Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
The Accuracy Performance of the Point of Care Test (POCT) Boditech I-CHROMA™ Testosterone Method using External Quality Assessment Schemes: RIQAS and UKNEQAS
*Corresponding author: J Bolodeoku, JB Consulting (MDP) Limited, Cherwell Innovation Centre, 77 Heyford Park, Upper Heyford, Oxfordshire, OX25 5HD, UK
Received: August 19, 2019;Published: August 28, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.04.000859
Abstract
The estimation of testosterone levels in the blood is an important part of urological practice. This study evaluated and compared the performance of the quantitative Boditech point of care test Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method with other laboratory testosterone methods enrolled in the external quality assurance services, RIQAS and UKNEQAS. Samples 1-12 of Cycle 41 from the RIQAS scheme and forty-six distributions of the UKNEQAS Testosterone scheme were analyzed using the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method. The Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method compared well with the laboratory methods registered in both schemes. The best correlation was with the Diasorin Liaison method (r2=0.96851) in the RIQAS and the TOSOH AIA method (r2=0.767) in the UKNEQAS. The method with the least bias from the RIQAS was the Diasorin Liaison (-2 ng/ mL) and from the UKNEQAS was the Tandem Mass Spectroscopy (0.049 ng/mL). In conclusion, the Boditech i-CHROMA™ POCT Testosterone method compared well with other laboratory methods and can be considered a reliable method for testosterone estimation within its limitations.
Introduction
The measurement of testosterone is crucial in managing several endocrinological disorders in males, such as hypogonadism and assessing adequate testosterone replacement and in females, to investigate hyperandrogenism seen in hirsutism; polycystic ovarian syndrome; congenital adrenal hyperplasia and androgen secreting tumours [1-7]. In the past, assays for testosterone were quite cumbersome and laborious and involved extraction and chromatography steps followed by radioimmunoassays (RIA). Then, testosterone assays were carried out using a direct chemiluminescent method run on automated immunoassay analyzers [8-9]. More recently, there have been a couple of point of care testing (POCT) methods for quantitatively estimating testosterone methods such as OPKO Claros and the Boditech i-CHROMA™ introduced into the market. We have extensively evaluated the comparative performance of the Boditech i-CHROMA™ for estimating Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) [10- 12], Vitamin D [13], Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (HCG)14, Luteinizing Hormone (LH) [14], Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) [14], C-Reactive Protein (CRP) [15], Microalbumin [15] and TSH [16] and found a very good correlation with other traditional laboratory methods. In this study, we set out to evaluate the performance of the Boditech i-CHROMA™ Testosterone method and compared it with a wide range of testosterone methods enrolled in the Randox International Quality Assessment Scheme (RIQAS) and the United Kingdom National External Quality Assessment Services (UKNEQAS).
Methods
Boditech i-CHROMA™ uses a sandwich immuno-detection principle, such that the fluorescence-labelled detector antibody binds to the target protein in the sample. The sample is then applied onto a test strip and the fluorescence labelled antigen-antibody complex is captured by a second antibody embedded in the solid phase. The signal intensity of fluorescence of the captured complex is directly proportional to the amount of testosterone present and thus allows for the calculation of sample testosterone concentration and the result is displayed on the reader as nanograms per milliliter (ng/mL). A fluorescence-labelled control protein is included in the reaction and the intensity of the control line is measured as a quality check.
Testosterone Method
The assay was performed following the manufacturer’s instructions:
1. Transfer 30μL of displacing reagent to the sample mixing tube.
2. Transfer 75μL of sample (control/serum/plasma) using a pipette to a sample mixing tube containing the displacing reagent.
3. Close the lid of the sample mixing tube.
4. Shake the tube up and down 10 times or more.
5. Incubate at room temperature for 3 minutes.
6. Pipette out 75μL of a sample mixture and dispense it into the tube containing detection buffer.
7. Shake the tube up and down 10 times or more.
8. Transfer the mixture onto the sample well of the test device.
9. Wait 12 minutes.
10. Insert test cartridge into Test Cartridge holder in the Boditech i-CHROMA™ Reader.
11. Press “Select”
12. Read the result on the display screen.
Materials
Testosterone Materials
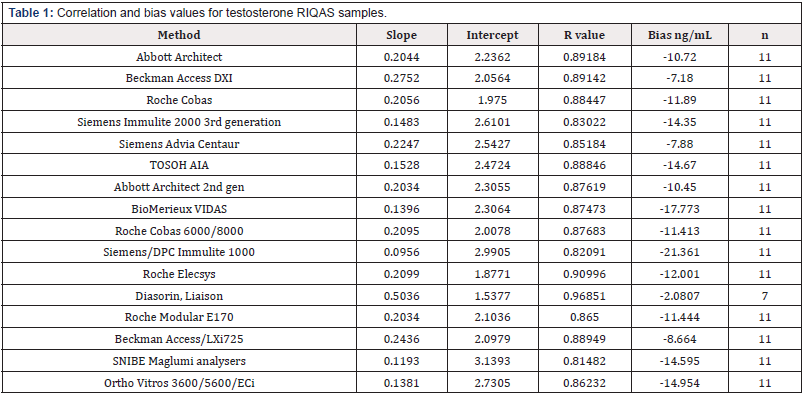
RIQAS: Samples 1-12 of Cycle 41 from the RIQAS were analyzed for testosterone, using the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method as described in testosterone concentration estimations. There were 16 methods registered with the scheme: Abbott Architect 2nd generation (n=11), Abbott architect (n=11), BioMerieux Vidas (n=11), Roche COBAS® 6000/8000 Test II (n=11), Siemens Centaur XP/XPT/Classic (n=11), Siemens/DPC Immulite 2000/2500 (n=11), Siemens/DPC Immulite 1000 (n=11), Beckman DXI 600/800 (n=11), Roche Elecsys Test II (n=11), Diasorin, Liaison (n=7), Roche Cobas 4000/e411 Test II (n=11), Roche Modular E170 Test II (n=11), Beckman, Access/LXi725 (n=11), SNIBE Maglumi analysers (n=11), Tosoh (n=11), and Ortho Vitros 3600/5600/ECi (n=11).
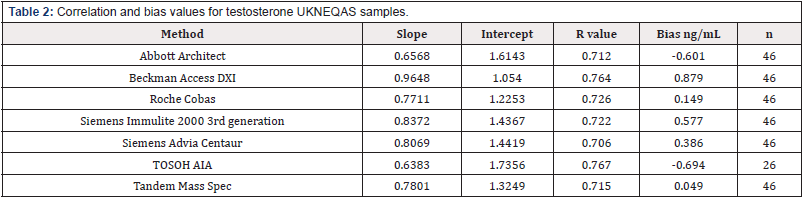
UKNEQAS: Forty-six distributions of the UKNEQAS Testosterone scheme were analysed for testosterone, using the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method as described in testosterone concentration estimations. There were 7 methods registered with the scheme: Abbott Architect (n=46), Beckman Access/Dxi (n=46), Roche COBAS® (n=46), Siemens Immulite 2000 3rd generation (n=46), Siemens Advia Centaur (n=46), Tandem Mass Spec (n=46), TOSOH AIA(n=26)
Results
Testosterone
External Quality Control (RIQAS and UKNEQAS) – Correlations: The results of the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method compared well with the methods in the RIQAS : Abbott Architect 2nd generation, Abbott architect, BioMerieux Vidas, Roche COBAS® 6000/8000, Siemens Centaur XP/XPT/Classic, Siemens/DPC Immulite 2000/2500, Siemens/DPC Immulite 1000, Beckman DXI 600 / 800, Roche Elecsys, Diasorin, Liaison, Roche Cobas 4000/e411, Roche Modular E170, Beckman, Access/LXi725, SNIBE Maglumi analysers, Tosoh, and Ortho Vitros 3600/5600/ ECi) and relatively well with the methods in the UKNEQAS : Abbott Architect, Beckman Access/Dxi, Roche COBAS®, SMS Immulite 2000 3rd generation, SMS Advia Centaur, Tandem Mass spec), Tosoh AIA - see correlations (Tables 1&2). The best correlation was with the Diasorin Liaison (r2=0.96851) in the RIQAS and the TOSOH AIA (r2=0.767) in the UKNEQAS (Figure 1).
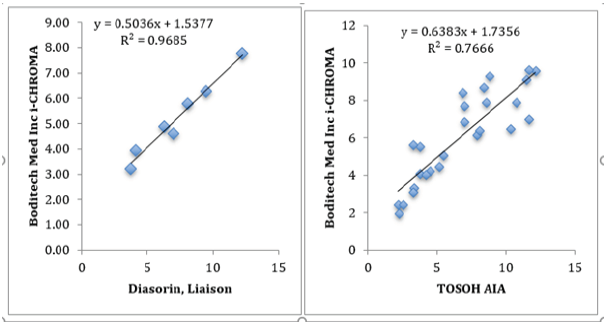
Figure 1(A): Best correlation was seen with Diasorin Liaison vs Boditech i-CHROMA™ using RIQAS testosterone methods, correlation = 0.96851. (B): Best correlation was seen with Tosoh AIA vs Boditech i-CHROMA™ using UKNEQAS testosterone methods, correlation = 0.76661.
External Quality Control (RIQAS and UKNEQAS) – Bias: The Bland-Altman plots for the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method and all the other testosterone methods showed very good means of differences, with over 95% of all data points falling within the two standard deviations proving that the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method and the other laboratory testosterone methods yielded similar results. Most of the data points were evenly distributed below and above that of the mean, indicating that the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone values were usually higher than those seen with other laboratory testosterone methods, but also sometimes lower.
The bias ranged between -21.361 ng/mL and -2.0807 ng/mL with an average of -11.72 ng/mL with the methods in the RIQAS and -0.694 ng/mL and +0.879 ng/mL with an average of +0.0925 ng/ mL with the methods in the UKNEQAS (Table1&2). The Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone had a negative bias when compared to all sixteen (100%) of the methods in the RIQAS. The Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone had a negative bias when compared to two out of the seven (29%) methods in the UKNEQAS. The method with the least bias from the RIQAS was the Diasorin Liaison and from the UKNEQAS was the tandem mass spectroscopy (Figure 2).
Discussion
In this study, the performance of the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method was evaluated with other traditional laboratory testosterone methods. All the following testosterone methods: Abbott Architect 2nd generation, Abbott Architect, BioMerieux Vidas, Roche COBAS® 6000/8000, Siemens Centaur XP/XPT/Classic, Siemens/DPC Immulite 2000/2500, Siemens/ DPC Immulite 1000, Beckman DXI 600 / 800, Roche Elecsys, Diasorin, Liaison, Roche Cobas 4000/e411, Roche Modular E170, Beckman, Access/LXi725, SNIBE Maglumi analysers, Tosoh, and Ortho Vitros 3600/5600/ECi enrolled in the RIQAS all compared well with the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method. In addition, all the following methods enrolled in the UKNEQAS scheme: Abbott Architect, Beckman Access/Dxi, Roche COBAS®, Siemens Immulite 2000 3rd generation, Siemens Advia Centaur, Tandem Mass Spectroscopy and Tosoh AIA also correlated well with the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method but not as well with the results from the RIQAS. The level of bias of the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method ranged from -21.361 ng/mL to -2.0807 ng/mL with the methods in the RIQAS. Therefore, there was an overall negative bias seen when the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method was compared with all other testosterone methods in this service. This may possibly be due to differences in standardization but may also be caused by matrix effects or cross reactivity. However, with the methods in the UKNEQAS the level of bias of the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method ranged from -0.6 ng/mL to +0.8 ng/mL and was more evenly spread out and there was no overall negative bias seen.
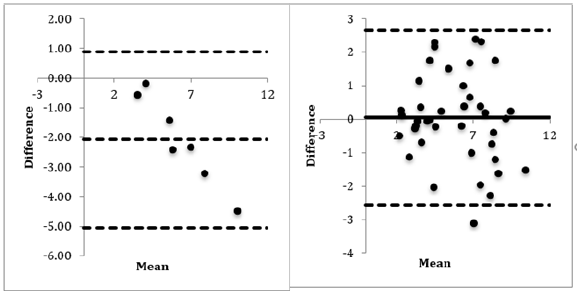
Figure 2(A): Best bland Altman plot was seen with Diasorin Liaison vs Boditech i-CHROMA™ using RIQAS testosterone estimations, bias = -2.0807ng/mL. (B): Best bland Altman plot was seen with tandem mass spectroscopy vs Boditech i-CHROMA™ using UKNEQAS testosterone estimations, bias = 0.049ng/mL.
In this study, the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method compared very well with the Abbott Architect 2nd generation (r2 0.87619), which is described as one of the assays that is quite sensitive and can estimate very low levels of testosterone [17]. In addition, the testosterone measurement using Tandem Mass Spectroscopy is regarded as one of the gold standard methods [18], this method correlated reasonably well with the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone (r2 0.715). Another corroborative study is described in the product leaflet where the testosterone concentrations of 36 samples were quantified using the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone and compared with results using the BioMerieux mini Vidas method and produced a correlation value of 0.9687 [19]. In this study, the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone, when compared with the BioMerieux Vidas method in the RIQAS, showed a correlation of 0.87473.
This is the first time that a POCT method for measuring testosterone has been evaluated extensively with traditional laboratory methods. This method could also lend itself to situations when the estimation of testosterone is required to evaluate testosterone replacement in conditions of testosterone deficiency.
In summary, the Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone method correlated reasonably well with a wide range of traditional laboratory methods. It is important to take the observed positive and negative biases in some of the external quality assurance schemes into consideration.
References
- Dobs AS (2008) The role of accurate testosterone testing in the treatment of male hypogonadism. Steroids 73 (13): 1305-1310.
- Goodman NF, Bledsoe MB, Cobin RH et al. (2001) American Association of Clinical Endocrinologists Medical Guidelines for the Clinical Practice for the diagnosis and treatment of hyperandrogenic disorders. Endocr Pract (2): 120-134.
- Robinson S, Rodin DA, Deacon A, Wheeler MJ, Clayton RN (1992) Which hormone tests for the diagnosis of polycystic-ovary-syndrome? Br J Obstet Gynaecol 99(3): 232-238.
- Araujo AB, Esche GR, Williams RE, Clark RV, McKinlay JB, et al. (2007) Prevalence of symptomatic androgen deficiency in men. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 92(11): 4241-4247.
- Kazi M, Geraci SA, Koch CA (2007) Considerations for the diagnosis and treatment of testosterone deficiency in elderly men. Am J Med 120(10): 835-840.
- Goodman NF, Cobin RH, Ginzburg SB, Katz IA, Woode DE (2001) American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the diagnosis and treatment of menopause: executive summary of recommendations. Endocr Pract 17(6): 949-954.
- Petak SM, Nankin HR, Spark RF, Swerdloff RS, Rodriguez-Rigau LJ (2002) American Association of Clinical Endocrinology Medical Guidelines for Clinical Practice for the evaluation and treatment of hypogonadism in adult male patients-2002 update. Endocr Pract 8(6): 440-456.
- Matsumoto AM, Bremner WJ (2004) Serum Testosterone Assays – Accuracy Matters. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89(2): 520-524.
- Sacks SS (2005) Are routine testosterone assays good enough. Clin Biochem Rev 26 : 43-45.
- Bolodeoku J, Bains S, Chand V, Bacon R, Weir P, et al. (2017) A screening evaluation of the Point of Care Test (POCT) i-CHROMA Prostate Specific Antigen (PSA) assay method in the community. Point of Care: The Journal of Near Patient Testing & Technology 16(2): 93-96.
- Beltran L, Leach E, de Fonseka S, Bolodeoku J, Chinegwundoh F (2018) An evaluation of the novel i-CHROMA point of care testing (POCT) method for the analysis of prostate specific antigen (PSA) in serum. Biomed J Sci & Tech Res 9 (4).
- Bolodeoku J, Coker O, Bains S, Anyaeche C, Kim TK, Chinegwundoh F. The performance of the point of care test (POCT) i-CHROMA PSA method using internal and external quality assessment schemes: United Kingdom External Quality Assessment Service (UKNEQAS) and Randox International Quality Assessment Service (RIQAS). Curr Trends Med Diagn
- Bolodeoku J, Pinkney S, Bains S, Andrade ML (2018) An assessment of automated Vitamin D measurement methods including a Point of Care Testing method, Boditech i-CHROMA™ using the Randox International Quality Assurance Scheme (RIQAS) Biomed J Sci & Tech Res 3(4).
- Bolodeoku J, Bains S, Pinkney S, Coker O, Fakokunde A (2017) Comparison of the Point of Care Test (POCT), Boditech i-CHROMA™ Human Chorionic Gonadotrophin (HCG), Leutinizing Hormone (LH) and Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH) methods in serum with the other methods in the Randox International Quality Assessment Scheme (RIQAS). Clin Obstet Gynecol Reprod Med 3(4): 1-7.
- Bains S, Anyaeche C, Wyatt A, Coker O, Bolodeoku J (2017) Evaluation of Point of Care Test (POCT), i-CHROMA serum C-Reactive Protein (CRP) assay and Microalbumin Urine (MAU) methods. Annals of Clinical and Laboratory Research 5(3): 192.
- Bolodeoku J, Bains S, Pinkney S, Coker O, Kim TK, Anyaeche C (2017) An evaluation of the Boditech i-CHROMA Thyroid Stimulating Hormone (TSH) method: Precision and Accuracy. Ann Clin Lab Res 7(2): 302.
- Groenestege WMT, Bui HN, ten Kate J, Menheere PPCA, Oosterhuis WP, et al. (2012) Accuracy of first- and second-generation testosterone assays and improvement through sample extraction. Clin Chem 58: 1154-1156.
- Wang C, Catlin DH, Demers LM, Starcevic B, Swerdloff RS (2004) Measurement of total serum testosterone in adult men: comparison of current laboratory methods versus liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89: 534-543.
- Boditech Med Inc Boditech i-CHROMA™ testosterone product leaflet. Document No: INS-TT-EN, Revision No. 07.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.