Research Article 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
Bioactivity of Peperomia Pellucida Leaves from Bangladesh
*Corresponding author:Mohammad Shoeb, Department of Chemistry, University of Dhaka, Dhaka-1000, Bangladesh.
Received: September 16, 2019; Published: October 29, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.06.000981
Abstract
Peperomia pellucida (L.) belonging to family Piperaceae mainly grows in rainy season in Bangladesh. n-Hexane, dichloromethane and methanol extracts of leaves of P. pellucida were tested for antioxidant activity, antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content, total flavonoid content and cytotoxicity. Dichloromethane extract of the plant showed significant phenolic, flavonoid and antioxidant capacity while the methanol extract possessed potent antioxidant activity. None of the extract exhibited any cytotoxicity against HeLa cell lines.
Keywords: Peperomia Pellucida; Piperaceae; Antioxidant Activity; Cytotoxicity
Introduction
Peperomia pellucida (L.) belongs to Piperaceae family. There are about 1500-1700 species of the genus Peperomia [1]. It is an herbaceous plant found in many south American, Asian and African countries and also known as shiny bush or silver bush [2]. The species usually develops during rainy seasons and blooms in loose, humid soils under the shade of trees [3-6]. It was reported that the plant contained various secondary metabolites including alkaloids, saponins, tannins, cardennolides, flavonoid, essential oils and carotol [7,8]. P. pellucida has been used for treating abdominal pain, abscesses, acne, boils, colic, fatigue, gout, headache, renal disorders, and rheumatic joint pain [8,9]. Bangladesh is a tropical country with six seasons and May-June are rainy seasons with heavy monsoon rain. P. pellucida usually grows abundant during monsoon time. The present study was aimed to study biological activities i.e., antioxidant activity, antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content and total flavonoid content and cytotoxicity assay of different extracts of P. pellucida leaves
Materials-and-Methods
Sample collection and extraction: Leaves of P. pellucida were collected from different places of Dhaka city in 2017. The plant was identified and confirmed by the Botanist of the Department of Botany, University of Dhaka. The fresh plants were washed with clean running water to remove all the soils and dirt and then air dried followed by grinding into powder (172.0 g). The finely ground powder of P. pellucida leaves (172.0 g) were extracted successively with n-hexane, dichloromethane and methanol at room temperature for 72 hours with 3 replications. All filtrates were dried separately by rotary vacuum evaporator at 40 °C and n-hexane (3.50 g), dichloromethane (3.80 g) and methanol (16.0 g) were obtained.
Total Phenolic Content
The total phenolic contents were determined by modified Folin-Ciocalteu method and expressed as mg gallic acid equivalents per gram of dry extract using the equation obtained from gallic acid calibration curve, y = 0.0036x - 0.0013, r² = 0.9979 [10].
Total Flavonoid Content
Aluminium chloride colorimetric method was used for the determination of total flavonoid content of the P. pellucida extracts which was determined as mg quercetin equivalent per gram of dry extract using the equation obtained from quercetin calibration curve y= 0.0422x+0.0029; r2 =0.9984 [11].
Total Antioxidant Capacity
The total antioxidant capacity of the P. pellucida extracts were evaluated by the Phosphomolybdenum assay method [12]. The total antioxidant capacity was determined and expressed as mg ascorbic acid equivalents per gram of dry extract using the equation obtained from ascorbic acid calibration curve, y=0.0021x-0.0044, r2=0.9924.
DPPH (2, 2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) Radical Scavenging Activity
The stable DPPH radical-scavenging activity was measured using the modified method described by Gupta [13].
DPPH radical-scavenging activity (I %),
= [(A0 – A) /A0] × 100
where A0 is the absorbance of the control solution; A is the absorbance of the DPPH solution containing plant extract.
Cytotoxicity assay on cancer cell line
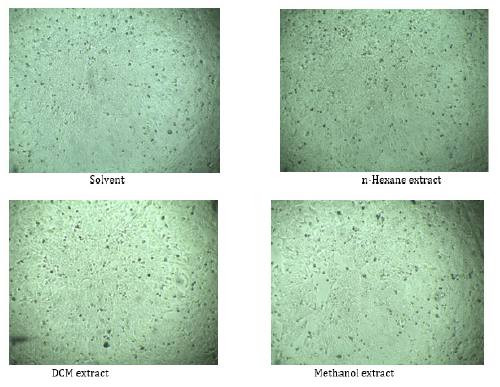
Cytotoxicity assay was examined against HeLa, a human cervical carcinoma cell line and was maintained in DMEM (Dulbecco’s modified Eagles medium) containing 1% penicillin–streptomycin (1:1) and 0.2% gentamycin and 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS). Cells (4×104/200 μl) were seeded onto 48-well plate and incubated at 37ºC + 5% CO2 . Next day, 50 μl sample (filtered) was added each well. Cytotoxicity was examined under an inverted light microscope after 48 hours of incubation. n-hexane, dichloromethane and methanol extracts of P. pellucida were tested against HeLa cell line (Figure 2). Duplicate wells were used for each sample.
Results and Discussion
Total Phenolic Content
The total phenolic content of the n-hexane, dichloromethane and methanol extracts were 43.528± 0.0016, 82.417 ± 0.0016 and 9.316± 0.0037 mg GAE/ g of dry extract, respectively.
Total Flavonoid Content
The total flavonoid content of the n-hexane, dichloromethane and methanol extracts were 64.65 ± 0.012, 94.72 ± 0.021 and 9.316± 0.0037 mg QE/ g of dry extract, respectively.
Total Antioxidant Capacity
The total antioxidant capacity was based on the reduction of Mo (VI) to Mo(V) by the extract and subsequent formation of green phosphate complex at acidic pH. It was observed that the DCM extract possssed significant total antioxidant capacity equivalent to 338 mg ascorbic acid/g of dry extract. However, MeOH and n-hexane extracts were found to be 9.429 ± 2.190 and 326.571 ± 2.810 mg ascorbic acid equivalent/g of dry extract, respectively.
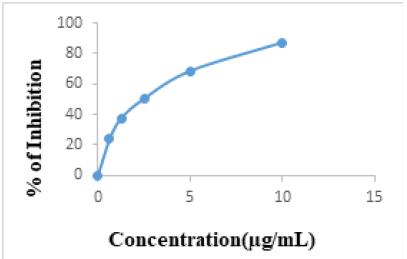
DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
Ascorbic acid was used as positive control (Figure 2). The IC50 value of n-hexane, DCM and MeOH extracts were 1041±0.140 μg/mL, 527.594± 0.0263 μg/mL and 135.831± 0.0086 μg/mL, respectively while that of ascorbic acid was 2.157± 0.0004 μg/mL. A lower IC50 value is associated with a higher radical scavenging activity.
Cytotoxicity Assay
Cytotoxicity assay of n-hexane, DCM and MeOH extracts of P. pellucida were tested against HeLa cell line. Samples were dissolved in 5% DMSO solvent. None of extracts of P. pellucida showed any activity against Hela cell lines.
Conclusion
Different extracts of P. pellucida exhibited different phenolic content, flavonoid content, antioxidant capacity and DPPH Free radical scavenging activity. The methanol extract possessed potent antioxidant activity. However, none of the extracts showed activity against HeLa cell line.
Acknowledgements
Authors are grateful to International Science Programme (ISP), Uppsala University, Sweden and Ministry of Education, Government of the People’s Republic of Bangladesh for all financial supports.
References
- Mathieu G, Samain MS, Reynders M, Goetghebeur P (2008) Taxonomy of the Peperomia species (Piperaceae) with pseudo-epiphyllous inflorescences, including four new species. Botanical Journal of the Linnean Society 157: 177-199.
- Adjanohoun JE, Aboukakar N, Dramane K, Ebot ME, Ekpere JA, et al. (1996) Traditional medicine and pharma- copoeia. Contribution to Ethnobotanical and Floristic Studies in Cameroon. Centre de Production de Manuels Scolaires, Porto-Novo (Rep. Du Benin) pp. 641.
- Dos Santos PR, de limas Moreira D, Guimaraes EF, Kaplan MA (2001) phytochem 58: 547-551
- de Fatima Arrigoni-Blank M, Dmitrieva EG, Franzotti EM, Antoniolli AR, Andrade MR, et al. (2004) Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activity of Peperomia pellucida (L.) HBK (Piperaceae). J Ethnopharmacol 91(2-3): 215-218.
- Arrigoni Blank Mde F, Oliveira RL, Mendes SS (2002) BMC pharmacol 2: 12-19.
- Bayma JD, Arruda MS, Muller AH, Arruda AC, Canto WC (2000) Phytochemistry 55:779-782.
- Khan A, Rahman M, Islam M (2010) Isolation and Bioactivity of a Xanthone Glycoside from Peperomia Pellucida, Life Sciences and Medicine Research, LSMR-1pp. 1-10.
- Khan MR, Omosolo AD (2002) Antibacterial activity of Hygrophila Stricta and Peperomia Pellucida. Fitoterapia 73: 251-254.
- Aziba PI, Adedeji A, Ekor M, Adeyemi O(2001) Analgesic activity of Peperomia pellucida aerial parts in mice. Fitoterapia 72(1): 57-58.
- Wolfe K, Wu X, Liu RH (2003) Antioxidant activity of apple peels. J Agri Food Chem 51: 609-614.
- Chang C, Yang M, Wen H, Chern J (2002) Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods. J Food Drug Analaysis 10: 178-182.
- Prieto P, Pineda M and Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a Phosphomolybdenum Complex: Specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Analytical Biochemistry 269: 337-341.
- Gupta M, Mazumder UK, Sivahkumar T, Vamis MlM, Karki S, et al. (2003) Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activities of Acalypha Nig J Prod Med 7: 25-29.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.