Short Communication 
 Creative Commons, CC-BY
Creative Commons, CC-BY
The Adrenergic Mechanism in the Implementation of the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory Pathway
*Corresponding author: Pavel F Zabrodsky, Saratov Medical University “REAVIZ”, Saratov, Russia.
Received: October 16, 2019; Published: October 31, 2019
DOI: 10.34297/AJBSR.2019.06.000990
Abstract
Experiments on random-bred albino mice showed that application of β2ARs agonist (hexaprenaline sulfate, 1,5 μg/kg, a single dose) and α7nAChRs agonist (GTS-21, 15 mg/kg, a single dose) cause a significant decrease in the mortality of mice from experimental sepsis (i.p., E. coli O157:H7) when it is modeling 2h after using these drugs due to a decrease of the concentration of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway).
It has been experimentally established that the adrenergic mechanism (action of β2ARs agonist) is an important component in the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. The combined use of β2ARs and α7nAChR agonists determines their additive effect.
Keywords: cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway; sepsis; β2ARs agonist; α7nAChR agonist; proinflammatory cytokines
Introduction
Mortality from sepsis, depending on various factors, ranges from 12 to 60% of all deaths associated with diseases and their complications [1], and there is an increase in the number of cases of sepsis and the mortality rate from it [2]. Cholinergic stimulation, as we established in 1987 [3] and in subsequent studies, significantly reduces the mortality of albino mice from sepsis caused by intraperitoneal or intrapulmonary administration, respectively of E. coli and P. vulgaris [3-7]. Thus, the cholinergic anti-inflammatory mechanism has been discovered in 1987 [3], named «cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in 2000 [8] after the research its implementation at the organismal, cellular and subcellular levels [4-9]. It should be noted that in 1995 it was proved the possibility of cholinomimetics for emergency activation of antimicrobial resistance of the organism in sepsis [4,5]. In the future, the study of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway caused by the action of acetylcholine on α7n-acetylcholine receptors (α7nAChRs) cells of the monocyte-macrophage system (MMC), followed by inhibition of the production by the cells of pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6) and reduced mortality from sepsis were devoted hundreds of articles various authors [6-15]. Reduced production of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 (anti-inflammatory effect occurrence) for cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway is provided kinase JAK2, transcription factor STAT3, NF-κB transcription factor) [8-17].
When the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway is realized, in addition to the excitation of α7nAChRs [9-19], which cause the effects already mentioned, nAChRs activation of the brain substance of the adrenal glands and sympathetic ganglia occurs, which leads to the production of epinephrine and norepinephrine (NE), which activation of macrophage-monocytic system cell (MMS) adrenergic receptors and reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [19]. At this n. vagus, releasing acetylcholine (ACh) in the celiac ganglion, causes excitation of the spleen nerve, the action of NE through its efferent fibers on T lymphocytes, the production of ACh by these lymphocytes, activation of ACh of α7nAChRs of MMS cells of the spleen [9,19]. Epinephrine and NE probably activating the adrenergic receptors of cells of the MMS (direct action) [19], β2-adrenergic receptors (β2ARs) of spleen T-lymphocytes (indirect effect) [10], cause the same effect as activation of α7nAChRs, leading to reduction in the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines by cells of the MMS [9,11,15].
Aim of the study
The aim of the study was to evaluate the combined action of β2-adrenergic and α7n-acetylcholinergic receptors agonists in the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway in sepsis in mice, to establish the role of the adrenergic mechanism (action of β2-adrenergic agonist) in the implementation in the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
Materials and Methods
Experiments were carried out on random-bred albino mice of both sexes weighing 18-22 g. The control group of mice (control group 1, n = 8) received i.p. 2.0 ml isotonic sodium chloride solution (saline) at 2 h after subcutaneous injection saline (0.5 ml) [20]. A second group of mice (control group 2, n = 55) were injected subcutaneously with 0.5 ml of saline once. After 2 h after administration of saline mice received (i.p.) 2.5×109 CFUs diurnal culture of E. coli O157:H7 in 2.0 ml of saline (sepsis modeling) [3,4,5,20]. As used β2ARs selective agonist hexoprenaline sulfate (Nycomed) subcutaneously a single dose of 1.5 μg/kg in 0.5 ml of saline (group 3; n = 35). The fourth group of mice were injected an α7nAChRs agonist GTS-21 [3-(2,4-dimethoxybenzylidene)- anabaseine dihydrochloride] (Sigma-Aldrich) subcutaneously, 15 mg/kg, a single dose [21]. The fifth group of mice received a combined effect of β2ARs selective agonist hexoprenaline sulfate (1.5 μg/kg) and α7nAChRs agonist GTS-21 (subcutaneously, a single dose of 15 mg/kg. Preparations (groups 3-5) were administered to mice 2 h before sepsis modeling.
Mortality in mice from experimental peritonitis was evaluated 4 and 24 h after the administration of 2.5 × 109 CFUs diurnal culture of E. coli O157:H7 in 2.0 ml of saline (i.p.).
The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL -6 were measured in mice blood of all groups (groups 1-5) using by ELISA (MyBioSoure) according to manufacturer’s instructions (4 and 24 h after the sepsis modeling). To determine the concentration of proinflammatory cytokines used monoclonal antibodies MyBioSource (cat. N - MBS494184, MBS494492, MBS335516 for TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6, respectively). Blood for analysis was collected from the retroorbital sinus. The date processed statistically using Student’s t test.
Results
The use of β2ARs agonist hexaprenaline sulfate and α7nAChRs agonist (GTS-21), as well as their combination 2 hours before the sepsis modeling, caused a decrease (p<0.05) mortality after 4 h compared with control group 2 (sepsis), respectively, in 2.13; 2.91 and 4.61 times (p<0,05) (p<0,05), respectively (Table 1) (by 19,3; 23,9 и 28,5%), and after 24 h – in 1.38; 1.59 и 3.15 times (by 25,2; 33,8 and 62,0%) (p<0,05), respectively (Table 1).
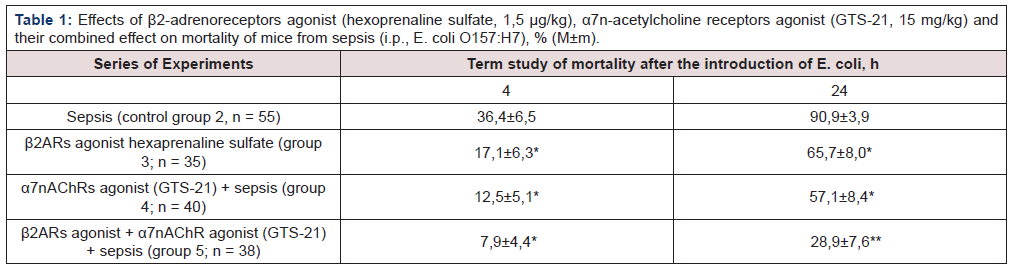
Table 1:Effects of β2-adrenoreceptors agonist (hexoprenaline sulfate, 1,5 μg/kg), α7n-acetylcholine receptors agonist (GTS-21, 15 mg/kg) and their combined effect on mortality of mice from sepsis (i.p., E. coli O157:H7), % (М±m).
* – p <0,05 as compared to control (group 2); ** – p<0,05 as compared to control (group 2) and group 3 and 4.
A similar effect was caused by β2ARs agonist (hexaprenaline sulfate). There was no significant difference in mortality of mice between the parameters in these groups when using β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists 4 and 24 h after the sepsis modeling (groups 3 and 4). It has been experimentally established that the adrenergic mechanism (action of β2ARs agonist) is an important component in the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway. The combined action (group 5) of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists caused a greater effect than the isolated effect of drugs.
The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 cytokines significantly increased in the blood of mice 4 h after the sepsis modeling of (control group 2) compared to control group 1 (intact animals), respectively, in 17.8; 19.5 and 57.7 times (p<0.05), after 24 h, the concentrations of these proinflammatory cytokines significantly decreased, exceeding the parameters of group 1 in 1.4 (p> 0.05), 4.5 and 8.2 times (p <0.05), respectively (Table 2).
Note. 4 and 24 - time after sepsis modeling, h; in parentheses is the number of mice; a -p <0.05 compared with control (group 1); b-p <0.05 compared with the corresponding parameter in sepsis (control group 2); с -p <0.05 compared with parameter after 4 h; d - p <0.05 compared with parameters with isolated exposure to β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists.
The obtained experimental data indicate that β2ARs agonist reduced the concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in blood 4 h after sepsis modeling (group 3) in comparison with the parameters of control group 2 (sepsis without drugs), respectively, 3,8; 3.3 and 11.2 times (p <0.05). In this case, the concentration of proinflammatory cytokines in the blood significantly (p <0.05) exceeded the corresponding parameters of control group 1. The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 24 h after sepsis modeling decreased compared to these parameters after 4 h, remaining below the values of group 2 in 1.3 (p> 0.05), 3.1 and 3.0 times (p <0.05), respectively.
The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the blood of mice after application of the α7nAChR GTS-21 agonist 4 hours after sepsis modeling (group 4) decreased compared to the parameters of control group 2, respectively, in 3.4; 2.9 and 9.3 times (p <0.05). There was a reduction of concentration of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 cytokines 24 h after sepsis modeling compared with the corresponding values after 4 h, remaining below the values of group 2, respectively, 1.6; 2.2 and 3.5 times (p <0.05).
There was no significant difference of concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the blood of mice when using β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists after modeling sepsis (groups 3 and 4).
The concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 in the blood of mice 4 h after sepsis modeling (group 5) decreased compared to the values of control group 2 (sepsis) with the combined action of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists, respectively, in 6.5; 6.0 and 21.9 times (p<0.05). The blood concentrations of these cytokines after 24 h significantly decreased compared to values after 4 h and compared with the parameters of group 2 their concentrations were lower in 1.4 (p>0.05), 6.2 and 6.4 times, respectively (p<0.05). The contents of proinflammatory cytokines in groups 3, 4, and 5 was statistically significant (p<0.05) higher than the corresponding values of control group 1 after 4 h after sepsis modeling.
The proinflammatory cytokines after the use of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists in sepsis (groups 3 and 4) decreased to a lesser extent (p <0.05) than with their combined effect (group 5). So, the combination of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists 4 h after the sepsis modeling reduced the concentrations of TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 in the blood of mice compared to the isolated action of these preparations, respectively, in 1.8; 1.8; 2.0 times (p <0.05) compared with group 3 and 1.9; 2.1; 2.4 times (p <0.05) compared with group 4. This suggests that the additive effect of these drugs (β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists) in the implementation of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway is noted.
Discussion
The data obtained suggest that the α7nAChRs agonist (GTS-21) due to the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway [6,22] leads to a decrease in mortality from sepsis [3,4,5] due to a decrease of MMS cell production of pro-inflammatory cytokines [23,24]. A similar effect was caused by β2ARs agonist (hexaprenaline sulfate). There was no significant difference in mortality of mice between the parameters in these groups (3 and 4) when using β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists after the sepsis modeling. It has been experimentally established that the adrenergic mechanism (action of β2ARs agonist) is an important component in the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway.
The literature data [6,10,25] suggest that the additive effect of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists (reduction in mortality from sepsis) is associated with a decrease of the concentrations of proinflammatory cytokines in the blood by hexaprenaline sulfate and GTS-21 due to activation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway and adrenergic mechanisms. Excitation of nAChRs of the adrenal glands and sympathetic ganglia causes activation of MMS cell adrenergic receptors by epinephrine and NE and suppression of the cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β and IL-6 [19,24,25]. The described effects are enhanced by a decrease in the synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines by the α7nAChRs agonist (GTS-21), acting directly on α7nAChRs of MMS cells [6,23,25,26].
It is known that monocytes and macrophages have βARs, and their activation usually leads to anti-inflammatory effect [19] due to inhibition of the nuclear transcription factor NF-κB [27]. Mechanisms of the reduction of synthesis of proinflammatory cytokines by the action of an agonist β2ARs (action on MMS cells) currently not well understood, but research results are inconsistent [18,19].
Conclusions
The application of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists (hexaprenaline sulfate and GTS-21) cause a significant decrease in the mortality of mice from experimental sepsis (i.p., E. coli O157:H7) when it is modeling 2 h after using these drugs due to a decrease of the concentration of proinflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway).
It has been experimentally established that the adrenergic mechanism (action of β2ARs agonist) is an important component in the implementation of the cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway
The combined use of β2ARs and α7nAChRs agonists determines their additive effect.
References
- Pruett SB, Fan R, Cheng B, Glover M, Tan W, et al. (2010) Innate immunity and inflammation in sepsis: mechanisms of suppressed host resistance in mice treated with ethanol in a binge-drinking model. Toxicol Sci 117(2): 314-324.
- Martin GS (2012) Sepsis, severe sepsis and septic shock: changes in incidence, pathogens and outcomes. Expert Rev Anti Infect Ther 10(6): 701-706.
- Zabrodskii PF (1987) Effect of armin on nonspecific resistance factors of the body and on the primary humoral immune response. Farmakol Toksikol 50(1): 57-60.
- Zabrodskii PF (1995) Variation in antiinfectious nonspecific resistance of the organism caused by cholinergic stimulation. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 12(2): 809-811.
- Zabrodskii PF (1995) Change in the non-specific anti-infection resistance of the body exposed to cholinergic stimulation. Biull Eksp Biol Med 120(8): 164-166.
- PF Zabrodskii (2016) Immunotoxicology of organophosphorus compounds. Saratov 289.
- Zabrodskii PF, Mandych VG (2007) Immunotoxicology of xenobiotics. Saratov Military Institute of Biological and Chemical Safety 420.
- Borovikova LV, Ivanova S, Zhang M, Yang H, Botchkina GI, et al. (2000) Vagus nerve stimulation attenuates the systemic inflammatory response to endotoxin. Nature 405(6785): 458-462.
- Bernik TR, Friedman SG, Ochani M, DiRaimo R, Ulloa L, et al. (2002) Pharmacological stimulation of the cholinergic antiinflammatory pathway. J Exp Med 195(6): 781-788.
- Bonaz BL, Bernstein CN (2013) Brain-gut interactions in inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology 144(1): 36-49.
- Fernandez R, Nardocci G, Navarro C, Reyes EP, Acuña Castillo C, et al. (2014) Neural reflex regulation of systemic inflammation: potential new targets for sepsis therapy”. Front Physiol 15(5): 489.
- Reardon C (2016) Neuro-immune interactions in the cholinergic anti-inflammatory reflex. Immunol Lett 178: 92-96.
- Zabrodskii PF (2011) Effect of acetylcholine on mortality of mice from sepsis and proinflammatory cytokine production. Bull Exp Biol Med 150(3): 340-342.
- Zabrodskii PF, Gromov MS, Maslyakov VV (2016) Effect of α7n-Acetylcholine Receptor Activation and Antibodies to TNF-α on Mortality of Mice and Concentration of Proinflammatory Cytokines During Early Stage of Sepsis. Bull Exp Biol Med 159(6): 740-742.
- Zabrodskii PF1, Gromov MS2, Maslyakov VV (2016) Role of β2-adrenoreceptors in adrenergic anti-Inflammatory mechanism in sepsis. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 162(12): 718-721.
- Zabrodskii PF, Gromov MS, Maslyakov VV (2017) Combined Effects of M1 Muscarinic Acetylcholine Receptor Agonist TBPB and α7n-Acetylcholine Receptor Activator GTS-21 on Mouse Mortality and Blood Concentration of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Sepsis. Bull Exp Biol Med 162(6): 750-753.
- Zabrodskii PF, Gromov MS, Maslyakov VV (2018) Combined Effect of NF-κB Inhibitor and β2-Adrenoreceptor Agonist on Mouse Mortality and Blood Concentration of Proinflammatory Cytokines in Sepsis. Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine 162(6):445-448.
- Link A, Selejan S, Maack C, Lenz M, Böhm M (2008) Phosphodiesterase 4 inhibition but not beta-adrenergic stimulation suppresses tumor necrosis factor-alpha release in peripheral blood mononuclear cells in septic shock. Critical Care 12(6): R159.
- Scanzano A, Cosentino M (2015) Adrenergic regulation of innate immunity: a review. Front Pharmacol 23(6):171.
- Song DJ, Huanq XY, Ren LC, Yang XH, Xiao MZ, et al. (2009) Effect of lentiviral vector encoding on triggering receptor expressed on myeloid cells 1 on expression of inflammatory cytokine in septic mice infected by Bacteroides fragilis. Zhonghua Shao Shang Za Zhi 25(1): 36-41.
- Norman GJ, Morris JS, Karelina K, Weil ZM, Zhang N, et al. (2011) Cardiopulmonary arrest and resuscitation disrupts cholinergic anti-inflammatory processes: a role for cholinergic α7 nicotinic receptors. Journal of Neuroscience 31(9): 3446-3452.
- Eftekhari G, Hajiasgharzadeh K, Ahmadi-Soleimani SM, Dehpour AR, Semnanian S, et al. (2014) Activation of central muscarinic receptor type 1 prevents development of endotoxin tolerance in rat liver. Eur J Pharmacol 740: 436-441.
- Kox M, Pickkers P (2015) Modulation of the innate immune response through the vagus nerve. Nephron 131(2): 79-84.
- Martelli D, McKinley MJ, McAllen RM (2014) The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a critical review. Autonomic Neuroscience 182: 65-69.
- Pavlov VA, Wang H, Czura CJ, Friedman SG, Tracey KJ (2003) The cholinergic anti-inflammatory pathway: a missing link in neuroimmunomodulation. Molecular Medicine 9(5-8): 125-134.
- Egea J, Buendia I, Parada E, Navarro E, León R, et al. (2015) Anti-inflammatory role of microglial alpha7 nAChRs and its role in neuroprotection. Biochem Pharmacol 97(4): 463-472.
- Tan KS, Nackley AG, Satterfield K, Maixner W, Diatchenko L (2007) Beta2 adrenergic receptor activation stimulates pro-inflammatory cytokine production in macrophages via PKA- and NF-kappaB-independent mechanisms. Cell Signal 19(2): 251-260.



 We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.
We use cookies to ensure you get the best experience on our website.