Short Communication 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Synthesis and Analgesic Activity of 5,6-difluoro-2- Methyl-4H-benzo(d) (1,3)-Oxazin-4-one and 3-Amino- 5,6-difluoro-2-Mehtyl-quinzolin 4(3H)-One
*Corresponding author: Department of Chemical Science, Ondo State University of Science and Technology, OkitipupaOndo State, Nigeriaa
Received: September 05, 2019;Published: September 16, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.05.000892
Abstract
The current study is aimed at the synthesis and Antibacterial evaluation of quinazolinone derivatives. The condensation of Methyl-2-amino- 5,6-diflorobenzoate with acetic anhydride yielded the cyclic compound 2-methyl 5,6-diflorobenzo [d] [1,3]-oxazine-4-one which further produce 3-Amino-2-Methyl 5,6-difloro quinazolin-4(3H)-ones via the reaction with hydrazine hydrate. The compounds synthesized were unequivocally confirmed by means of Infrared, Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (1H and 13C), Gas Chromatography Mass Spectrophotometry and Elemental analysis. The synthesized compounds were screened against various strains of microorganism, Staphylococcus aureus, Bacillus species, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, Serratia Marcensces, and Candida albicans. The compounds 1and 2 showed significant activity as an Anagesic agent
Keywords: 5,6-difloro-2-methyl-4H-benzo [d] [1,3]-oxazine-4-one; 3-amino-5,6-difloro-2-methyl-quinazolin-4(3H)-one; Nucleophile; Quinazoline- 4(3H)-one; Analgesic
Introduction
Heterocyclic chemistry comprises at least half of all organic chemistry research worldwide. In particular, heterocyclic structures form the basis of many pharmaceutical, agrochemical and veterinary products. Among a wide variety of nitrogen heterocycles that have been explored for developing role in medicinal chemistry and subsequently have emerged as a pharmacophore [1].
Quinazolinone derivatives represent one of the most active classes of compounds possessing a wide spectrum of biological activity. They are widely used in pharmaceutical and agrochemicals. Several reports have been published on the biological activities of quinazolinone derivatives, including their anti-inflammatory [1-7], antimalarial [8-16], anticonvulsant [17-20], and antitumor [21,22], activities.
Quinazolinone peptides were reported for their anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, anthelminthic, antibacterial and antifugal activities [23].
Materials-and-Methods
General Experimental Procedure
All reagents and solvents were purchased from sigma-Aldrich, in Germany. Melting points were determined on a kofler hot stage apparatus and were uncorrected. IR spectra were recorded on a Buck scientific IR M500 instrument. The 1H and 13C NMR spectra were recorded in DMSO-d6 at 400 MHz with HAZ VOLATILE V2. M Chemical shifts Sare reported in ppm relative to tetramethylsilane. Gas chromatography mass spectra were obtained on a Finingan MAT 44S mass spectrophotometer operating at 70eV. Elemental analysis agreed favourably with the calculated values. Analytical thin layer chromatography (TLC) was used to monitor the reactions.
Elemental Analysis
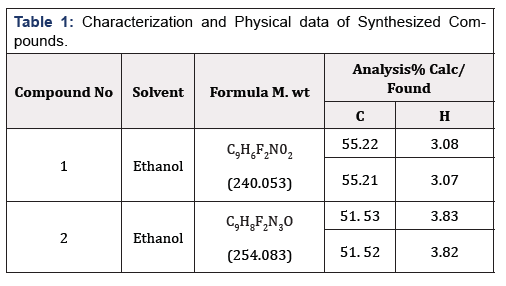
The compositions of the compounds are summarized in (Table 1). The C and H contents (both theoretically calculated values and actual values) are indicated.
General procedure for the synthesis of 5,6-difloro-2- methyl-4H-benzo [d] [1,3]-oxazine-4-one, (1)
This involved the condensation of 0.76g (0.005mol) Methyl 2-amino-5,6-diflorobenzoate with 10ml, 1.02g, (0.01mol) acetic anhydride in 30ml ethanol medium. The reaction was heated under reflux with stirring using a magnetic stirrer until the reaction mixture showed no trace of starting material when the TLC was developed (2 hours). Yield was 2.01g (96%), mp: 149-151°C [24].
General procedure for the synthesis of 3-amino-5,6-difloro- 2-methyl-quinazoline-4(3h)-one (2)
Equimolar amounts (1.61g, 0.01mol) of 5,6-diflöro-2-methyl- 4H-benzo [d] [1,3]-oxazine-4-one, and (0.51g, 0.01mol) hydrazine hydrate were heated under reflux in 30ml ethanol with stirring using a magnetic stirrer until the reaction mixture showed no trace of starting material when the TLC was developed (3 hours). At the end of the reaction, the reaction mixture was concentrated in vacuum under reduced pressure using rotary evaporator. The white precipitate formed was then filtered, washed three times with 20ml of distilled water [20ml x 3]. The white crystals were dried and recrystallized from dimethylformamide (DMF) to give pure 3-amino- 5,6-difloro-2-methyl-quinazolin-4(3H)–one. Yield was 1.50g(95%) mp : 138-140°C [25].
Chemistry
The introduction of 2-amino substituent is a successful strategy to improve the chemical stability of benzoxazinone. Due to the pharmacological activities of 4(3H)-quinazolinone derivatives, 2,3-disubstituted derivative of quinazoline-4-one were synthesized via the interaction of the benzoxazinone derivative with nitrogen nucleophile with the aim of obtaining more pricise information about the course of the reaction and some interesting pharmaceutical compounds. The reaction of 4, 5-disubstituted derivatives of methylanthranilate and acetic anhydride yielded the cyclic compound 5,6-diforo-2-methyl-4H-benzo[d] [1,3]-oxazin-4-one. The reaction of this compound with hydrazine hydrate yielded 3-amino- 5,6-difloro-2-methyl-quinazoline-4(3H)-one (Table 1-3).
Characterization of 5,6-difloro 2-methyl-4H-benzo [d] [1,3] -oxazin-4-one.(1)
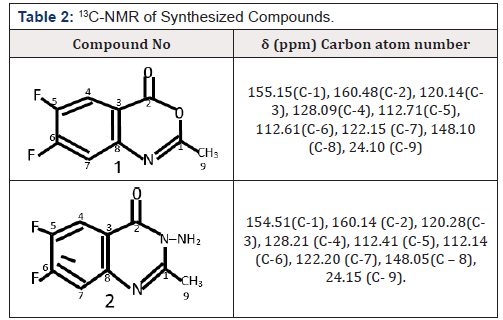
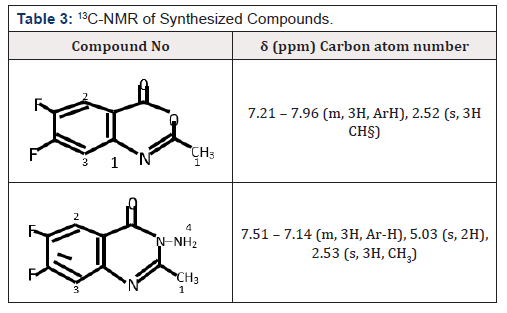
1H NMR (400MHz, DMSO) δ 7.21 – 7.96 (m, 3H, ArH ), 2.52 (s, 3H CH§), 13CNMR (400MHz, DMSO) δ 160.48, 155.15,148.10, 128.09, 120.14, 122.15, 112.71, 112.61, 24.10,. IR (KBr,cm1) 3135, (NH4), 3018 (CH aromatic), 2951, 2871, 2718 (CH aliphatic), 1730(C=0),1150 (C-0).Anal. Cal for C9H6BrN02 ; C 55.21; H 3.07. Found: C 55.22, H 3.08. Yield was 2.01g (96%), mp: 149-151°C.
Characterization of 3-amino- 5,6-difloro 2-methylquinazoline- 4(3H)-one. (2).
1H NMR (400 MHz, DMSO) δ 7.51 – 7.14 (m, 3H, Ar-H), 5.03 (s, 2H), 2.53 (s, 3H, CH3), 13C NMR (400MHz, DMSO) δ 160.14, 154.51, 148.08, 128.21, 122.20, 120.28, 112.41, 112.14, 24.15, IR (KBr,cm1) 3350(NH4),1685 (C=0),1620 (C=N), Anal. Cal. for C9H8BrN30; C 51. 52, H 3.82; Found, C 51.53, H 3.83.Yield was 1.00g (95%) mp: 98-100°C
Discussion
The present study reported the synthesis of two derivatives of quinazolinone, 5,6-difluoro-2-methyl-4H-benzo [d] [1,3]-oxazin- 4-one,(1) and 3-amino-6,7-difluoro-2-methyl quinazolin-4(3H)- one(2).The compounds were investigated for their Antimicrobial activity.
Structural elucidations of compounds synthesized were characterized by correct elemental analysis and careful inspections of spectral data. Looking at the 1H NMR spectra of the compounds synthesized, compound 1 displayed a singlet at δ 3.68 which was due to methyl group. Other singlets appeared at δ7.16 and 6.41 attributed to aromatic protons. Also, 1H NMR spectrum of compound 2 showed a characteristic signal at δ 2.58 (singlet) corresponding to methyl group. Two singlets appeared at δ7.41 and 7.10 attributed to aromatic protons. Another signal appeared at 5.80 which was attributed to the protons of the amino group. For the IR spectra, compound 1 were characterized by absence of υ NH4and presence of υ C-O stretch in 1102cm-1 region of the compound. Compound 2 was characterized by absence of υ C-0 and presence of υNH4 in 3301cm-1 region of the compound.
The 13C NMR spectrum of compound 1, revealed signals at δ16.95, attributed to methyl group, while the aromatic carbon at oms appeared between δ values 100.05-168.28 with the carbonyl carbon atom appearing as the highest δ value of 168.28. Similarly, compound 2 showed signals at δ22.58, attributed to methyl group, while the aromatic carbon atoms appeared between δ values 105.64-160.28, with the carbonyl carbon atom appearing as the highest δ value of 160.28. The compounds synthesized exhibited promising antimicrobial activities against Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas Aeroginosa, Escherichia coli, Klebsiella pneumonia, and candida albicans stock cultures.
Conclusion
The present study has showed that the quinazolinone derivatives 1 and 2 have antibacterial activity. Compound 2 has a higher activity against Serratia Marcescens compared to Compound 1.
Conflict-of-Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
Funding
No fund was obtained during the research.
Author declaration
The author hereby declares that the work presented in this article is original and that any liability for claims relating to the content of this article will be borne by me.
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
Ethic approval, consent to participate and the procedure used was approved by the Ethic approval committee of Ondo State University of Science and Technology, Okitipupa, Ondo State, Nigeria
Acknowledgements
The author acknowledges the assistance of Baba Haruna of the Department of Pharmaceutical Chemistry of Niger Delta University, Wilberforce Island, Yenogoa and Dr. Marris, in England for running the spectra.
Declaration Statement
The author declares there is no conflict of interest
References
- HaseenaBanu B, Bharathi K, Prasad KVSRG (2002) Synthesis, characterization and evaluation of in vitro antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity of 2- (4-oxo-2-phenylquinazoline-3 (4H)-yl) substituted acetic acids. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy 2(1): pp. 097-104.
- Kumar A, Sharma S, Archana, Bajaj K, Sharma S, et al. (2003) Some new 2,3,6-trisubstituted quinazolinones as potent anti-inflammatory, analgesic and COX-II inhibitors. Bioorg Med Chem 11(23): 5293-5299.
- Maggio B, Daidone G, Raffa D, Plescia S , Mantione L, et al. (2001) Synthesis and pharmacological study of ethyl 1-methyl-5-(substituted 3,4-dihydro-4-oxoquinazolin-3-yl)-lH-pyrazole-4-acetates. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 36(9): 737-742.
- Manivannan E, Chaturvedi SC (2011) Analogue-based design, synthesis and molecular docking analysis of 2,3-diaryl quinazolinones as non-ulcerogenic anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem 19(15): 4520-4528.
- Kumar A, Rajput CS, Bhati SK (2007) Synthesis of 3-[4'-(p-chIorophenyl)-thiazol-2'-yl]-2-[(substituted azetidinone/thiazolidinone)-aminomethyl]-6-bromoquinazolin-4-ones as anti-inflammatory agent. Bioorg Med Chem 15(8): 3089-3096.
- Giri RS, Thaker HM, Giordano T, Williams J, Rogers D, et al. (2010) Design, synthesis and evaluation of novel 2-thiophen-5-yl-3//-quinazolin-4-one analogues as inhibitors of transcription factors NF-xB and AP-1 mediated transcriptional activation: their possible utilization as anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer agents. Bioorg Med Chem 18(7): 2796-2808.
- Bansal E, Srivastava VK, Kumar A (2001) Synthesis and anti-inflammatory activity of 1-acetyl-5-substitute daryl-3-(/?-aminonaphthyl)-2-pyrazolines and (substitute daminoethyl) amidonaphthalenes. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 36(l): 81-92.
- Zhu S, Wang J, Chandrashekar G, Smith E, Liu X, et al. (2010) Synthesis and evaluation of 4-quinazolinone compounds as potential antimalarial agents. Eur J Med Chem 45(9): 3864-3869.
- Zhu S, Zhang Q, Gudise C, Wei L, Smith E, et al. (2009) Synthesis and biological evaluation of febrifugine analogues as potential antimalarial agents. Bioorg Med Chem 17(13): 4496-4502.
- Suresha GP, Suhas R, Kapfo W, ChanneGowda D (2011) Urea/thiourea derivatives of quinazolinone-lysine conjugates: synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a new series of antimicrobials. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 46(6): 2530-2540.
- Mo hameda MS, Kamel MM, Kassem EM, Abotaleb N, AbdEl Moez SI, et al. (2010) Novel 6,8-dibromo-4(3//)quinazolinone derivatives of anti-bacterial and anti-fungalactivities. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 45(8): 3311-3319.
- Patel DR, Patel KC (2011) Synthesis, antimicrobial activity and application of some novel quinazolinone based monoazo reactive dyes on various fibres. Dyes and Pigments 90(1): 1-10.
- Kohli D, Hashim SR, Vishal S, Sharma M, Simgh AK (2009) Synthesis and antibacterial activity of quinazolinone derivatives. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences 1(1): 163-169.
- Patel NB, Patel JC (2011) Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of Schiff bases and 2-azetidinones derived from quinazolin-4(3H)-one. Arabian Journal of Chemistry 4(4): 403-411.
- Pandeya SN, Sriram D, Nath G, De Clercq E (1999) Synthesis, antibacterial, antifungal and anti-HIV evaluation of Schiff and Mannich bases of isatin derivatives with 3-amino-2-methylmercapto quinazolin-4(3H)-one. Pharmaceutica Acta Helvetiae 74(1): 11-17.
- Kumar A, Sharma P, Kumari P, Lal Kalal B (2011) Exploration of antimicrobial and antioxidant potential of newly synthesized 2,3-disubstituted quinazoline-4(3H/)-ones. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 21(14): 4353-4357.
- Zappalà M, Grasso S, Micale N, Zuccalà G, Menniti FS, et al. (2003) l-Aryl-6,7-methylenedioxy-J3H-quinazolin-4-ones as anticonvulsant agents. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 13(24): 4427-4430.
- Jatav V, Mishra P, Kashaw S, Stables JP (2008) CNS depressant and anticonvulsant activities of some novel 3-[5-substituted l,3,4-thiadiazole-2-yl]-2-styryl quinazoline-4(3H)-ones. Eur J Med Chem 43(9): 1945-1954.
- El Azab AS, EITahir KEH (2012) Synthesis and anticonvulsant evaluation of some new 2,3,8-trisubstituted-4(3H)-quinazoline derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 22(l): 327-333.
- Kashaw SK, Kashaw V, Mishra P, Jain NK, Stables JP (2009) Synthesis, anticonvulsant and CNS depressant activity of some new bioactive l-(4-substituted-phenyl)-3-(4-oxo-2-phenyl/ethyl-4H-quinazolin-3-yl)-urea. Eur J Med Chem 44(11): 4335-4343.
- Cao SL, Feng YP, Jiang YY, Liu SY, Ding GY, et al. (2005) Synthesis and in vitro antitumor activity of 4(3H)-quinazolinone derivatives with dithiocarbamate side chains. Bioorganic and Medicinal Chemistry Letters 15(7): 1915-1917.
- Al-Obaid AM, Abdel Hamide SG, El Kashef HA, Abdel Aziz AA, El Azab AS, et al. (2009) Substituted quinazolines, part 3. Synthesis, in vitro antitumor activity and molecular modeling study of certain 2-thieno-4(3H)-quinazolinone analogs. Eur J Med Chem 44(6): 2379-2391.
- Burger's Medicinal Chemistry and Drug Discovery, Fifth Edition: Principles and Practice, Edited by Manfred E. Wolf, Volume 1.
- Amar R Desai, Kishor R Desai (2005) Niementowski reaction: microwave induced and conventional synthesis of quinazolinones and 3-methyl-lH-5-pyrazolones and their antimicrobial activity. ARKIVOC (xiii) 98-108.
- Sachin S Laddha, Satyendra p Bhatnagar (2009) A new therapeutic approach in Parkinson's disease: some novel quinazoline derivatives as dual selective phosphodiesterase 1 inhibitors and anti-inflammatory agents. Bioorg Med Chem 17(19): 6796-6802.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.