition test, (AC 40; Eclipse, Interacoustics, Denmark).
In pure-tone audiometry, hearing thresholds 500, 1000, 2000, 3000, 4000, 6000 Hz frequencies were received. The pure tone average (PTA) was determined by calculating the arithmetic mean of amount of the 500, 1000, 2000 and 4000Hz thresholds. The audiograms could be characterized like a normal line at different thresholds. To assess the subjective feeling, a test was used THI test recommended by Hearing Loss Association of America. Oneway ANOVA and Kruskal–Wallis tests were used for comparing numerical variables. For subgroup analyses, t-Student and Mann– Whitney U tests were chosen for parametric and nonparametric evaluations, respectively.
Results
The study involved 40 individuals an equal man (N=23) and women (N=17) in the middle age at 32,31 ± 10 years (95% CI 18- 55 years). The principle of dividing into groups included patients (N=40), that were divided into 2 groups: 1 group (соntrol) - patients with tinnitus with standard treatment plus white noise masking, 2 group (experience) –patients with tinnitus who were managed with personalized approach. Emoxipine, Vinpocetinum, Betahestine were prescribed for the standard treatment. The personal approach included taking into account the results of the study of otoacoustic emission, amplitude and latency of the first ABR wave. Drug treatment includes Ipidacrine in case of elongation of the first ABR wave and in the case of shortening–Phenibutum. Depending on the results, drug treatment was prescribed together with music therapy with delta waves at a frequency of 5000 Hz. Medical treatment was prescribed for 2 weeks, music therapy – for 3 months.
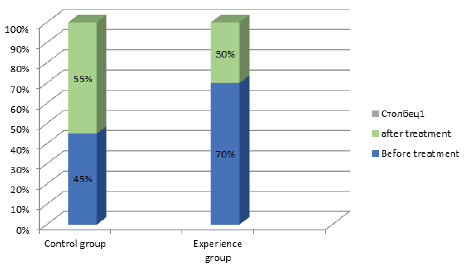
The quality of life was assessed before and after treatment by Tinnitus Handicap Inventory Test (THI). А significant difference was established after the start of treatment in the experience group, so the quality of life with a moderate degree of severity was changed to light or normal. However, there was no difference in the change in the quality of life before and after treatment in the control group.
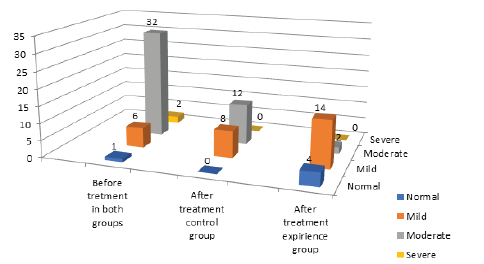
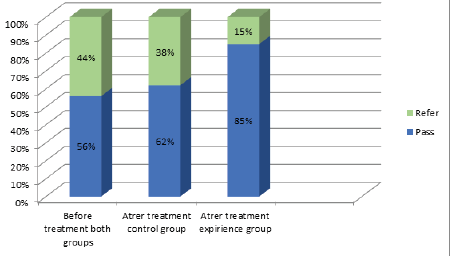
(Figure 1) Tympanogram type A was registered in all the patients in two groups (N=40) with bilateral acoustic reflexes. High-frequency audiometry showed any changes only in 1/3 of the studied both groups (N=7). It was found that statistically significant difference was observed between the both groups diagnosed with DPOAE and TEOAE. All patients successfully passed the TEOAE-test from 2 groups. But all patients showed lower results at 1501, 2002, 6000, 8000 Hz frequencies by the distortion-product otoacoustic emissions before treatment. Though it was significantly found that the DPOAE test was completely passed at all frequencies in 80% (N=16) of the experimental group. And no significant difference was obtained in the control group by DPOAE.
(Figure 2) It was significantly revealed an elongation or the shortening of the peak of I wave (t≥ 0,95) with an increase in the amplitude and an increase in the latency. Speech intelligibility was 80±5% (t≥ 0,95)in both groups Significant difference was achieved in the experiment group after treatment and was accompanied by the restoration of the amplitude of the peak of I wave to 61,3 ± 5.8 % to normal and completely passing DPOEA during 6 months (Figure 3).
Discussion
In this study, we established that patients with tinnitus in otologic health people can include signs of auditory synaptopathy. The diagnostics of hearing impairment in patients with tinnitus should contain in addition to standard battery tests and first wave peak analysis. The treatment with personalized approach showed better results in this kind of patients. The effect of Delta waves at a frequency of 5000 Hz can be explained by a violation of the pathological loop of increased neuronal activity between the brain stem and geniculum laterale [6]. Delta waves are produced by the brain during a deep sleep state, which can also affect the synchronization of the activity of the cerebral cortex, indirectly affecting the primary and secondary auditory cortex.
Conclusion
Personalized approach increases the effectiveness of treatment of tinnitus and the quality of life this kind of patients.
Disclosure
No financial support was provided for this study. No author has any financial interest in the companies or products reported in this paper has any financial disclosures related to this work.
References
- Eggermont JJ (1990) On the pathophysiology of tinnitus: A rewiew and a peripheral model. Hearing Research 48(1-2): 111-124.
- Pozo K, Goda Y (2010) Unraveling mechanisms of homeostatic synaptic plasticity. Neuron 66: 337-351.
- Baguley DM, Andersson G, McKenna L and McFerran DJ (2013) Tinnitus: A multidisciplinary approach (2nd edn). Chichester, Wiley, UK.
- Won JY, Yoo S, Lee SK, Choi HK, Yakunina N, et al. (2013) Prevalence and factors associated with neck and jaw muscle modulation of tinnitus. Audiology and Neurootology 18(4): 261-273.
- Hazzell JWP (1987) A cochlear model for tinnitus. H Feldman (Eds), Proceeding III International Tinnitus Seminar. Harsch Verlag, Karlsrune, Munster, Germany, pp. 121-128.
- Ambrosetti U and Del Bo L (2011) Audiological clinical assessment. AR Moller, B Langguth, D deRidder and T Kleinjung (Eds.), Textbook of tinnitus, Springer, New York, USA, pp. 279-284.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.